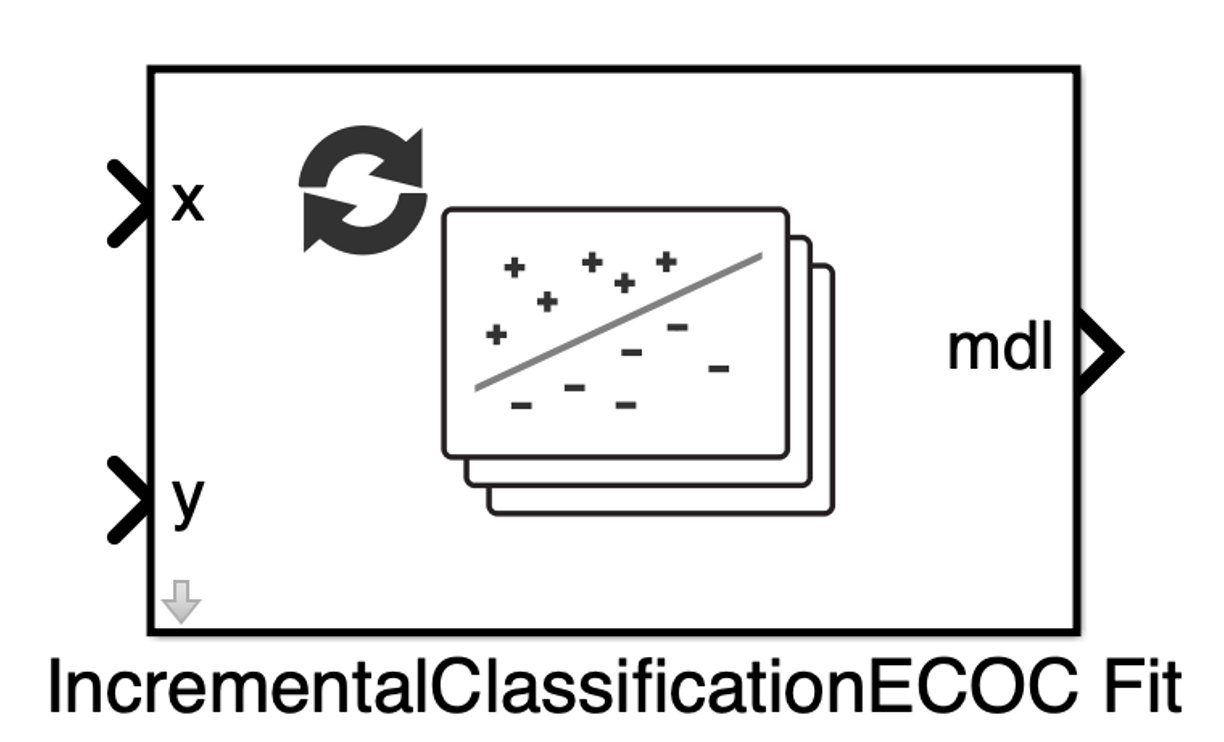
IncrementalClassificationECOC Fit
Libraries:
Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox /
Incremental Learning /
Classification /
ECOC
Description
The IncrementalClassificationECOC Fit block fits a configured incremental
error-correcting output codes (ECOC) classification model (incrementalClassificationECOC) for multiclass classification to streaming
data.
Import an initial ECOC classification object into the block by specifying the name of a
workspace variable that contains the object. The input port x receives a
chunk of predictor data (observations), and the input port y receives a
chunk of responses (labels) to which the model is fit. The output port returns an updated
incrementalClassificationECOC model mdl. The
optional input port w receives a chunk of observation weights and the optional input port reset resets
the learned parameters.
