gsmDownlinkConfig
Create GSM downlink TDMA frame configuration object
Description
The gsmDownlinkConfig object is a GSM downlink TDMA frame
configuration object. Use gsmDownlinkConfig objects to create GSM downlink
waveforms.
Creation
Syntax
Description
cfggsmdl = gsmDownlinkConfig
cfggsmdl = gsmDownlinkConfig(sps)SamplesPerSymbol property to
sps.
cfggsmdl = gsmDownlinkConfig(___,Name=Value)gsmDownlinkConfig(RiseTime=4) sets the burst rise time to
4 symbols. Specify name-value arguments after all other input
arguments.
Properties
Samples per symbol, specified as a positive integer multiple of 4.
Data Types: double
Burst types for time slots 0–7 in the TDMA frame, specified as one of these options:
Eight-element row vector where each value is
"NB","FB","SB","Dummy", or"Off"— Each element specifies the burst type for the corresponding time slot."NB"— Transmit data using a normal burst for every time slot."FB"— Transmit data using a frequency correction burst for every time slot."SB"— Transmit data using a time synchronization burst for every time slot."Dummy"— Transmit data using a dummy burst for every time slot."Off"— All eight time slots contain no data.
For more information, see GSM Frames, Time Slots, and Bursts.
Note
The BurstType property is an enumeration. To perform code
generation, see Code Generation and the MEX Generation for GSM Downlink Waveform example.
Example: ["NB" "AB" "AB" "NB" "Off" "NB" "AB" "Off"] configures
the frame to use normal bursts in time slots 0, 3, and 5, use access bursts in time
slots 1, 2, and 6, and transmit no data in time slots 4 and 7.
Training sequence code (TSC) for normal bursts in time slots 0 – 7 in the TDMA frame, specified as one of these options:
Eight-element row vector of integers in the range [0, 7] — Each element specifies the TSC value for the corresponding normal burst time slot.
Integer in the range [0, 7] — Specifies the TSC value for every normal burst time slot.
For more information, see Training Sequence Code (TSC).
Example: [5 7 0 0 0 0 0 0] configures the frame to use training
sequence 5 in time slot 0, training sequence 7 in
time slot 1, and training sequence 0 in time slots 2 through
7.
Dependencies
To enable this property for a time slot, set the corresponding element of
BurstType to "NB".
Data Types: double
Power attenuation in dB for time slots 0–7 in the TDMA frame, specified as one of these options:
Eight-element row vector of nonnegative integers — Each element specifies the attenuation power value for the corresponding time slot.
Nonnegative integer — Specifies the power attenuation value for every time slot.
Example: [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3] configures the frame to apply 0 dB
attenuation to the burst signal power in time slot 0 through 6 and 3 dB of attenuation
to the burst signal power in time slot 7.
Data Types: double
Gaussian pulse length in symbol durations, specified as a positive integer.
Data Types: double
Burst rise time in symbols, specified as a positive scalar in the range
[1/SamplesPerSymbol, 29], where the increment resolution is
1/SamplesPerSymbol. The total ramp-up and ramp-down duration
(RiseTime - RiseDelay +
FallTime + FallDelay) must be less than 9.25
symbols. The characteristic shape of the rising edge of the burst is sinusoidal.
For more information, see GSM Frames, Time Slots, and Bursts.
Data Types: double
Burst rise delay in symbols, specified as a positive scalar in the range [–10, 10],
where the increment resolution is 1/SamplesPerSymbol. The total
ramp-up and ramp-down duration (RiseTime -
RiseDelay + FallTime +
FallDelay) must be less than 9.25 symbols. The burst rise delay
is measured with respect to the start of the useful part of the burst. For more
information, see GSM Frames, Time Slots, and Bursts.
When the burst rise delay is 0, the burst reaches full amplitude
at the start of the useful part of the burst. When the burst rise delay is positive, the
burst reaches full amplitude RiseDelay symbols after the start of
the useful part. When the burst rise delay is negative, the burst reaches full amplitude
RiseDelay symbols before the start of the useful part.
Data Types: double
Burst fall time in symbols, specified as a positive scalar in the range
[1/SamplesPerSymbol, 29], where the increment resolution is
1/SamplesPerSymbol. The total ramp-up and ramp-down duration
(RiseTime - RiseDelay +
FallTime + FallDelay) must be less than 9.25
symbols. The characteristic shape of the falling edge of the burst is sinusoidal.
