transmit
Description
Examples
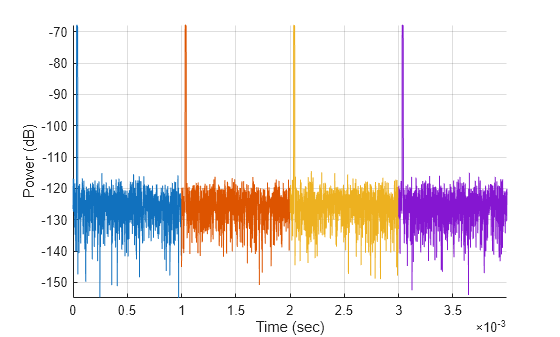
This example shows how to create a simple bistatic scenario with a moving target. Transmit and collect pulses until the completion of 1 receive window and plot the results.
Configure the bistatic transmitter and receiver. Use a pulse repetition frequency of 1000 Hz.
prf = 1e3; wav = phased.LinearFMWaveform(PRF=prf,PulseWidth=1e-5); ant = phased.SincAntennaElement(Beamwidth=10); tx = bistaticTransmitter(Waveform=wav, ... Transmitter=phased.Transmitter(Gain=20), ... TransmitAntenna=phased.Radiator(Sensor=ant)); rx = bistaticReceiver( ... ReceiveAntenna=phased.Collector(Sensor=ant), ... WindowDuration=0.005); freq = tx.TransmitAntenna.OperatingFrequency;
Create bistatic transmitter and bistatic receiver platforms spaced 10 km apart and add a target platform. Use radarScenario to crreate the platforms for this example. Define the transmitter platform, receiver platform, and target platform using platform and give the target a trajectory.
scene = radarScenario(UpdateRate=prf); platform(scene,Position=[-5e3 0 0], ... Orientation=rotz(45).'); platform(scene,Position=[5e3 0 0], ... Orientation=rotz(135).'); traj = kinematicTrajectory( ... Position=8e3*[cosd(60) sind(60) 0],Velocity=[0 150 0]); tgtPlat= platform(scene,Trajectory=traj);
Create an empty plot.
hFig = figure; hAxes = axes(hFig);
Transmit and collect pulses for one receive window. First, update platform positions by calling advance on the scene and then get the platform positions using platformPoses. Next, get the propagation paths using bistaticFeeSpacePath. Then, transmit the signal and receive pulses. Finally, plot the received signals.
t = nextTime(tx); tEnd = nextTime(rx); while t < tEnd advance(scene); % Get platform positions poses = platformPoses(scene); % Calculate paths proppaths = bistaticFreeSpacePath(freq, ... poses(1),poses(2),poses(3)); % Transmit [txSig,txInfo] = transmit(tx,proppaths,t); % Receive pulses [iq,rxInfo] = receive(rx,txSig,txInfo,proppaths); t = nextTime(tx); % Plot received signals rxTimes = (0:(size(iq,1) - 1))*1/rxInfo.SampleRate ... + rxInfo.StartTime; plot(hAxes,rxTimes,mag2db(abs(sum(iq,2)))) hold(hAxes,'on') end
Label the plot.
grid(hAxes,'on') xlabel(hAxes,'Time (sec)') ylabel(hAxes,'Power (dB)') axis(hAxes,'tight')
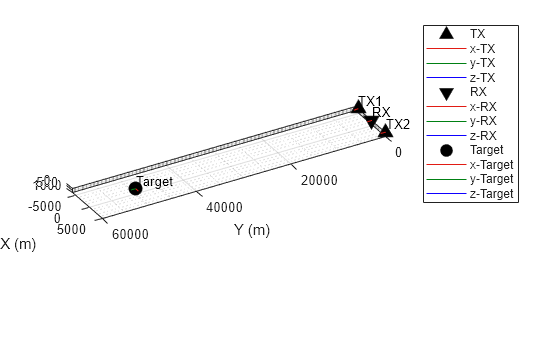
This example shows how to create a bistatic scenario with two bistatic transmitters. The receiver is located between the transmitters and there is a target with a custom radar cross section. Transmit and collect pulses for four receive windows and plot the results.
