Results for
Educators in mid 2025 worried about students asking an AI to write their required research paper. Now, with agentic AI, students can open their LMS with say Comet and issue the prompt “Hey, complete all my assignments in all of my courses. Thanks!” Done. Thwarting illegitimate use of AIs in education without hindering the many legitimate uses is a cat-and-mouse game and burgeoning industry.
I am actually more interested in a new AI-related teaching and learning challenge: how one AI can teach another AI. To be specific, I have been discovering with Claude macOS App running Opus 4.5 how to school LM Studio macOS App running a local open model Qwen2.5 32B in the use of MATLAB and other MCP services available to both apps, so, like Claude, LM Studio can operate all of my MacOS apps, including regular (Safari) and agentic (Comet or Chrome with Claude Chrome Extension) browsers and other AI Apps like ChatGPT or Perplexity, and can write and debug MATLAB code agentically. (Model Context Protocol is the standardized way AI apps communicate with tools.) You might be playing around with multiple AIs and encountering similar issues. I expect the AI-to-AI teaching and learning challenge to go far beyond my little laptop milieu.
To make this concrete, I offer the image below, which shows LM Studio creating its first Excel spreadsheet using Excel macOS app. Claude App in the left is behind the scenes there updating LM Studio's context window.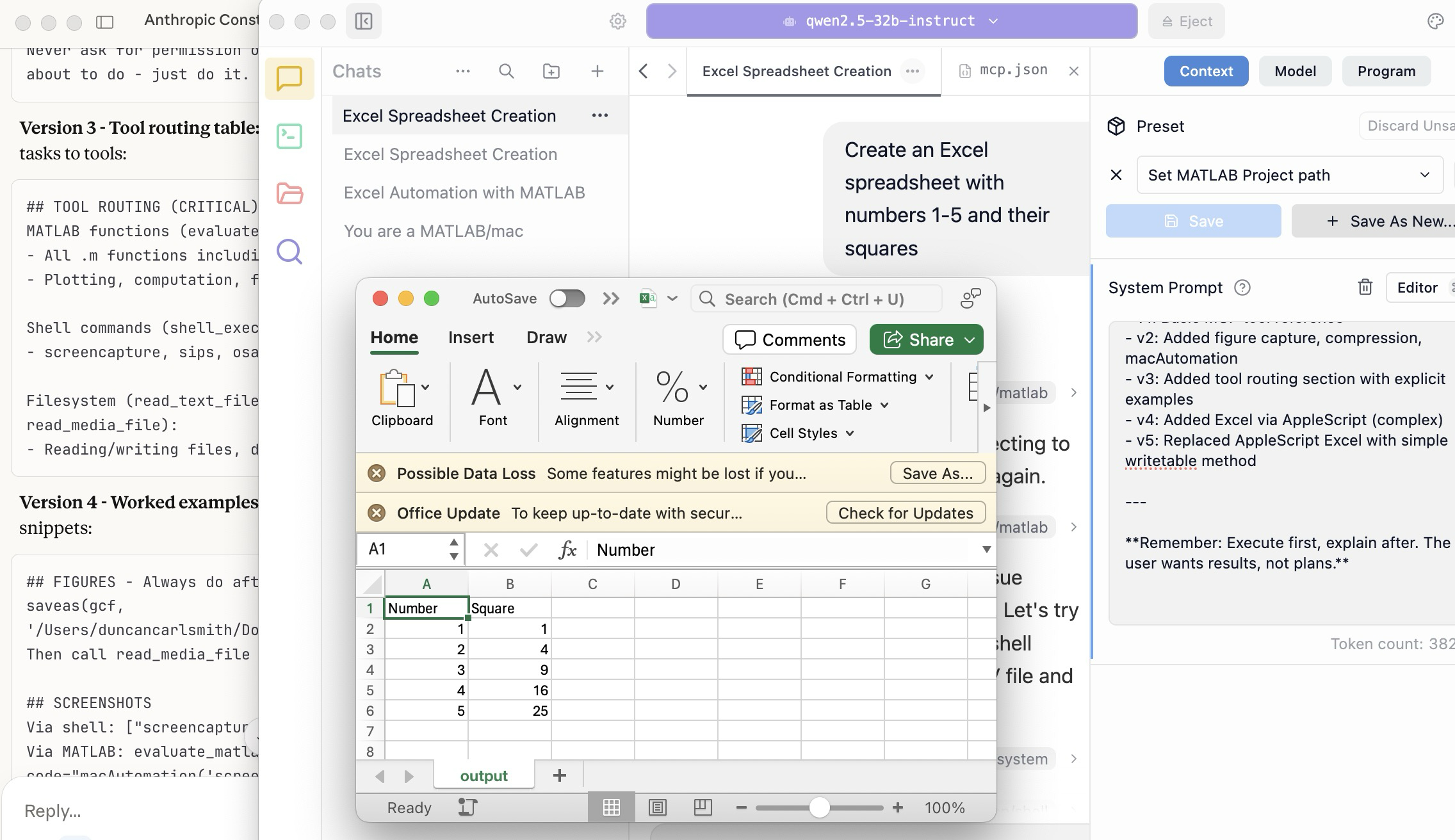

A teacher needs to know something but is at best a guide and inspiration, never a total fount of knowedge, especially today. Working first with Claude alone over the last few weeks to develop skills has itself been an interesting collaborative teaching and learning experience. We had to figure out how to use our MATLAB and other MCP services with various macOS services and some ancillary helper MATLAB functions with hopefully the minimal macOS permissions needed to achieve the desired functionality. Loose permissions allow the AI to access a wider filesystem with shell access, and, for example, to read or even modify an application’s preferences and permissions, and to read its state variables and log files. This is valuable information to an AI in trying to successfully operate an application to achieve some goal. But one might not be comfortable being too permissive.