Examples
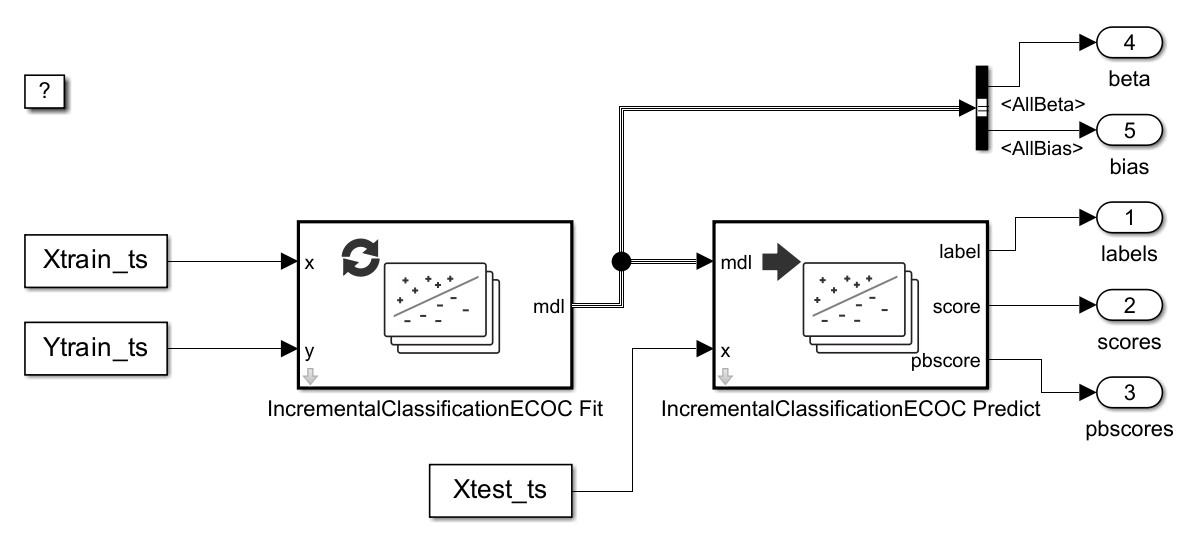
Perform Incremental Learning Using IncrementalClassificationECOC Fit and Predict Blocks
Perform incremental learning with the IncrementalClassificationECOC Fit block and predict labels with the IncrementalClassificationECOC Predict block.
- Since R2024a
- Open Live Script
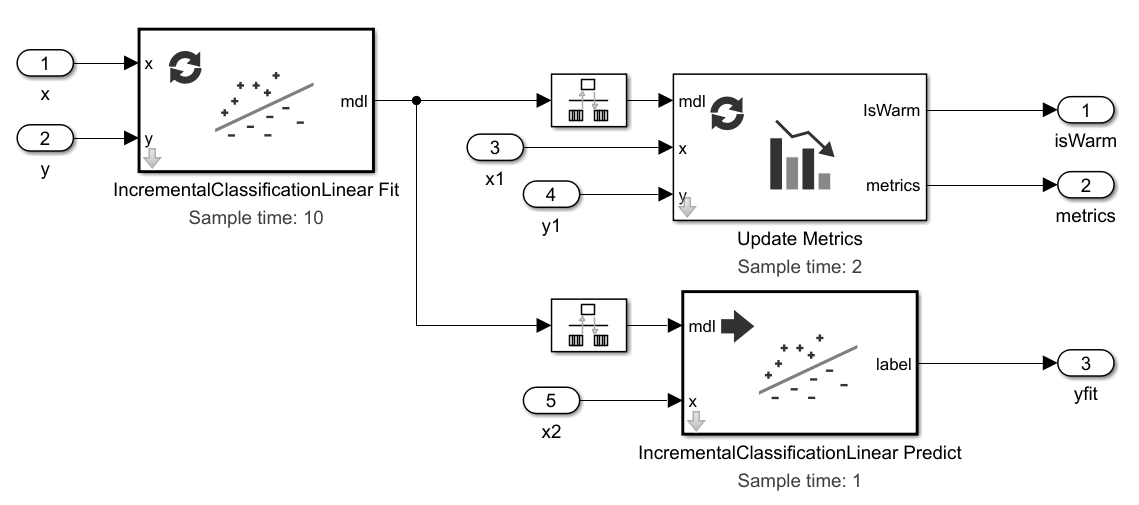
Configure Simulink Template for Rate-Based Incremental Linear Classification
Configure the Simulink Rate-Based Incremental Learning template to perform incremental linear classification.
