findgroups
Find groups and return group numbers
Syntax
Description
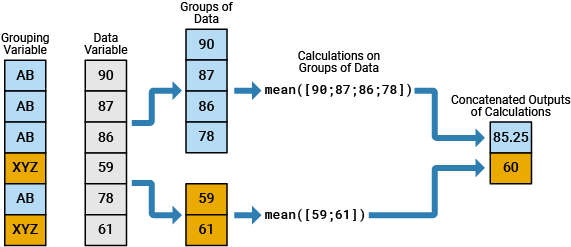
To split data into groups and apply a function to the groups, use the
findgroups and splitapply functions
together. For more information about calculations on groups of data, see Calculations on Groups of Data.
G = findgroups(A)G, a vector of group numbers created from the grouping
variable A. The output argument G contains
integer values from 1 to N, indicating N
distinct groups for the N unique values in
A. For example, if A is
["b","a","a","b"], then findgroups
returns G as [2 1 1 2]. In other words,
the group numbers in G correspond to the sorted unique values
in A.
To use G to split groups of data out of other variables,
pass it as an input argument to the splitapply function.
The findgroups function treats empty character vectors and
NaN, NaT, and undefined categorical
values in A as missing values and returns
NaN as the corresponding elements of
G.
G = findgroups(A1,...,AN)A1,...,AN. The
findgroups function defines groups as the unique
combinations of values across A1,...,AN. For example, if
A1 is ["a","a","b","b"] and
A2 is [0 1 0 0], then
findgroups(A1,A2) returns G as
[1 2 3 3], because the combination "b"
0 occurs twice.
[
also returns the sorted unique values for each group across
G,ID1,...,IDN] = findgroups(A1,...,AN)ID1,...,IDN. The values across
ID1,...,IDN define the groups. For example, if
A1 is ["a","a","b","b"] and
A2 is [0 1 0 0], then
findgroups(A1,A2) returns G as
[1 2 3 3], and ID1 and
ID2 as ["a","a","b"] and [0 1
0].
Examples
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
More About
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2015b
See Also
splitapply | pivot | unique | ismember | rowfun | varfun | arrayfun | groupsummary | discretize | histcounts | accumarray | convertvars | vartype