addlink
Syntax
Description
linkIDs = addlink(graph,statePairs)navGraph
object.
linkIDs = addlink(graph,statePairs,metadata1,...metadataN)Weights, in addition to the state pairs.
However, the first column of the table must always specify the state pairs to be
connected.
Examples
Load navGraph object into MATLAB® workspace and inspect its properties.
load("navGraphData.mat")
disp(navGraphObj) navGraph with properties:
States: [8×3 table]
Links: [7×3 table]
LinkWeightFcn: @nav.algs.distanceEuclidean
Inspect the states table of the graph.
disp(navGraphObj.States)
StateVector Name Lanes
_______________________ _____ _____
8 2 0.72176 {'A'} 2
1 1 0.29188 {'B'} 2
7 7 0.91777 {'C'} 2
8 10 0.71458 {'D'} 2
5 1 0.54254 {'E'} 2
3 6 0.14217 {'F'} 2
2 9 0.37334 {'G'} 3
8 7 0.67413 {'H'} 2
Inspect the links table of the graph. The first column contains the indices of states from the states table. The two-element vectors in the first column of the table represent the pairs of states that are connected. Note that the links table also contains 'Weight' and 'Curvature' metadata in addition to the connected state pairs.
disp(navGraphObj.Links)
EndStates Weight Curvature
_________ ______ _________
1 3 1.5089 0.0034635
3 7 8.921 0.0063649
5 4 2.387 0.0060558
6 2 19.452 0.0041751
7 1 38.776 0.0051347
7 8 13.938 0.0076324
8 2 43.893 0.0031493
Display the graph.
show(navGraphObj)

From the graph, you can infer that the states 'D' and 'E' are not connected to any other states, and no path exists when a start or goal point lies on one of these states. To connect these states, use the addlink function. Specify the state pairs to be connected using either the indices or state names from the states table.
Specify State Indices to Add Links
From the states table of the input graph you can find that the indices for the states with names "E" and "F" are 5 and 6, respectively. Specify these indices as input to connect states "E" and "F".
Id = addlink(navGraphObj,[5 6],2.5,0.001)
Id = 4
Inspect the updated links table for new states and the related metadata. Note that the state indices of the new state pairs are added to the fifth row of the links table. The entries in the links table are sorted according to the index of the first state in each state pair listed in the first column. The rows that have the same index for the first state are sorted based on the index of the second state in each state pair.
disp(navGraphObj.Links)
EndStates Weight Curvature
_________ ______ _________
1 3 1.5089 0.0034635
3 7 8.921 0.0063649
5 4 2.387 0.0060558
5 6 2.5 0.001
6 2 19.452 0.0041751
7 1 38.776 0.0051347
7 8 13.938 0.0076324
8 2 43.893 0.0031493
Display the updated graph. Now all the states in the input graph are connected, you can compute path for any start and goal point that lie between these states.
show(navGraphObj)

Specify State Names to Add Links
Add a link between states with names "C" and "D". In addition to the state pair, you must also specify the value for associated Weight and Curvature metadata in the links table.
Id = addlink(navGraphObj,["C" "D"],5,0.004)
Id = 2
Inspect the updated links table for new state pairs and the related metadata. Note that the state indices of the new state pairs are added to the second row of the links table.
disp(navGraphObj.Links)
EndStates Weight Curvature
_________ ______ _________
1 3 1.5089 0.0034635
3 4 5 0.004
3 7 8.921 0.0063649
5 4 2.387 0.0060558
5 6 2.5 0.001
6 2 19.452 0.0041751
7 1 38.776 0.0051347
7 8 13.938 0.0076324
8 2 43.893 0.0031493
show(navGraphObj)

Load navGraph object into MATLAB® workspace and inspect its properties.
load("navGraphData.mat")
disp(navGraphObj) navGraph with properties:
States: [8×3 table]
Links: [7×3 table]
LinkWeightFcn: @nav.algs.distanceEuclidean
Inspect the states table of the graph.
disp(navGraphObj.States)
StateVector Name Lanes
_______________________ _____ _____
8 2 0.72176 {'A'} 2
1 1 0.29188 {'B'} 2
7 7 0.91777 {'C'} 2
8 10 0.71458 {'D'} 2
5 1 0.54254 {'E'} 2
3 6 0.14217 {'F'} 2
2 9 0.37334 {'G'} 3
8 7 0.67413 {'H'} 2
Inspect the links table of the graph. The first column contains the indices of states from the states table. The two-element vectors in the first column of the table represent the pairs of states that are connected. Note that the links table also contains 'Weight' and 'Curvature' metadata in addition to the connected state pairs.
disp(navGraphObj.Links)
EndStates Weight Curvature
_________ ______ _________
1 3 1.5089 0.0034635
3 7 8.921 0.0063649
5 4 2.387 0.0060558
6 2 19.452 0.0041751
7 1 38.776 0.0051347
7 8 13.938 0.0076324
8 2 43.893 0.0031493
Display the graph. From the graph, you can infer that the states 'D' and 'E' are not connected to any other states, and no path exists when a start or goal point lies on one of these states.
show(navGraphObj)