- Since R2024a
- Open Live Script
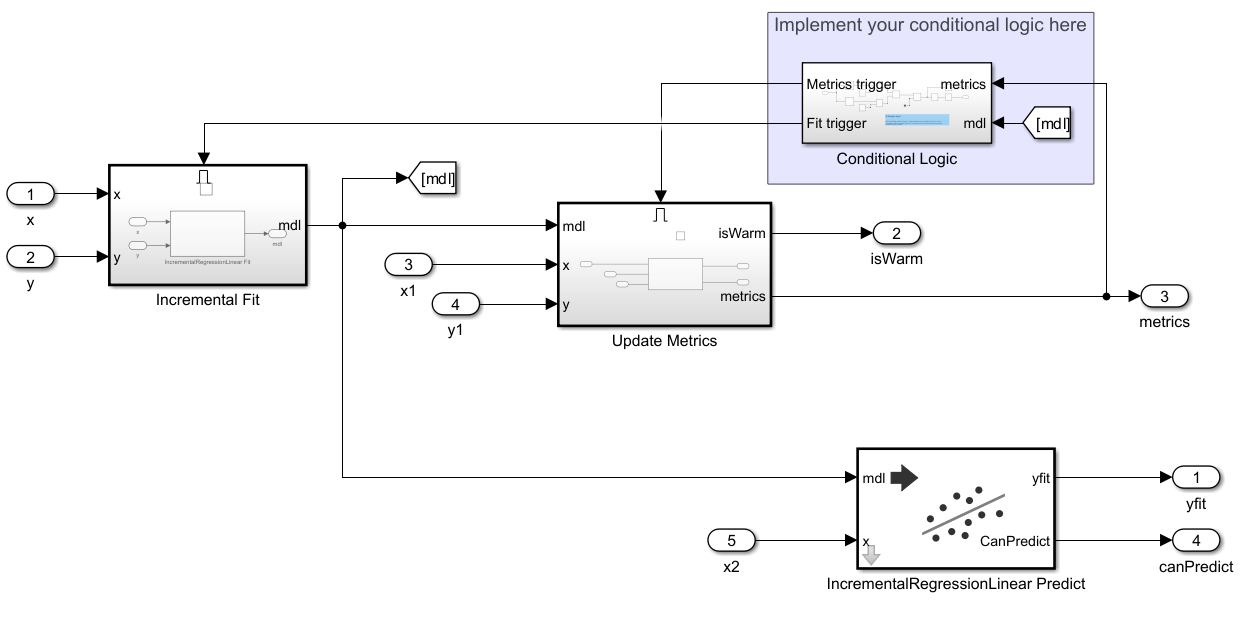
Configure Simulink Template for Conditionally Enabled Incremental Linear Classification
Configure the Simulink Enabled Execution Incremental Learning template to perform incremental linear classification.
- Since R2024a
- Open Live Script
Ports
Input
Chunk of predictor data to which the model is fit, specified as a numeric matrix.
The orientation of the variables and observations is specified by Predictor data observation
dimension. The default orientation is rows, which
indicates that the observations in the predictor data are oriented along the rows of
x.
The length of the observation responses y and the number of
observations in x must be equal;
y( is the
response of observation j (row or column) in
x.j)
Note
The number of predictor variables in x must be equal to the
NumPredictors property value of the initial model. If the
number of predictor variables in the streaming data changes from
NumPredictors, the block issues an error.
Data Types: single | double | half | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point
Chunk of class labels to which the model is trained, specified as a numeric, logical, or enumerated vector.
The length of the observation responses y and the number of observations in x must be equal; y(
j) is the response of observation j (row or column) in x.Each label must correspond to one row of the array.