Configure the bistatic transmitters. Use a pulse repetition frequencey of 1000 Hz.
prf = 1e3; wav = phased.LinearFMWaveform(PRF=prf,PulseWidth=0.2/prf); ant = phased.SincAntennaElement(Beamwidth=10); tx1 = bistaticTransmitter(Waveform=wav, ... Transmitter=phased.Transmitter(Gain=40), ... TransmitAntenna=phased.Radiator(Sensor=ant)); tx2 = clone(tx1); prf = 2e3; tx2.Waveform = phased.RectangularWaveform( ... PRF=prf,PulseWidth=0.2/prf); tx2.Transmitter.PeakPower = 2e3;
Configure the bistatic receiver.
rx = bistaticReceiver( ... ReceiveAntenna=phased.Collector(Sensor=ant), ... WindowDuration=0.0025); freq = tx1.TransmitAntenna.OperatingFrequency;
Create bistatic transmitter platforms spaced 10 km apart. Put the receiver platform between the two transmitters. For this example, create the platforms in radarScenario. Define the platforms using platform.
scene = radarScenario(UpdateRate=prf); tx1Plat = platform(scene,Position=[-5e3 0 0], ... Orientation=rotz(85).'); tx2Plat = platform(scene,Position=[5e3 0 0], ... Orientation=rotz(95).'); rxPlat = platform(scene,Position=[0 0 0], ... Orientation=rotz(90).');
Place a stationary target platform down range and assign the target a radar cross section.
rcsSig = rcsSignature(Pattern=20);
tgtPlat = platform(scene,Position=[0 50e3 0], ...
Signatures=rcsSig);Show platform locations and orientations.
tp = theaterPlot(Parent=axes(figure)); txPltr = orientationPlotter(tp,Marker="^", ... DisplayName="TX",LocalAxesLength=1e3); rxPltr = orientationPlotter(tp,Marker="v", ... DisplayName="RX",LocalAxesLength=1e3); tgtPltr = orientationPlotter(tp,Marker="o", ... DisplayName="Target",LocalAxesLength=1e3); poses = platformPoses(scene); plotOrientation(txPltr,[poses(1:2).Orientation], ... reshape([poses(1:2).Position],3,[]).',["TX1" "TX2"]); plotOrientation(rxPltr,poses(3).Orientation,poses(3).Position,"RX"); plotOrientation(tgtPltr,poses(4).Orientation,poses(4).Position,"Target");
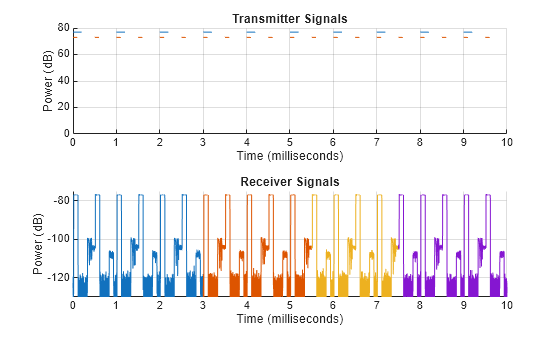
Transmit and collect pulses for four receive windows. First, update platform positions by calling advance on the scene. Then set up the for loop to iterate over the receive windows. Next, get platform positions using platformPoses. Get the propogation paths for both transmitters using bistaticFeeSpacePath. Then, transmit the signal and collect pulses. Finally, receive the transmissions and plot the received signals.
