matrixProfile
Compute matrix profile between all pairs of subsequences in a single-variable or multivariable time series
Since R2024b
Syntax
Description
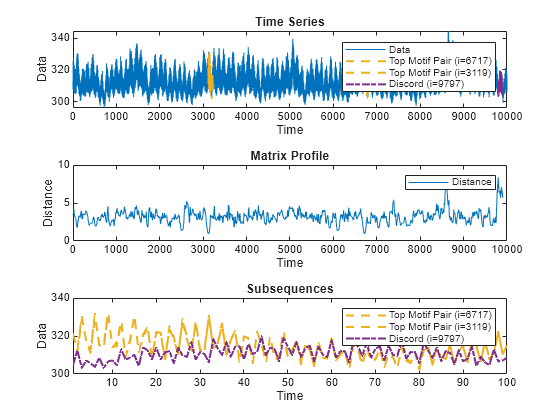
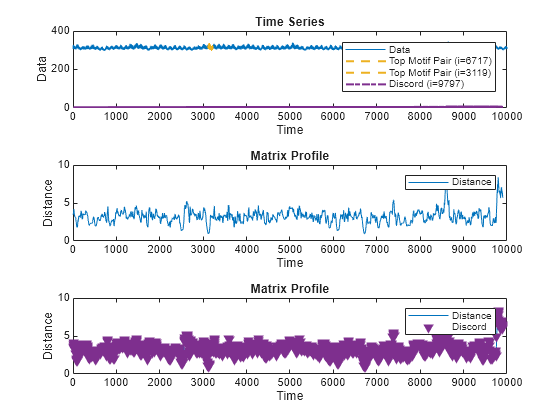
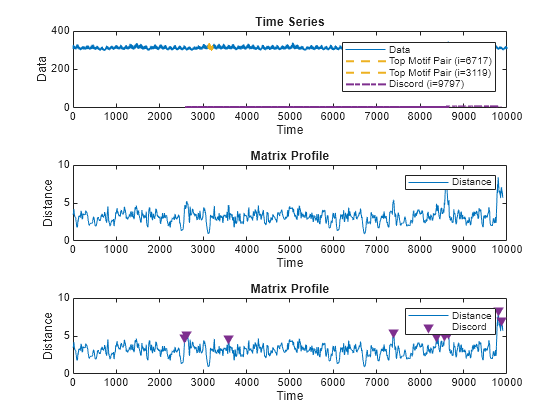
Return Matrix Profile
MP = matrixProfile(X,len)X. The matrix profile is the vector of minimum
z-normalized Euclidean distances between each subsequence of X with
length len and its closest neighbor.
If
Xis a vector, then the software treats it as a single channel.If
Xis a matrix, then the software computes the matrix profile independently for each column (multivariable solution).
matrixProfile provides two different algorithms for performing
the computations.
The STAMP algorithm (scalable time series anytime matrix profile) supports anytime and parallel computation, and works with both single-variable and multivariable data sets. Anytime capability allows you to stop the algorithm before it completes and still obtain an acceptably accurate solution. This is especially useful when computing a complete solution requires a significant amount of time. The
MaxIterationname-value argument determines when to stop the computation.The STOMP algorithm (scalable time series ordered matrix profile) is approximately log2(n) times faster than the STAMP algorithm, and is useful for single-variable time series if you have a GPU and do not need anytime capability.
You can use the functions findDiscord and findMotif
to find the locations of the top discords and motifs in MP.
[___] = matrixProfile(___,Name=Value)
specifies options using one or more name-value arguments in addition to the arguments in
previous syntaxes. For example, to use parallel processing, set
UseParallel to true.
Plot Matrix Profile
matrixProfile(___) plots an interactive plot of the
matrix profile. You can use this syntax with any of the previous input-argument
combinations.
Examples
Input Arguments
Name-Value Arguments
Output Arguments
References
[1] Yeh, Chin-Chia Michael, et al. “Matrix Profile I: All Pairs Similarity Joins for Time Series: A Unifying View That Includes Motifs, Discords and Shapelets.” 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), IEEE, 2016, pp. 1317–22. DOI.org (Crossref), https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2016.0179.
[2] Zhu, Yan, et al. “Matrix Profile II: Exploiting a Novel Algorithm and GPUs to Break the One Hundred Million Barrier for Time Series Motifs and Joins.” 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), IEEE, 2016, pp. 739–48. DOI.org (Crossref), https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2016.0085.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2024bSee Also
findDiscord | findMotif | distanceProfile | similarityDistance