Data Types: single | double | half | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point | enumerated
Chunk of observation weights, specified as a vector of positive values. The IncrementalClassificationECOC Fit block weights the observations in x with the corresponding values in w. The size of w must be equal to the number of observations in x.
Dependencies
To enable this port, select the check box for Add input port for observation weights on the Main tab of the Block Parameters dialog box.
Data Types: single | double
Since R2025a
Reset signal, specified as 0 (false) or
1 (true) or a numeric scalar. When the
reset signal is a positive scalar (greater than 0), the block
resets the learned parameters, if any, of the incremental learning model. If any
hyperparameters of mdl are estimated during incremental training,
those get reset as well. mdl.NumPredictors are always
preserved.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | Boolean | fixed point
Output
Updated incremental learning model parameters fit to streaming data, returned as a
bus signal (see Composite Signals (Simulink)).
Parameters
Main
Specify the name of a workspace variable that contains the configured
incrementalClassificationECOC model object. The initial model
must have following properties specified:
The
NumPredictorsproperty which must be a positive integer scalar equal to the number of predictors in x.The
ClassNamesproperty.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
InitialLearner |
| Type: workspace variable |
Values:
incrementalClassificationECOC model object |
Default:
"ecocMdl" |
Select the check box to include the input port w for observation weights in the IncrementalClassificationECOC Fit block.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
ShowInputWeights |
| Type: character vector |
Values:
"off" | "on" |
Default:
"off" |
Since R2025a
Select the check box to include the input port reset for the reset signal in the IncrementalClassificationECOC Fit block.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
ShowInputReset |
| Type: character vector or string |
Values:
"off" | "on" |
Default:
"off" |
Specify the observation dimension of the predictor data. The default value is
rows, which indicates that observations in the predictor data are
oriented along the rows of x.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
ObservationsIn |
| Type: character vector |
Values:
"rows" | "columns" |
Default:
"rows" |
Specify the discrete interval between sample time hits or specify another type of sample
time, such as continuous (0) or inherited (–1). For more
options, see Types of Sample Time (Simulink).
By default, the IncrementalClassificationECOC Fit block inherits sample time based on the context of the block within the model.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
SystemSampleTime |
| Type: string scalar or character vector |
| Values: scalar |
Default:
"–1" |
Data Types
Fixed-Point Operational Parameters
Specify the rounding mode for fixed-point operations. For more information, see Rounding Modes (Fixed-Point Designer).
Block parameters always round to the nearest representable value. To control the rounding of a block parameter, enter an expression into the mask field using a MATLAB® rounding function.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
RndMeth |
| Type: character vector |
Values:
"Ceiling" | "Convergent" | "Floor" | "Nearest" | "Round" | "Simplest" |
"Zero" |
Default:
"Floor" |
Specify whether overflows saturate or wrap.
| Action | Rationale | Impact on Overflows | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Select this check box
( | Your model has possible overflow, and you want explicit saturation protection in the generated code. | Overflows saturate to either the minimum or maximum value that the data type can represent. | The maximum value that the |
Clear this check box
( | You want to optimize the efficiency of your generated code. You want to avoid overspecifying how a block handles out-of-range signals. For more information, see Troubleshoot Signal Range Errors (Simulink). | Overflows wrap to the appropriate value that the data type can represent. | The maximum value that the |
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
SaturateOnIntegerOverflow |
| Type: character vector |
Values:
"off" | "on" |
Default:
"off" |
Select this parameter to prevent the fixed-point tools from overriding the data type you specify for the block. For more information, see Use Lock Output Data Type Setting (Fixed-Point Designer).
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
LockScale |
| Type: character vector |
Values:
"off" | "on" |
Default:
"off" |
Data Type
Specify the data type for the linear coefficient estimates (beta) output. The type
can be inherited, specified as an enumerated data
type, or expressed as a data type object such as
Simulink.NumericType.
For more information about data types, see Control Data Types of Signals (Simulink).