tl = tiledlayout(figure,2,1); hAxes = [nexttile(tl) nexttile(tl)]; hold(hAxes,"on"); tx = {tx1 tx2}; advance(scene); for iRxWin = 0:4 [propSigs,propInfo] = collect(rx,scene.SimulationTime); t = min([nextTime(tx{1}) nextTime(tx{2})]); tEnd = nextTime(rx); while t <= tEnd % Get platform positions poses = platformPoses(scene); % Include target RCS signature on the pose tgtPose = poses(4); tgtPose.Signatures = {rcsSig}; for iTx = 1:2 % Calculate propogation paths proppaths = bistaticFreeSpacePath(freq, ... poses(iTx),poses(3),tgtPose); % Transmit [txSig,txInfo] = transmit(tx{iTx},proppaths,scene.SimulationTime); % Plot transmitted signal txTimes = (0:(size(txSig,1) - 1))*1/txInfo.SampleRate ... + txInfo.StartTime; plot(hAxes(1),txTimes*1e3,mag2db(max(abs(txSig),[],2)),SeriesIndex=iTx); % Collect transmitted pulses collectSigs = collect(rx,txSig,txInfo,proppaths); % Accumulate collected transmissions sz = max([size(propSigs);size(collectSigs)],[],1); propSigs = paddata(propSigs,sz) + paddata(collectSigs,sz); end t = min([nextTime(tx{1}) nextTime(tx{2})]); advance(scene); end % Receive collected transmissions [iq,rxInfo] = receive(rx,propSigs,propInfo); % Plot received transmissions rxTimes = (0:(size(iq,1) - 1))*1/rxInfo.SampleRate ... + rxInfo.StartTime; plot(hAxes(2),rxTimes*1e3,mag2db(abs(iq))); end
Label plots.
grid(hAxes,"on") title(hAxes(1),"Transmitter Signals") title(hAxes(2),"Receiver Signals") xlabel(hAxes,"Time (milliseconds)") ylabel(hAxes,"Power (dB)") ylim(hAxes(1),[0 80]); ylim(hAxes(2),[-130 -75]) xlim(hAxes(1),xlim(hAxes(2)))
Input Arguments
Bistatic transmitter, specified as a bistaticTransmitter object.
Propagation paths, specified as a 1-by-P array of path configuration
structures, where P is the number of propagation paths. Propagation paths
are determined in the radar mounting frame. The bistaticFreeSpacePath function returns propPaths. Each
propPaths structure describes a propagation path and contains these
fields.
| Field | Description |
PathLength | Propagation path length, specified as a positive scalar in units of meters (m). |
PathLoss | Propagation loss along the path, specified as a scalar in units of decibels (dB). |
ReflectionCoefficient | Cumulative reflection coefficients for all reflections along the path, specified as a scalar. Reflections along the path might include contributions from scatterers or targets. |
AngleOfDeparture | Propagation path angle of departure, specified as a two-element vector in the form of [azimuth; elevation] in units of degrees (deg). The angle of departure is determined in the transmit antenna mounting frame. |
AngleOfArrival | Propagation path angle of arrival, specified as a two-element vector in the form of [azimuth; elevation] in units of degrees (deg). The angle of arrival is determined in the receive antenna mounting frame. |
DopplerShift | Cumulative Doppler shift along the path, specified as a scalar in units of hertz (Hz). |
Data Types: struct
Current simulation time, specified as a non-negative scalar in units of seconds.
Data Types: double
Output Arguments
Returns the signal that is transmitted and propagated in the direction of the
receiver and targets. The size of TXsig depends on the transmit
antenna configuration.
CombineRadiatedSignalsproperty of theTransmitAntennainTXis set totrue—TXsigreturns anM-by-Pcomplex-valued array with columns that contain the transmitted signal, whereMis the number of samples in each transmitted pulse or sweep andPis the number of propagation paths inpropPaths.CombineRadiatedSignalsproperty of theTransmitAntennainTXis set tofalse—TXsigreturns a1-by-Pcell array, wherePis the number of propagation paths. Each cell contains anM-by-Lcomplex-valued array with columns that contain the transmitted signal for each transmit antenna.Mis the number of samples andLis the number of elements in theTransmitAntenna.
Returns a structure with two fields that contains information pertaining to the transmitted signal.
| Field | Description |
StartTime | Start time of the transmitted signal, specified in units of seconds (sec). |
SampleRate | Sample rate of the transmitted signal, specified in units of hertz (Hz). |
Version History
Introduced in R2025a
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)