For more information, see GSM Frames, Time Slots, and Bursts.
Data Types: double
Burst fall delay in symbols, specified as a positive scalar in the range [–10, 10],
where the increment resolution is 1/SamplesPerSymbol. The total
ramp-up and ramp-down duration (RiseTime -
RiseDelay + FallTime +
FallDelay) must be less than 9.25 symbols. The burst fall delay
is measured with respect to the end of the useful part of the burst. For more
information, see GSM Frames, Time Slots, and Bursts.
When the burst fall delay is 0, the burst begins decreasing from
full amplitude at the end of the useful part of the burst. When the burst fall delay is
positive, the burst begins decreasing from full amplitude FallDelay
symbols after the end of the useful part. When the burst fall delay is negative, the
burst begins decreasing from full amplitude FallDelay symbols
before the end of the useful part.
Data Types: double
Output Arguments
GSM downlink TDMA frame configuration, returned as a structure.
Data Types: struct
Examples
Create a GSM downlink TDMA frame configuration object with default settings, and then create a GSM waveform containing one TDMA frame. The GSM TDMA frame has eight time slots, each separated by a guard period of 8.25 symbols or about 30.46x10e-3 ms. Plot the GSM waveform.
Create a GSM downlink TDMA frame configuration object with default settings.
cfggsmdl = gsmDownlinkConfig
cfggsmdl =
gsmDownlinkConfig with properties:
BurstType: [NB NB NB NB NB NB NB NB]
SamplesPerSymbol: 16
TSC: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7]
Attenuation: [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
PulseLength: 4
RiseTime: 2
RiseDelay: 0
FallTime: 2
FallDelay: 0
Display information about the configured gsmDownlinkConfig object by using the gsmInfo function. Assign the sample rate to a variable, Rs, for use in computing the plot timescale.
wfInfo = gsmInfo(cfggsmdl)
wfInfo = struct with fields:
SymbolRate: 2.7083e+05
SampleRate: 4.3333e+06
BandwidthTimeProduct: 0.3000
BurstLengthInSymbols: 156.2500
NumBurstsPerFrame: 8
BurstLengthInSamples: 2500
FrameLengthInSamples: 20000
Rs = wfInfo.SampleRate;
Create the GSM waveform by using the gsmFrame function, and then plot the GSM waveform.
waveform = gsmFrame(cfggsmdl); t = (0:length(waveform)-1)/Rs*1e3; subplot(2,1,1) plot(t,abs(waveform)) grid on axis([0 5 0 1.2]) title('GSM Downlink Waveform - Amplitude') xlabel('Time (ms)') ylabel('Amplitude') subplot(2,1,2) plot(t,unwrap(angle(waveform))) grid on title('GSM Downlink Waveform - Phase') xlabel('Time (ms)') ylabel('Phase (rad)')
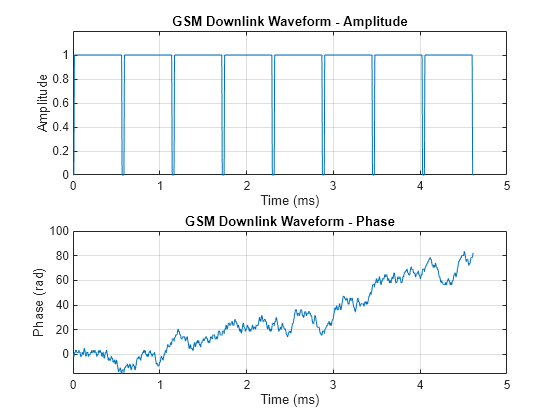
Create a GSM downlink TDMA frame configuration object that specifies 8 samples per symbol, and then create a GSM waveform containing one GSM downlink TDMA frame. The GSM TDMA frame are eight time slots, each separated by a guard period of 8.25 symbols or about 30.46x10e-3 ms separates each time slot. Plot the GSM waveform.
