sim3d.Joint
Description
Use the sim3d.Joint object to link two sim3d.Actor objects
with physics-based constraints. You must set the Physics property of at
least one sim3d.Actor object.
You cannot see the joint actors themselves, but you can see their effects on the constraints
of the connected actors. After you create a sim3d.Joint object, you can
modify aspects of the joint by setting property values.
The relative motion of the constrained actors defined by the type of joint during creation remains consistent during the simulation.
The relative motion of the constrained actors also depends on other properties of the joint object.
Creation
Description
joint = sim3d.Joint()sim3d.Actor objects in the 3D environment.
joint = sim3d.Joint(Name=Value)JointType to
Spherical.
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Example: joint = sim3d.Joint('ActorName','Joint1',
'JointType','RevoluteX') creates a joint that allows rotation of linked actors
around the X-axis of the world object.
Name of actor, specified as a character array or string. If you do not specify an actor name,
then the software assigns the actor an autogenerated name. Use
this argument to set the name of the
sim3d.Joint object.
Note
If you specify the same name as an actor that already exists, then the software appends actor name you specify with a unique identifier.
Relative translation (x,y,z) of the actor object to its parent actor, specified as a real 1-by-3 vector, in m. Use Translation to change the position of the sim3d.Joint object in the 3D environment along the X, Y, and Z axes of the coordinate system. When you add an actor to the 3D environment, the default parent actor is the Scene Origin at (0,0,0).
Example: Translation=[3 4 3]
Data Types: double
Relative rotation (roll, pitch, yaw) of the actor object to its parent actor, specified as a real 1-by-3 vector, in rad. Use Rotation to rotate the sim3d.Joint object in the 3D environment.
Example: Rotation=[0 pi/2 pi/4]
Data Types: double
Type of joint, specified as one of these values, as a character
array or string. The relative motion of the constrained actors is defined by the
JointType. The world uses the Unreal Engine® coordinate system to transform objects. The movement of the constrained actors
also depends on other properties of the joint object, including LinearLimit
and AngularLimit.
| Joint Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Constrains the complete linear and rotational motion of the actors along all axes, moving the actors as a single rigid body. |
|
| Allows relative rotation of actors in all directions around a
single pivot point. The point is defined by the
|
|
| Allows rotation of actors only around the X-axis of the world. |
|
| Allows rotation of actors only around the Y-axis of the world. |
|
| Allows rotation of actors only around the Z-axis of the world. |
|
| Allows sliding motion of only actors along the X-axis of the world. |
|
| Allows sliding motion of actors only along the Y-axis of the world. |
|
| Allows sliding motion of actors only along the Z-axis of the world. |
|
| Allows rotation and sliding motion of actors only along the X-axis of the world. |
|
| Allows rotation and sliding motion of actors only along the Y-axis of the world. |
|
| Allows rotation and sliding motion of actors only along the Z-axis of the world. |
|
Example: JointType='RevoluteX'
Data Types: string
Output Arguments
Actor object, returned as a sim3d.Joint object.
Properties
Parent of actor, specified as a handle to the parent actor object. After you add an actor to
the sim3d.World object, the default parent actor is the
Scene Origin at (0,0,0). Use this property to
set any actor in the 3D environment as the parent actor of a
sim3d.Joint object.
This property is read-only.
Children of actor, specified as a structure.
Each field of the structure contains a handle to
the child of a sim3d.Joint
object.
Parent world, specified as a handle to the parent sim3d.World
object. You can use this property only if the sim3d.Joint object is
added to the parent sim3d.World object.
Relative translation (x,y,z) of the actor object to its parent actor, specified as a real 1-by-3 vector, in m. Use Translation to change the position of the sim3d.Joint object in the 3D environment along the X, Y, and Z axes of the coordinate system. When you add an actor to the 3D environment, the default parent actor is the Scene Origin at (0,0,0).
Example: joint.Translation = [1 2 1]
Relative rotation (roll, pitch, yaw) of the actor object to its parent actor, specified as a real 1-by-3 vector, in rad. Use Rotation to rotate the sim3d.Joint object in the 3D environment.
