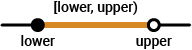mustBeBetween
Syntax
Description
mustBeBetween(
throws an error if any element in A,lower,upper)A is outside the range defined by
lower and upper. A value is within the range if it
is greater than or equal to lower, and less than or equal to
upper. This function does not return a value.
mustBeBetween calls the allbetween
function to determine if all elements in A are within the specified
range.
Class support: All numeric classes, logical, char,
string, categorical, datetime,
duration, and MATLAB® classes that overload allbetween or
isbetween.
mustBeBetween(
specifies the type of interval. For example,
A,lower,upper,intervalType)mustBeBetween(A,lower,upper,"open") validates that all elements in
A are within the open interval (lower,
upper).
mustBeBetween(___,DataVariables=
specifies the table or timetable variables to operate on in addition to any of the input
argument combinations in previous syntaxes. For example, for table vars)A,
mustBeBetween(A,lower,upper,DataVariables="Var1") validates that elements
in table variable Var1 are within the specified range.
Examples
Input Arguments
Tips
mustBeBetweenis designed to be used for property and function argument validation.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2025a
![Closed interval [lower, upper]](interval-notation-02.png)

![Half-open interval (lower, upper]](interval-notation-04.png)