Create a GSM downlink TDMA frame configuration object, specifying 8 samples per symbols.
sps = 8; cfggsmdl = gsmDownlinkConfig(sps)
cfggsmdl =
gsmDownlinkConfig with properties:
BurstType: [NB NB NB NB NB NB NB NB]
SamplesPerSymbol: 8
TSC: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7]
Attenuation: [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
PulseLength: 4
RiseTime: 2
RiseDelay: 0
FallTime: 2
FallDelay: 0
Display information about the configured gsmDownlinkConfig object by using the gsmInfo function. Assign the sample rate to a variable, Rs, for use in computing the plot timescale.
wfInfo = gsmInfo(cfggsmdl)
wfInfo = struct with fields:
SymbolRate: 2.7083e+05
SampleRate: 2.1667e+06
BandwidthTimeProduct: 0.3000
BurstLengthInSymbols: 156.2500
NumBurstsPerFrame: 8
BurstLengthInSamples: 1250
FrameLengthInSamples: 10000
Rs = wfInfo.SampleRate;
Create the GSM waveform by using the gsmFrame function, and then plot the GSM waveform.
waveform = gsmFrame(cfggsmdl); t = (0:length(waveform)-1)/Rs*1e3; subplot(2,1,1) plot(t,abs(waveform)) grid on axis([0 5 0 1.2]) title('GSM Downlink Waveform - Amplitude') xlabel('Time (ms)') ylabel('Amplitude') subplot(2,1,2) plot(t,unwrap(angle(waveform))) grid on title('GSM Downlink Waveform - Phase') xlabel('Time (ms)') ylabel('Phase (rad)')
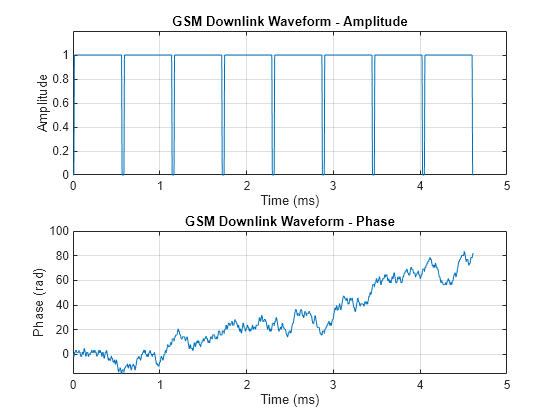
Create two GSM downlink TDMA frame configuration objects. Specify default settings for the first gsmDownlinkConfig object and adjust the signal power per time slot for the second. Generate GSM waveforms for both configurations. Plot the waveforms to show the signal attenuation per time slot in the second waveform.
Create a GSM downlink TDMA frame configuration object with default settings.
cfggsmdl = gsmDownlinkConfig
cfggsmdl =
gsmDownlinkConfig with properties:
BurstType: [NB NB NB NB NB NB NB NB]
SamplesPerSymbol: 16
TSC: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7]
Attenuation: [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
PulseLength: 4
RiseTime: 2
RiseDelay: 0
FallTime: 2
FallDelay: 0
Create another GSM downlink TDMA frame configuration object, adjusting the signal attenuation settings per time slot.
cfggsmdl2 = gsmDownlinkConfig('Attenuation',[1 0 3 4 5 6 4 2])cfggsmdl2 =
gsmDownlinkConfig with properties:
BurstType: [NB NB NB NB NB NB NB NB]
SamplesPerSymbol: 16
TSC: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7]
Attenuation: [1 0 3 4 5 6 4 2]
PulseLength: 4
RiseTime: 2
RiseDelay: 0
FallTime: 2
FallDelay: 0
Display information about the configured gsmDownlinkConfig object by using the gsmInfo function. Assign the sample rate to a variable, Rs, for use in computing the plot timescale.
wfInfo = gsmInfo(cfggsmdl)
wfInfo = struct with fields:
SymbolRate: 2.7083e+05
SampleRate: 4.3333e+06
BandwidthTimeProduct: 0.3000
BurstLengthInSymbols: 156.2500
NumBurstsPerFrame: 8
BurstLengthInSamples: 2500
FrameLengthInSamples: 20000
Rs = wfInfo.SampleRate;
Create the GSM waveforms, containing one TDMA frame, by using the gsmFrame function. GSM TDMA frames have are eight time slots, each separated by a guard period of 8.25 symbols or about 30.46x10e-3 ms separates each time slot. Plot each GSM waveform.