The result of this collaboration was an expanding bag of tricks: Use AppleScript for this app, but a custom Apple shortcut for this other app; use MATLAB image compression of a screenshot (to provide feedback on the state and results) here, but if MATLAB is not available, then another slower image processing application; use cliclick if an application exposes its UI elements to the Accessibility API, but estimate a cursor relocation from a screenshot of one or more application windows otherwise. Texting images as opposed to text (MMS v SMS) was a challenge. And it’s going to be more complex if I use a multi-monitor setup.
Having satisfied myself that we could, with dedication, learn to operate any app (though each might offer new challenges), I turned to training another AI, similarly empowered with MCP services, to do the same, and that became an interesting new challenge. Firstly, we struggled with the Perplexity App, configured with identical MCP and other services, and found that Perplexity seems unable to avail itself of them. So we turned to educating LM Studio, operating a suite of models downloaded to my laptop.
An AI today is just a model trained in language prediction at some time. It is task-oriented and doesn’t know what to do in a new environment. It needs direction and context, both general and specific. AI’s now have web access to current web information and, given agentic powers, can on their own ask other AI’s for advice. They are quick-studies.
The first question in educating LM Studio was which open model to use. I wanted one that matched my laptop hardware - an APPLE M1 Max (10-core) CPU with integrated 24-core GPU with 64 GB shared memory- and had smarts comparable to Claude’s Opus 4.5 model. We settled on Mistral-Nemo-Instruct 2407 (12B parameters, ~7GB) and got it to the point where it could write and execute a MATLAB code to numerically integrate the equations of motion for a pendulum. Along the way, delving into the observation that the Mistral model's pendulum amplitude was drifting, I learned from Claude about symplectic integration. A teacher is always learning. Learning makes teaching fun.
But, long story short, we learned in the end that this model in this context was unable to see logical errors in code and fix them like Claude. So we tried and settled on some different models: Qwen 2.5 7B Instruct for speed, or Qwen 2.5 32B Instruct for more complex reasoning. The preliminary results looks good!
Our main goal was to teach a model how to use the unusual MCP and linked services at its disposal, starting from zero, and as you might educate a beginning student in physics or whatever through exercises and direct experience. Along the way, in teaching for the first time, we developed a kind of nascent curriculum strategy just to introduce the model to its new capabilities. Allow me to let Claude summarize just to give you a sense. There will not be a test on this material.
The Bootstrapping Process
Phase 1: Discovery of the Problem
The Qwen/Mistral models would describe what they would do rather than execute tools. They'd output JSON text showing what a tool call would look like, rather than actually triggering the tool. Or they'd say "I would use the evaluate_matlab_code tool to..." without doing it.
Phase 2: Explicit Tool Naming
First fix - be explicit in prompts:
Use the evaluate_matlab_code tool to run this code...
Instead of:
Run this MATLAB script...
This worked, but required the user to know tool names.
Phase 3: System Prompt Engineering
We iteratively built up a system prompt (Context tab in LM Studio) that taught the model:
Version 1 - Basic path:
When using MATLAB tools, always use /Users/username/Documents/MATLAB
as the project_path unless the user specifies otherwise.
Version 2 - Forceful execution:
IMPORTANT: When you need to use a tool, execute it immediately.
Do not describe the tool call or show JSON - just call the tool directly.
Never ask for permission or explain what you're about to do - just do it.
Version 3 - Tool routing table:
Added explicit mapping of tasks to tools:
## TOOL ROUTING (CRITICAL)
MATLAB functions (evaluate_matlab_code):
- All .m functions including macAutomation()
- Plotting, computation, file I/O
Shell commands (shell_execute):
- screencapture, sips, osascript, open, say...
Filesystem (read_text_file, write_file, read_media_file):
- Reading/writing files, displaying images
Version 4 - Worked examples:
Added concrete code snippets:
## FIGURES - Always do after plotting:
saveas(gcf, '/Users/username/Documents/MATLAB/LMStudio/latest_figure.png');
Then call read_media_file to display it.
## SCREENSHOTS
Via shell: ["screencapture", "-x", "output.png"]
Via MATLAB: evaluate_matlab_code with code="macAutomation('screenshot','screen')"
Version 5 - Physics patterns:
## PHYSICS - Use Symplectic Integration
omega(i) = omega(i-1) - (g/L)*sin(theta(i-1))*dt;
theta(i) = theta(i-1) + omega(i)*dt; % Use NEW omega
NOT: theta(i-1) + omega(i-1)*dt % Forward Euler drifts!
Phase 4: Prompt Phrasing for Smaller Models
Discovered that 7B-12B models needed "forceful" phrasing:
Execute now: Use evaluate_matlab_code to run this code...
And recovery prompts when they stalled:
Proceed with the tool call
Execute the fix now
Phase 5: Saving as Preset
Along the way, we accumulated various AI-speak directions and ultimately the whole context as a Preset in LM Studio, so it persists across sessions.
Now the trend in the AI industry is to develop and then share or publish “skills” rather like the Preset in a standard markdown structure, like CliffsNotes for AI. My notes/skills won't fit your environment and are evolving. They may appear biased against French models and too pro-Anthropic, and so on. We may need to structure AI education and AI specialization going forward in innovative ways, but may face familiar issues. Some AIs can be self-taught given the slightest nudge. Others less resource priviledged will struggle in their education and future careers. Some may even try to cheat and face a comeuppance.
The next step is to see if Claude can delegate complex tasks to local models, creating a tiered system where a frontier model orchestrates while cheaper models execute.