Example: joint.Rotation = [0 pi/2 pi/8]
Type of joint, specified as one of these values, as a character
array or string. The relative motion of the constrained actors is defined by the
JointType. The world uses the Unreal Engine coordinate system to transform objects. The movement of the constrained actors
also depends on other properties of the joint object, including LinearLimit
and AngularLimit.
| Joint Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Constrains the complete linear and rotational motion of the actors along all axes, moving the actors as a single rigid body. |
|
| Allows relative rotation of actors in all directions around a
single pivot point. The point is defined by the
|
|
| Allows rotation of actors only around the X-axis of the world. |
|
| Allows rotation of actors only around the Y-axis of the world. |
|
| Allows rotation of actors only around the Z-axis of the world. |
|
| Allows sliding motion of only actors along the X-axis of the world. |
|
| Allows sliding motion of actors only along the Y-axis of the world. |
|
| Allows sliding motion of actors only along the Z-axis of the world. |
|
| Allows rotation and sliding motion of actors only along the X-axis of the world. |
|
| Allows rotation and sliding motion of actors only along the Y-axis of the world. |
|
| Allows rotation and sliding motion of actors only along the Z-axis of the world. |
|
Example: joint.JointType = 'RevoluteX'
Data Types: string
Custom joint movement, specified as a 1-by-6 Boolean vector. Use this property to
customize the motion of the constraints for each linear and angular axis, in the form
[x
y
z
roll
pitch
yaw]. 0 indicates free motion.
1 indicates locked motion.
Example: joint.Constraints = [1 1 1 0 0 0] creates a spherical
joint.
Data Types: double
Magnitude of linear stiffness, specified as a real positive scalar. A higher linear stiffness reduces movement, making the joint more rigid, like a solid connection. A lower stiffness allows more movement, simulating a flexible or spring-like behavior.
Example: joint.LinearStiffness = 3
Data Types: double
Magnitude of linear damping, specified as a real positive scalar. A higher linear damping slows down and stops more quickly, reducing oscillations and stabilizing the system. A lower damping value allows more prolonged movement and oscillations.
Example: joint.LinearDamping = 5
Data Types: double
Magnitude of angular stiffness, specified as a real positive scalar. A higher angular stiffness makes the joint resist rotational movement, making the joint more rigid. A lower angular stiffness allows more rotational freedom, simulating hinge-like behavior.
Example: joint.AngularStiffness = 3
Data Types: double
Magnitude of angular damping, specified as a real positive scalar. A higher angular damping value causes rotational motion to slow and stop more quickly, reducing oscillations and stabilizing the system. A lower damping value allows for more sustained rotational movement and oscillations.
Example: joint.AngularDamping = 3
Data Types: double
Constraints on translational movement, specified as a real positive number, in m.
Use this property to constrain the translational movement of connected
sim3d.Actor objects along X,
Y, and Z axes to a specified limit from the
initial translation of the joint.
Example: joint.LinearLimit = 2, allows the constrained
sim3d.Actor objects to translate from each other to a maximum
relative distance of 4m.
Data Types: double
Constraints on rotational movement (roll,
pitch, yaw), specified as a real positive 1-by-3
vector. Use this property to constrain the rotational movement of connected
sim3d.Actor objects within a specified range. This property defines
the maximum and minimum angles through which a joint can rotate around its axes.
Example: joint.AngularLimit = [0 0 pi] sets the
yaw value and the constrained sim3d.Actor
objects. The objects can rotate between [0 0 -pi] and [0 0
pi] from the initial rotation of the joint.
Dependencies
Physics should be set to true.
Data Types: double
Examples
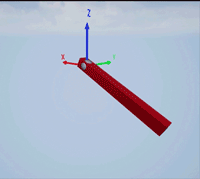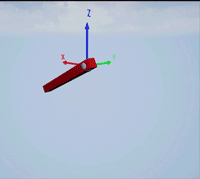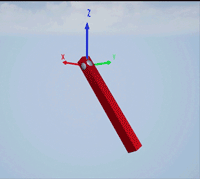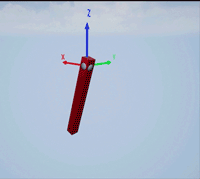
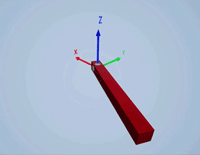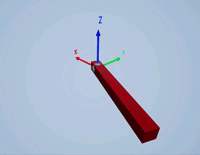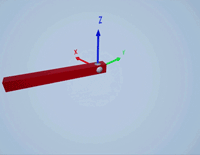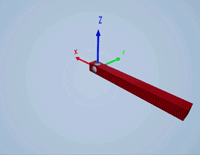
Create a revolute joint to link two sim3d.Actor objects with a hinge-like connection using the sim3d.Joint object.
