spectralKurtosis
Spectral kurtosis for signals and spectrograms
Syntax
Description
kurtosis = spectralKurtosis(x,f,Name=Value)
[
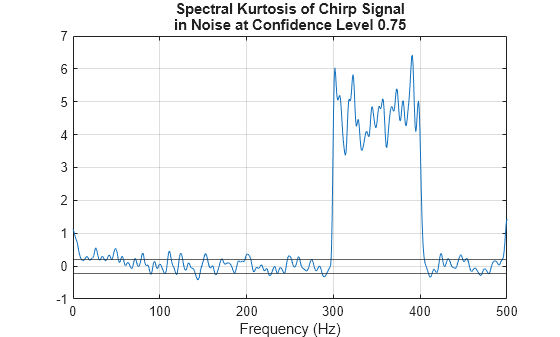
additionally returns the spectral kurtosis threshold using the confidence level
kurtosis,spread,centroid,threshold] = spectralKurtosis(___,ConfidenceLevel=p)p. Kurtosis values beyond threshold indicate
regions where the signal has a probability 1 – p of being a stationary Gaussian process. (since R2024b)
spectralKurtosis(___) with no output arguments plots
the spectral kurtosis.
If the input is in the time domain, the spectral kurtosis is plotted against time.
If the input is in the frequency domain, the spectral kurtosis is plotted against frame number.
Examples
Input Arguments
Name-Value Arguments
Output Arguments
More About
References
[1] Antoni, J. "The Spectral Kurtosis: A Useful Tool for Characterising Non-Stationary Signals." Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing. Vol. 20, Issue 2, 2006, pp. 282–307.
[2] Antoni, J., and R. B. Randall. "The Spectral Kurtosis: Application to the Vibratory Surveillance and Diagnostics of Rotating Machines." Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing. Vol. 20, Issue 2, 2006, pp. 308–331.
[3] Peeters, G. "A Large Set of Audio Features for Sound Description (Similarity and Classification) in the CUIDADO Project." Technical Report; IRCAM: Paris, France, 2004.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2019aSee Also
kurtogram | pspectrum | spectralCentroid (Audio Toolbox) | spectralEntropy | spectralSkewness | spectralSpread (Audio Toolbox)
Topics
- Spectral Descriptors (Audio Toolbox)