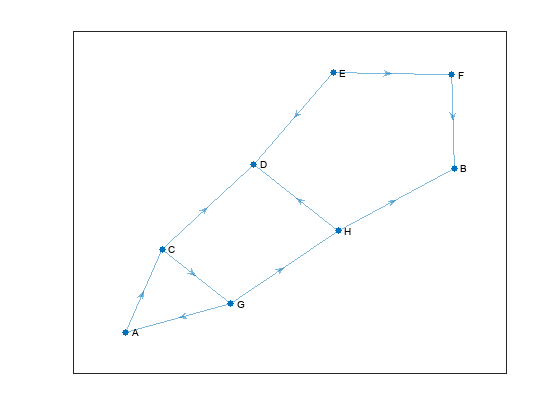
Add links between these state pairs:
States with names "
C" and "D".States with names "
E" and "F".States with names "
H" and "D"
In addition to the state pairs, you must also specify the values for associated Weight and Curvature metadata in the links table. The function returns the indices of the new state pairs in the links table.
Id = addlink(navGraphObj,["C" "D";"E" "F";"H" "D"],[5;2.5;50],[0.005;0.003;0.004])
Id = 3×1
2
5
10
Inspect the updated links table for new state pairs and their associated metadata. Note that the state indices of the new state pairs are added to the second, fifth, and tenth rows of the links table. The entries in the links table are sorted according to the index of the first state in each state pair listed in the first column. The rows that have the same index for the first state are sorted based on the index of the second state in each state pair.
disp(navGraphObj.Links)
EndStates Weight Curvature
_________ ______ _________
1 3 1.5089 0.0034635
3 4 5 0.005
3 7 8.921 0.0063649
5 4 2.387 0.0060558
5 6 2.5 0.003
6 2 19.452 0.0041751
7 1 38.776 0.0051347
7 8 13.938 0.0076324
8 2 43.893 0.0031493
8 4 50 0.004
Display the updated graph.
show(navGraphObj)
Input Arguments
Graph object, specified as a navGraph
object.
Data Types: double
Indices or names of the states to be linked, specified as a two-element column vector, M-by-2 matrix, or a cell array of strings. The indices or names of the states to be linked must be taken from the states table of the input graph. M specifies the number of state pairs to be linked.
The values in the column vector or matrix can be
Numeric data, specifying the indices of the states to be connected. For example, when you specify
statePairsas [1 3], the function connects the states listed in the first and third rows of the states table of the input graph.String data, specifying the names of the states to be connected. For example, when you specify
statePairsas ["A" "B"], the function fetches states with names "A" and "B" from the states table of the input graph and connects those two states.
Note
If the specified state pairs already exist in the links table of the input graph, the function will not add the duplicate pair to the graph.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | string | cell
Metadata containing additional information about the links connecting the states, specified as a numeric array, cell array of character vectors, string array, or cell array of strings.
Data Types: double | string | cell
Output Arguments
Link identifiers, returned as a column vector of positive integers. Link identifiers represent the indices of the state pairs added to the links table of the graph. The length of the vector specifies the number of new state pairs that are linked in the graph.
The addlink function sorts the rows of the links table in
ascending order based on the index of the first state in each state pair listed in the
first column of the table. If two or more rows have the same index for the first state,
the function will then sort those rows according to the index of the second state in
each state pair.
Since R2025a
Status indicating if new links are added, returned as an
M-element column vector containing 0's and 1's. Each element
indicates whether the corresponding link specified in the input argument
statePairs is added to the graph (1 for added,
0 for not added). The size of this vector matches the number of
state pairs specified in statePairs.
The function does not add links between the same state (self-links). If you specify a link between identical states, the function ignores it.
Data Types: logical
Extended Capabilities
For code generation,
Declare states variable in the
Statestable of thenavGraphobject as a variable-size data, prior to constructing the table.coder.varsize("states")State names are not supported.
Specify state pairs as numeric array.
Version History
Introduced in R2024aStarting in R2025a, the addlink function outputs a second
argument states to indicate new state pair links specified in the input
statePairs is added to the graph.
See Also
addstate | rmstate | rmlink | findlink | findstate | index2state | state2index | successors | show | copy
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)