Click the Show data type
assistant button ![]() to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the data type attributes. For more
information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the data type attributes. For more
information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
BinaryBetaDataTypeStr |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "Inherit: auto"
| "double" | "single" |
"half" | "int8" |
"uint8" | "int16" |
"uint16" | "int32" |
"uint32" | "int64" |
"uint64" | "boolean" |
"fixdt(1,16,0)" | "fixdt(1,16,2^0,0)" |
"<data type expression>" |
Default: "Inherit: auto"
|
Specify the lower value of the beta output range that Simulink® checks.
Simulink uses the minimum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as software-in-the-loop (SIL) mode or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
Note
The Binary learner beta data type Minimum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual beta output. To do so, use the Saturation (Simulink) block instead.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
BinaryBetaOutMin |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the upper value of the beta output range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the maximum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as SIL or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
Note
The Binary learner beta data type Maximum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual beta output. To do so, use the Saturation (Simulink) block instead.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
BinaryBetaOutMax |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the data type for the intercept estimates (bias) output. The type can be
inherited, specified as an enumerated data type, or
expressed as a data type object such as Simulink.NumericType.
For more information about data types, see Control Data Types of Signals (Simulink).
Click the Show data type
assistant button ![]() to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the data type attributes. For more
information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the data type attributes. For more
information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
BinaryBiasDataTypeStr |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "Inherit: auto"
| "double" | "single" |
"half" | "int8" |
"uint8" | "int16" |
"uint16" | "int32" |
"uint32" | "int64" |
"uint64" | "boolean" |
"fixdt(1,16,0)" | "fixdt(1,16,2^0,0)" |
"<data type expression>" |
Default: "Inherit: auto"
|
Specify the lower value of the bias output range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the minimum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as software-in-the-loop (SIL) mode or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
Note
The Binary learner bias data type Minimum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual bias output. To do so, use the Saturation (Simulink) block instead.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
BinaryBiasOutMin |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the upper value of the bias output range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the maximum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as SIL or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
Note
The Binary learner bias data type Maximum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual bias output. To do so, use the Saturation (Simulink) block instead.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
BinaryBiasOutMax |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the data type for the binary learner internal states output. The type can
be inherited, specified as an enumerated data type,
or expressed as a data type object such as Simulink.NumericType.
For more information about data types, see Control Data Types of Signals (Simulink).
Click the Show data type
assistant button ![]() to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the data type attributes. For more
information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the data type attributes. For more
information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
BinaryStatesDataTypeStr |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "Inherit: auto"
| "double" | "single" |
"half" | "int8" |
"uint8" | "int16" |
"uint16" | "int32" |
"uint32" | "int64" |
"uint64" | "boolean" |
"fixdt(1,16,0)" | "fixdt(1,16,2^0,0)" |
"<data type expression>" |
Default: "Inherit: auto"
|
Specify the lower value of the binary learner internal states range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the minimum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as software-in-the-loop (SIL) mode or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
BinaryStatesOutMin |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the upper value of the binary learner internal states range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the maximum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as software-in-the-loop (SIL) mode or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
BinaryStatesOutMax |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the data type for the internal prior term. The type can be inherited,
specified directly, or expressed as a data type object such as
Simulink.NumericType.
For more information about data types, see Control Data Types of Signals (Simulink).
Click the Show data type
assistant button ![]() to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the data type attributes. For more
information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the data type attributes. For more
information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
PriorDataTypeStr |
| Type: character vector or string |
Values: "double" |
"single" | "half" |
"int8" | "uint8" |
"int16" | "uint16" |
"int32" | "uint32" |
"int64" | "uint64" |
"boolean" | "fixdt(1,16,0)" |
"fixdt(1,16,2^0,0)" |"<data type
expression>" |
Default: "double"
|
Specify the lower value of the prior term range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the minimum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as software-in-the-loop (SIL) mode or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
The Prior data type Minimum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual prior term value. To do so, use the Saturation (Simulink) block instead.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
PriorOutMin |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the upper value of the prior term range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the maximum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as SIL or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
The Prior data type Maximum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual prior term value. To do so, use the Saturation (Simulink) block instead.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
PriorOutMax |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the data type for the binary learner mu (predictor means) output. The type
can be inherited, specified as an enumerated data
type, or expressed as a data type object such as
Simulink.NumericType.