waveform = gsmFrame(cfggsmdl); waveform2 = gsmFrame(cfggsmdl2); t = (0:length(waveform)-1)/Rs*1e3; subplot(2,1,1) plot(t,[abs(waveform),abs(waveform2)]) grid on axis([0 5 0 1.2]) title('GSM Downlink Waveform - Amplitude') xlabel('Time (ms)') ylabel('Amplitude') subplot(2,1,2) plot(t,[unwrap(angle(waveform)),unwrap(angle(waveform2))]) grid on title('GSM Downlink Waveform - Phase') xlabel('Time (ms)') ylabel('Phase (rad)')
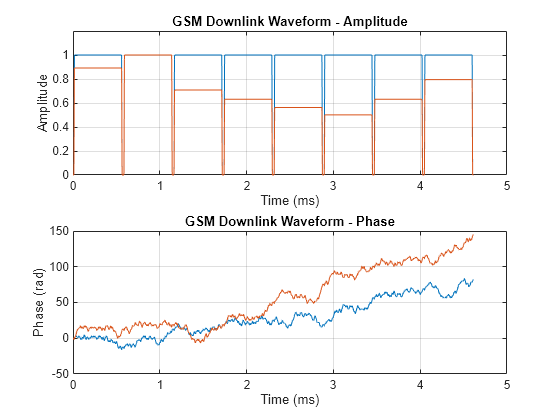
Generate and run a GSM waveform MEX function from the helper function createDownlinkWaveform. The createDownlinkWaveform helper function creates a GSM downlink waveform.
Write MATLAB Function
Open createDownlinkWaveform.m to see the code. The createDownlinkWaveform helper function generates a GSM downlink waveform by using the gsmDownlinkConfig object and the gsmInfo and gsmFrame functions.
Generate GSM Waveform
Use the createDownlinkWaveform helper function to create a GSM waveform containing two TDMA frames, and then plot the waveform.
[x,t] = createDownlinkWaveform(2); figure subplot(2,1,1); plot(t,abs(x)); grid on; title('GSM Downlink Waveform - Amplitude'); xlabel('Time (ms)'); ylabel('Amplitude') subplot(2,1,2); plot(t,unwrap(angle(x))); grid on; title('GSM Downlink Waveform - Phase'); xlabel('Time (ms)'); ylabel('Phase (rad)')
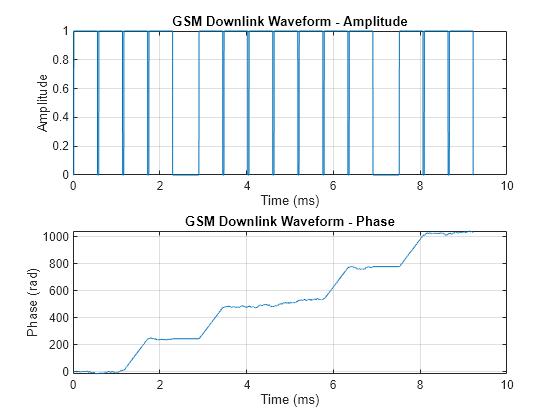
Generate MEX Function
Code generation defaults to MEX code generation when you do not specify a build target. By default, codegen names the generated MEX function createDownlinkWaveform_mex. Generate a MEX function from the createDownlinkWaveform helper function, and then run the MEX function to create two TDMA frames.
codegen createDownlinkWaveform -args 3
Code generation successful.
Generate Waveform Using MEX Function
Run the MEX function and plot the results. Since the waveform is created using random data, the phase plot changes each time you run the generateDownlinkFrame helper function or createDownlinkWaveform_mex function.