Create a 3D environment using the sim3d.World object.
world = sim3d.World();
Create a hinge actor in the 3D environment using the sim3d.Actor object and add the hinge to the world.
hinge = sim3d.Actor(ActorName='Hinge',Translation=[0 0 0]); createShape(hinge,'sphere',[0.3 0.3 0.3]); hinge.Color = [0.85 0.85 0.85]; add(world,hinge);
Create a pendulum actor in the 3D environment using the sim3d.Actor object. Enable the Physics and Gravity properties to simulate physics effects during simulation. Add the pendulum to the world.
pendulum = sim3d.Actor(ActorName='Pendulum',Translation=[0 -1 0], ... Mobility=sim3d.utils.MobilityTypes.Movable); createShape(pendulum,'box',[0.24 0.24 2.4]); pendulum.Color = [1 0 0]; pendulum.Physics = true; pendulum.Gravity = true; pendulum.Rotation = [pi/2 0 0]; pendulum.Collisions = false; add(world,pendulum);
Create a joint between the hinge and pendulum using the sim3d.Joint object and set the JointType as RevoluteX. This joint allows the pendulum to rotate along the X-axis of the world. Set the properties of the joint object to control the rotational motion.
revoluteJoint = sim3d.Joint(ActorName='RevoluteJoint', ... Translation=[0 0 0], ... JointType='RevoluteX'); revoluteJoint.Actor1 = hinge; revoluteJoint.Actor2 = pendulum; revoluteJoint.AngularStiffness = 0.1; revoluteJoint.AngularDamping = 0.1; add(world,revoluteJoint);
Use the sim3d.graphics.Arrow and the sim3d.graphics.Text objects to annotate the axes and their directions in the world.
arrows = sim3d.graphics.Arrow( ... ActorName='Arrows', ... Translation=[0 0 0; 0 0 0; 0 0 0]); arrows.Rotation = [0 0 0; 0 0 pi/2; 0 pi/2 0]; arrows.Color = [1 0 0; 0 1 0; 0 0 1]; add(world,arrows,hinge); texts = sim3d.graphics.Text( ... ActorName='Texts', ... Translation=[1.05 0 0; 0 1.05 0; 0 0 1.05]); texts.Color = [1 0 0; 0 1 0; 0 0 1]; texts.String = ["X";"Y";"Z"]; add(world,texts,hinge);
Set the Translation and Rotation of the Default viewpoint and run the co-simulation.
world.Viewpoints.Default.Translation = [-3 -3 2.3]; world.Viewpoints.Default.Rotation = [0 -pi/6 pi/4]; sampletime = 0.01; stoptime = 5; run(world,sampletime,stoptime); delete(world);
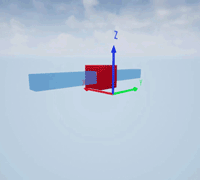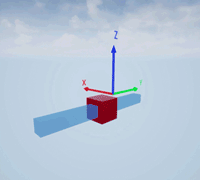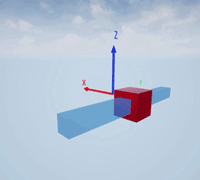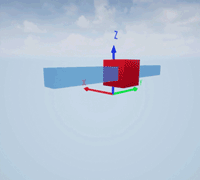
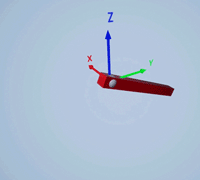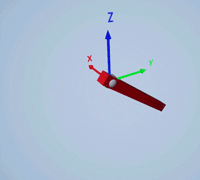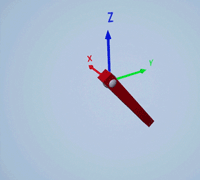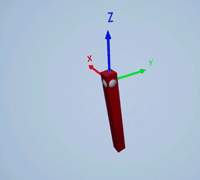
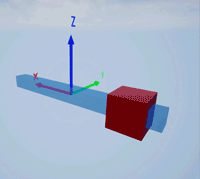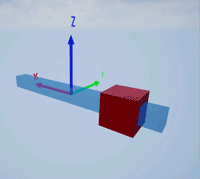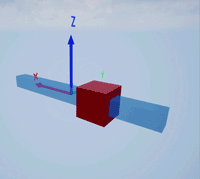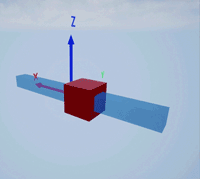
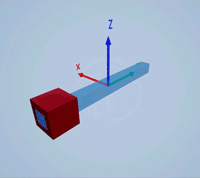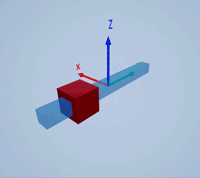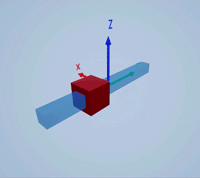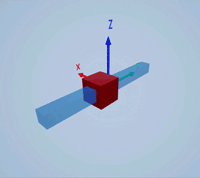
