Create Fault-Embedded Models
When you add faults to models by using Simulink® Fault Analyzer™, you do not directly change the model design. You can create versions of your models that embed your faults directly on the model canvas. These models, called fault-embedded models, replicate the faults in your original design by using subsystems that duplicate the fault functionality. Create this model to export models to Simulink versions that predate the release of Simulink Fault Analyzer or to generate code from a model that has faults.
Export the Model
When you export a model to a fault-embedded model, Simulink copies the original model and converts the faults to subsystems in the copy of the model. To create a fault-embedded model:
Open a model that contains faults.
Open the Fault Analyzer app. In the Apps tab, click Fault Analyzer.
In the Fault Table pane, activate the faults that you want to export. See Enable, Modify, and Select Active Faults. The fault-embedded model only exports the active faults.
In the Fault Analyzer tab, in the Share section, click Export Embedded Model. The Export Embedded Model window opens.
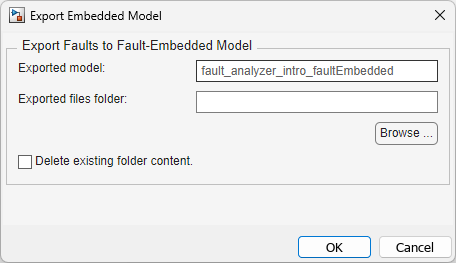
Specify the name and location of the new model by entering the name of the model in Exported model and the path to the folder in Exported files folder. The specified folder must exist and be empty. To delete the files in the specified folder before exporting the model, select Delete existing folder content.
Click OK.
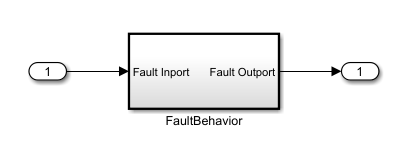
Simulink Fault Analyzer exports the model and an SVG file of the fault badge in the specified folder. The fault-embedded model has each active fault and its behavior in a masked atomic subsystem connected to the same element as in the original model. Each masked subsystem uses the fault badge as the mask image.
Note
When you create a fault-embedded model, the software copies Simscape™ blocks but does not convert the faults on those blocks to fault subsystem blocks.
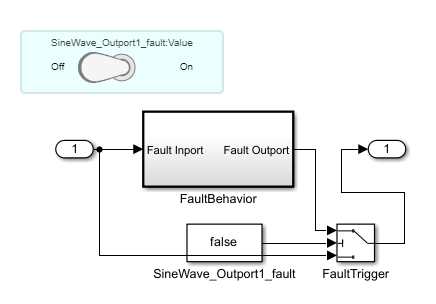
For example, this model contains a fault that adds noise to the output port of a Sine Wave block.
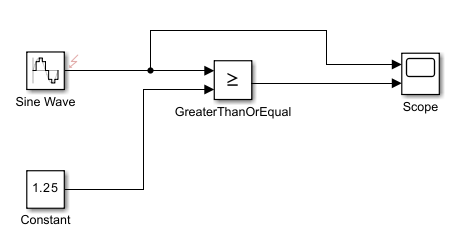
The fault-embedded model adds the fault as a subsystem connected to the output port of the Sine Wave block.
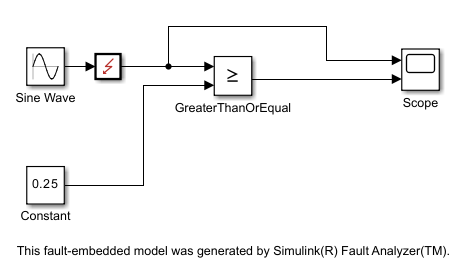
To view the behavior, open the subsystem.
Create Fault-Embedded Models that Contain Referenced Models
If your model contains referenced models, Simulink Fault Analyzer creates fault-embedded models for each referenced model depending on these circumstances.
| Use of Model Reference | Fault-Embedded Model Result |
|---|---|
| The referenced model or other models in the referenced model hierarchy do not have active faults. | Simulink Fault Analyzer creates a fault-embedded model of the top model only, and does not create a copy the referenced model. The top model references the referenced model in the original model folder. |
| The referenced model or other models in the referenced model hierarchy its hierarchy have active faults. | Simulink Fault Analyzer creates a fault-embedded model of the top model and creates a fault-embedded model version of each referenced model instance in the hierarchy that has faults. |
For more information on created faults in referenced models, see Manage Faults in Referenced Models.
Programmatically Export the Model
To programmatically export the model, use the Simulink.fault.exportEmbeddedModel function. You can specify the
same options in the Export Embedded Model window.
Model Trigger Types
Each masked subsystem that represents the embedded fault contains another atomic
subsystem that models the original fault behavior, labeled
FaultBehavior. Depending on the trigger type of each active
fault, the fault-embedded model attaches different blocks to the behavior.
| Trigger Type | Modeling |
|---|---|
Always
On | The subsystem connects to the Inport and Outport blocks that correspond to the input and output of the masked subsystem.
|
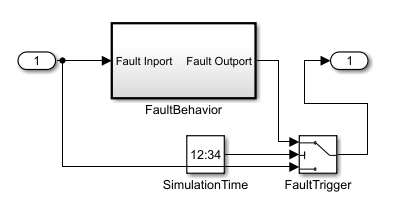
Timed | The subsystem connects to a Switch block that switches when the simulation time equals the value specified by the trigger time of the original fault.
|
Manual | The subsystem connects to a Switch block that switches depending on the status of a Toggle Switch block. Each manually triggered fault has a Toggle Switch block.
|
Conditional | The fault-embedded model converts the conditional trigger to a manual
trigger. See the Manual entry in this table
to view the configuration. |
For more information on defining triggers and trigger types, see Define and Model Faults, Define Trigger Properties and Trigger type.
Generate Code From Model
If you have Simulink Coder™ or Embedded Coder®, you can generate code from the fault-embedded model. For an example, see Generate Code from Fault-Embedded Models.
Note
Fault-embedded models might not support code generation when you first create them. You must configure them to conform to MATLAB® and Simulink code standards and guidelines. See Code Interface Configuration (Simulink Coder).
Limitations
If the model has Requirements Toolbox™ links, the fault-embedded model that you create does not have those links. If you need to establish traceability in the fault-embedded model, you must recreate the links.
You cannot export models with active faults that contain Fault Data Inport blocks in their behaviors.
See Also
Simulink.fault.exportEmbeddedModel