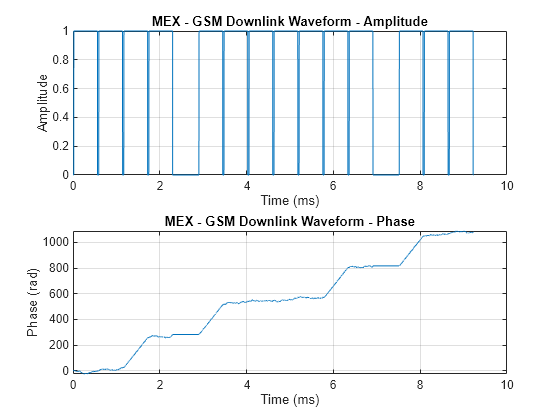
[x,t] = createDownlinkWaveform_mex(2); figure subplot(2,1,1); plot(t,abs(x)); grid on; title('MEX - GSM Downlink Waveform - Amplitude'); xlabel('Time (ms)'); ylabel('Amplitude') subplot(2,1,2); plot(t,unwrap(angle(x))); grid on; title('MEX - GSM Downlink Waveform - Phase'); xlabel('Time (ms)'); ylabel('Phase (rad)')
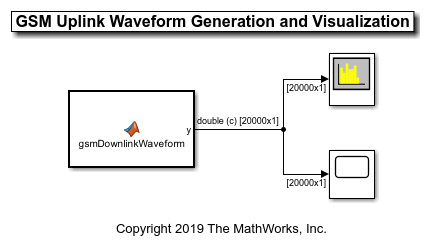
Model a GSM waveform generator in Simulink® by using the MATLAB® Function block and Communications Toolbox™ functions.
GSM Downlink Waveform Generation
The MATLAB Function (Simulink) block contains the gsmDownlinkWaveform function code. The code in the MATLAB Function block creates a GSM waveform by using the gsmDownlinkConfig object and the gsmFrame function.
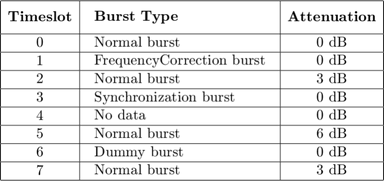
The gsmDownlinkConfig object specifies 16 samples per symbol and the time slot configuration for the GSM downlink TDMA frame shown is this table.
The output waveform has 16 samples for each GMSK symbol. The gsmFrame function generates the samples of the waveform.
Explore the Model
In compliance with GSM standards 3GPP TS 45.001 and 3GPP TS 45.002, the sample time of the MATLAB Function block that contains the gsmDownlinkWaveform function code is set to the GSM symbol rate of 1625e3/6 symbols per second. Display the current gsmDownlinkConfig object settings by using the gsmInfo function.
wfInfo =
struct with fields:
SymbolRate: 2.7083e+05
SampleRate: 4.3333e+06
BandwidthTimeProduct: 0.3000
BurstLengthInSymbols: 156.2500
NumBurstsPerFrame: 8
BurstLengthInSamples: 2500
FrameLengthInSamples: 20000
The model sample time of the MATLAB Function (Simulink) block is set to wfInfo.FrameLengthInSamples/wfInfo.SampleRate. To view the Sample time parameter, open the Block Parameters dialog box by right-clicking the MATLAB Function block and selecting Block Parameters (Subsystem).
Before the simulation runs, you must configure the sample rate of the MATLAB Function block. The PreLoadFcn and InitFcn callback functions configure the MATLAB Function block by creating a gsmDownlinkConfig object and wfInfo structure. To view the callback functions, on the Modeling tab, in the Setup section, select Model Settings > Model Properties. Then, on the Callbacks tab, select the PreLoadFcn or InitFcn callback function in the Model callbacks pane.
Results
Display the time domain signal and the spectrogram by running the simulation.

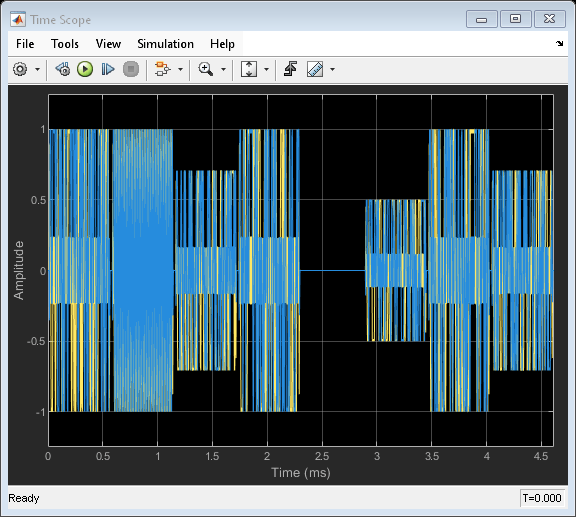
More About
In GSM, transmissions consist of TDMA frames. Each GSM TDMA frame consists of eight time slots. The transmission data content of a time slot is called a burst. As described in Section 5.2 of 3GPP TS 45.011, a GSM time slot has a 156.25-symbol duration when using the normal symbol period, which is a time interval of 15/26 ms or about 576.9 microseconds. A guard period of 8.25 symbols or about 30.46 microseconds separates each time slot. The GSM standards describes a symbol as one bit period. Since GSM uses GMSK modulation, there is one bit per bit period. The transmission timing of a burst within a time slot is defined in terms of the bit number (BN). The BN refers to a particular bit period within a time slot. The bit with the lowest BN is transmitted first. BN0 is the first bit period, and BN156 is the last quarter-bit period.
