phased.SteppedFMWaveform
Stepped FM pulse waveform
Description
The phased.SteppedFMWaveform object System object™ creates a stepped FM pulse waveform.
To create a stepped FM pulse waveform:
Create the
phased.SteppedFMWaveformobject and set its properties.Call the object with arguments, as if it were a function.
To learn more about how System objects work, see What Are System Objects?
Creation
Syntax
Description
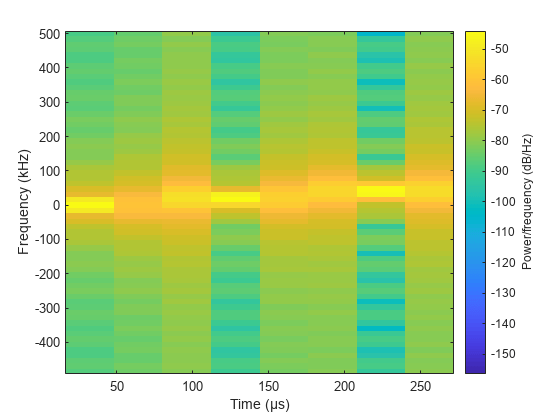
steppedFMWaveform = phased.SteppedFMWaveform creates a stepped FM
pulse waveform System object, steppedFMWaveform. The object generates samples of a
linearly stepped FM pulse waveform.
steppedFMWaveform = phased.SteppedFMWaveform(
sets properties using optional name-value arguments.Name=Value)
Properties
Usage
Syntax
Description
Y = steppedFMWaveform() returns samples of the stepped FM pulses in
a column vector, Y. The output, Y, results from
increasing the frequency of the preceding output by an amount specified by the
FrequencyStep property. If the total frequency increase is larger
than the value specified by the SweepBandwidth property, the object
returns the samples of a rectangular pulse.
Y = steppedFMWaveform(prfidx) uses the
prfidx index to select the PRF from the predefined vector of values
specified by in the PRF property. This syntax applies when you set
the PRFSelectionInputPort property to true.
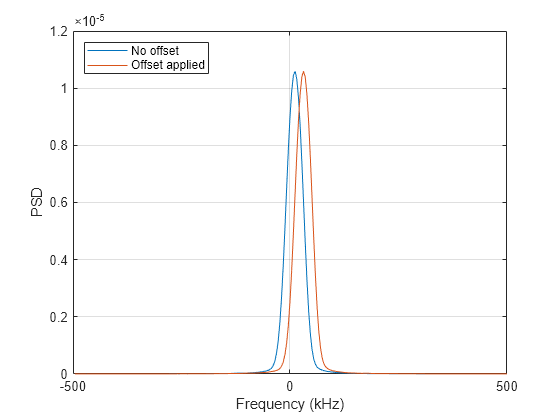
Y = steppedFMWaveform(freqoffset), uses the
freqoffset to generate the waveform with an offset as specified at
step time. Use this syntax for cases where the transmit pulse frequency needs to be
dynamically updated. This syntax applies when you set the
FrequencyOffsetSource property to "Input
port".
[Y,prf] = steppedFMWaveform(___) also returns the
current pulse repetition frequency, prf. To enable this syntax, set
the PRFOutputPort property to true and set the
OutputFormat property to "Pulses".
[Y,coeff] = steppedFMWaveform(___) returns the
matched filter coefficients, coeff, for the current pulse. To enable
this syntax, set CoefficientsOutputPort to true.
coeff is returned as either an
NZ-by-1 vector or an
NZ-by-M matrix.
You can combine optional input and output arguments when their enabling properties are
set. Optional inputs and outputs must be listed in the same order as the order of the
enabling properties. For example, [Y,prf,coeff] =
steppedFMWaveform(sRFM,prfidx,freqoffset).
Note
The object performs an initialization the first time the object is executed. This
initialization locks nontunable properties
and input specifications, such as dimensions, complexity, and data type of the input data.
If you change a nontunable property or an input specification, the System object issues an error. To change nontunable properties or inputs, you must first
call the release method to unlock the object.
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
Object Functions
To use an object function, specify the
System object as the first input argument. For
example, to release system resources of a System object named obj, use
this syntax:
release(obj)
Examples
More About
References
[1] Richards, M. A. Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2005.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2011a