rfckt.txline
General transmission line
Description
Use the rfckt.txline object to create transmission lines
that are characterized by line loss, line length, stub type, and
termination.
Note
txlineEquationBased is recommended over
rfckt.txline because it enables you to:
Create an equation-based transmission line. You can set the loss, the phase velocity, and the interpolation type in this object.
Build a
circuitobject with a equation-based transmission line.Model an equation-based transmission line element in an RF chain created using an
rfbudgetobject or the RF Budget Analyzer app, and then export this element to RF Blockset™ or torfsystemSystem object™ for circuit envelope analysis.
(since R2023b)
Creation
Description
h = rfckt.txlinereturns a transmission line object
whose properties are set to their default values.
h = rfckt.txline(Name,Value) sets properties using
one or more name-value pairs. For example,
rfckt.txline('Z0',75) creates a transmission line
object with characteristic impedance of 75 ohms. You can specify multiple
name-value pairs. Enclose each property name in a quote. Properties not
specified retain their default values.
Properties
Object Functions
analyze | Analyze RFCKT object in frequency domain |
calculate | Calculate specified parameters for rfckt objects or rfdata objects |
plotyy | Plot parameters of RF circuit or RF data on xy-plane with two Y-axes |
circle | Draw circles on Smith Chart |
loglog | Plot specified circuit object parameters using log-log scale |
plot | Plot circuit object parameters on X-Y plane |
listparam | List valid parameters for specified circuit object |
getz0 | Calculate characteristic impedance of RFCKT transmission line object |
semilogx | Plot RF circuit object parameters using log scale for x-axis |
semilogy | Plot RF circuit object parameters using log scale for y-axis |
polar | Plot specified object parameters on polar coordinates |
smith | Plot circuit object parameters on Smith Chart |
write | Write RF data from circuit or data object to file |
Examples
Algorithms
The analyze method treats the transmission line, which can be lossy
or lossless, as a 2-port linear network. It computes the
AnalyzedResult property of a stub or as a stubless line using the
data stored in the rfckt.txline object properties as follows:
If you model the transmission line as a stub less line, the
analyzemethod first calculates the ABCD-parameters at each frequency contained in the modeling frequencies vector. It then uses theabcd2sfunction to convert the ABCD-parameters to S-parameters.The
analyzemethod calculates the ABCD-parameters using the physical length of the transmission line, d, and the complex propagation constant, k, using the following equations:Z0 is the specified characteristic impedance. k is a vector whose elements correspond to the elements of the input vector
freq. Theanalyzemethod calculates k from the specified properties as k = αa + iβ, where αa is the attenuation coefficient and β is the wave number. The attenuation coefficient αa is related to the specified loss, α, byThe wave number β is related to the specified phase velocity, Vp, by
where f is the frequency range specified in the
analyzeinput argumentfreq. The phase velocity Vp is derived from therfckt.txlineobject properties. It is also known as the wave propagation velocity.If you model the transmission line as a shunt or series stub, the
analyzemethod first calculates the ABCD-parameters at the specified frequencies. It then uses theabcd2sfunction to convert the ABCD-parameters to S-parameters.When you set the
StubModeproperty to'Shunt', the 2-port network consists of a stub transmission line that you can terminate with either a short circuit or an open circuit as shown in the following figure.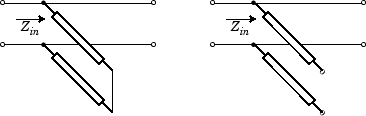
Zin is the input impedance of the shunt circuit. The ABCD-parameters for the shunt stub are calculated as:
When you set the
StubModeproperty to'Series', the 2-port network consists of a series transmission line that you can terminate with either a short circuit or an open circuit as shown in the following figure.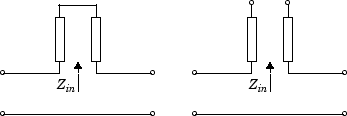
Zin is the input impedance of the series circuit. The ABCD-parameters for the series stub are calculated as:
References
[1] Ludwig, R. and P. Bretchko, RF Circuit Design: Theory and Applications, Prentice-Hall, 2000.
Version History
Introduced in R2009a
See Also
rfckt.amplifier | rfckt.cascade | rfckt.coaxial | rfckt.cpw | rfckt.datafile | rfckt.delay | rfckt.hybrid | rfckt.hybridg | rfckt.mixer | rfckt.microstrip | rfckt.passive | rfckt.parallel | rfckt.parallelplate | rfckt.rlcgline | rfckt.series | rfckt.seriesrlc | rfckt.shuntrlc | rfckt.twowire
![Figure contains an axes object. The axes object with xlabel Freq [GHz], ylabel Angle (degrees) contains an object of type line. This object represents S_{21}.](../../examples/rf/win64/CreativeTitleExample_01.png)