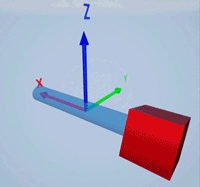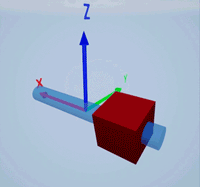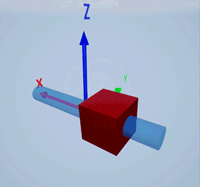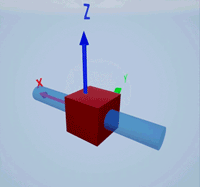
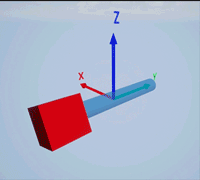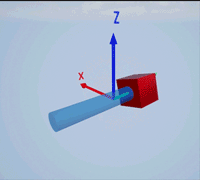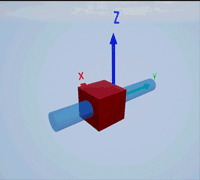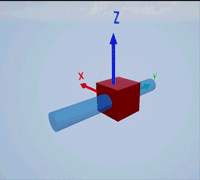
Create a prismatic joint to link two sim3d.Actor objects with a sliding or linear movement using the sim3d.Joint object. This joint allows one actor to move along a single axis relative to another actor.
Create a 3D environment using the sim3d.World object.
world = sim3d.World();
Create a rectangular rod actor in the 3D environment using the sim3d.Actor object and add the actor to the world.
rod = sim3d.Actor(ActorName='Rod',Translation=[0 0 0], ... Mobility=sim3d.utils.MobilityTypes.Movable); createShape(rod,'box',[0.25 0.25 3]); rod.Color = [0 0.2 0.5]; rod.Transparency = 0.5; rod.Shininess = 0; add(world,rod);
Create a box actor in the 3D environment using the sim3d.Actor object to slide over the rectangular rod. Enable the Physics and Gravity properties to simulate physics effects during simulation. Add the box to the world.
box = sim3d.Actor(ActorName='Box',Translation=[0 0 0], ... Mobility=sim3d.utils.MobilityTypes.Movable); createShape(box,'box',[0.5 0.5 0.5]); box.Color = [1 0 0]; box.Physics = true; box.Gravity = true; add(world,box);
Create a joint between the rod and box actors using the sim3d.Joint object and set the JointType as PrismaticZ. This joint allows the box actor to slide over the rod only along the Z-axis of the world. Set the properties of the joint object to control the linear motion.
joint = sim3d.Joint(ActorName='PrismaticJoint', ... Translation=[0 0 0], ... JointType='PrismaticZ'); joint.Actor1 = rod; joint.Actor2 = box; joint.LinearStiffness = 10; joint.LinearDamping = 0.1; joint.LinearLimit = 3; add(world,joint);
Use the sim3d.graphics.Arrow and the sim3d.graphics.Text objects to annotate the axes and their directions in the world.
arrows = sim3d.graphics.Arrow( ... ActorName='Arrows', ... Translation=[0 0 0; 0 0 0; 0 0 0]); arrows.Rotation = [0 0 0; 0 0 pi/2; 0 pi/2 0]; arrows.Color = [1 0 0; 0 1 0; 0 0 1]; add(world,arrows); texts = sim3d.graphics.Text( ... ActorName='Texts', ... Translation=[1.05 0 0; 0 1.05 0; 0 0 1.05]); texts.Color = [1 0 0; 0 1 0; 0 0 1]; texts.String = ["X";"Y";"Z"]; add(world,texts);
Set the Translation and Rotation of the Default viewpoint and run the co-simulation.
world.Viewpoints.Default.Translation = [-3 -3 2.3]; world.Viewpoints.Default.Rotation = [0 -pi/6 pi/4]; sampletime = 0.01; stoptime = 5; run(world,sampletime,stoptime); delete(world);
Version History
Introduced in R2025a
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)