For more information about data types, see Control Data Types of Signals (Simulink).
Click the Show data type
assistant button ![]() to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the data type attributes. For more
information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the data type attributes. For more
information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter: Binary
MuDataTypeStr |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "Inherit: auto"
| "double" | "single" |
"half" | "int8" |
"uint8" | "int16" |
"uint16" | "int32" |
"uint32" | "int64" |
"uint64" | "boolean" |
"fixdt(1,16,0)" | "fixdt(1,16,2^0,0)" |
"<data type expression>" |
Default: "Inherit: auto"
|
Specify the lower value of the binary learner mu range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the minimum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as software-in-the-loop (SIL) mode or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
Note
The Binary learner mu data type Minimum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual mu output. To do so, use the Saturation (Simulink) block instead.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
BinaryMuOutMin |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the upper value of the binary learner mu range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the maximum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as software-in-the-loop (SIL) mode or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
Note
The Binary learner mu data type Maximum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual mu output. To do so, use the Saturation (Simulink) block instead.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
BinaryMuOutMax |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the data type for the binary learner sigma (predictor standard deviations)
output. The type can be inherited, specified as an enumerated data
type, or expressed as a data type object such as
Simulink.NumericType.
For more information about data types, see Control Data Types of Signals (Simulink).
Click the Show data type
assistant button ![]() to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the data type attributes. For more
information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the data type attributes. For more
information, see Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink).
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter: Binary
SigmaDataTypeStr |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "Inherit: auto"
| "double" | "single" |
"half" | "int8" |
"uint8" | "int16" |
"uint16" | "int32" |
"uint32" | "int64" |
"uint64" | "boolean" |
"fixdt(1,16,0)" |
"fixdt(1,16,2^0,0)"|"<data type
expression>" |
Default: "Inherit: auto"
|
Specify the lower value of the binary learner sigma range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the minimum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as software-in-the-loop (SIL) mode or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
Note
The Binary learner sigma data type Minimum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual sigma output. To do so, use the Saturation (Simulink) block instead.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
BinarySigmaOutMin |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Specify the upper value of the binary learner sigma range that Simulink checks.
Simulink uses the maximum value to perform:
Parameter range checking for some blocks (see Specify Minimum and Maximum Values for Block Parameters (Simulink)).
Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink) and Enable Simulation Range Checking (Simulink)).
Optimization of the code that you generate from the model. This optimization can remove algorithmic code and affect the results of some simulation modes, such as software-in-the-loop (SIL) mode or external mode. For more information, see Optimize using the specified minimum and maximum values (Embedded Coder).
Note
The Binary learner sigma data type Maximum parameter does not saturate or clip the actual sigma output. To do so, use the Saturation (Simulink) block instead.
Programmatic Use
Block Parameter:
BinarySigmaOutMax |
| Type: character vector |
Values: "[]" |
scalar |
Default: "[]" |
Block Characteristics
Data Types |
|
Direct Feedthrough |
|
Multidimensional Signals |
|
Variable-Size Signals |
|
Zero-Crossing Detection |
|
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using Simulink® Coder™.
Fixed-Point Conversion
Design and simulate fixed-point systems using Fixed-Point Designer™.
Version History
Introduced in R2024aThe IncrementalClassificationECOC Fit has a new reset inport that allows the resetting of the learned parameters, if any, of the incremental learning model. If any hyperparameters of the model are estimated during incremental training, those get reset as well. Use the reset signal when performing drift-aware learning to reset the model parameters when drift is detected.
See Also
Blocks
Objects
Functions
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)