This image from 3GPP TS 45.011 shows the relationship between different frame types and the relationship between different burst types.

This table shows the supported burst types and their characteristics.
| Burst Type | Description | Link Direction | Useful Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
NB | Normal burst | Uplink/Downlink | 147 |
FB | Frequency correction burst | Downlink | 147 |
SB | Synchronization burst | Downlink | 147 |
Dummy | Dummy burst | Downlink | 147 |
AB | Access burst | Uplink | 87 |
Off | No burst sent | Uplink/Downlink | 0 |
Useful duration, described in Section 5.2.2 of 3GPP TS 45.002, is a characteristic of GSM bursts. The useful duration, or useful part, of a burst is defined as beginning halfway through BN0 and ending half a bit period before the start of the guard period. The guard period is the period between bursts in successive time slots. This figure, from Section 2.2 of 3GPP TS 45.004, shows the leading and trailing ½ bit difference between the useful and active parts of the burst.

For more information, see GSM TDMA Frame Parameterization for Waveform Generation.
Normal bursts include a training sequence bits field assigned a bit pattern based on the specified TSC. For GSM, you can select one of these eight training sequences for normal burst type time slots.
Training Sequence Code (TSC) | Training Sequence Bits (BN61, BN62, …, BN86) |
|---|---|
0 | (0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,1) |
1 | (0,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,1,1) |
2 | (0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0) |
3 | (0,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,0) |
4 | (0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,1) |
5 | (0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,1,0) |
6 | (1,0,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,1,1,1,1) |
7 | (1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,0,0) |
For more information, see Section 5.2.3 in 3GPP TS 45.002.
References
[1] 3GPP TS 45.001. "GSM/EDGE Physical layer on the radio path. General description." 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network.
[2] 3GPP TS 45.002. "GSM/EDGE Multiplexing and multiple access on the radio path." 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network.
[3] 3GPP TS 45.004. "GSM/EDGE Modulation." 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network.
Extended Capabilities
Usage notes and limitations:
The
SamplesPerSymbol,RiseTime,RiseDelay,FallTime, andFallDelayproperties must be set when creating the object, and their settings are static in the generated code.The
BurstTypeproperty must be set using the enumeration type instead of the string representation. Use thesegsmDownlinkBurstTypeenumerations:gsmDownlinkBurstType.NB,gsmDownlinkBurstType.FB,gsmDownlinkBurstType.SB,gsmDownlinkBurstType.Dummy, andgsmUplinkBurstType.Off. For example, this code assigns a frequency correction burst in time slot 2 and 5.cfg = gsmDownlinkConfig
cfg = gsmDownlinkConfig with properties: BurstType: [NB NB NB NB NB NB NB NB] SamplesPerSymbol: 16 TSC: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7] Attenuation: [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0] RiseTime: 2 RiseDelay: 0 FallTime: 2 FallDelay: 0cfg.BurstType([2 5] +1) = gsmDownlinkBurstType.FB
cfg = gsmDownlinkConfig with properties: BurstType: [NB NB FB NB NB FB NB NB] SamplesPerSymbol: 16 TSC: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7] Attenuation: [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0] RiseTime: 2 RiseDelay: 0 FallTime: 2 FallDelay: 0
Version History
Introduced in R2019bSpecify Gaussian filter pulse length in symbol durations using the
PulseLength name-value argument. The default value sets pulse length
to 4. The gsmFrame function
now also implements raised cosine roll-off instead of sine roll-off for the spectral shape
of the rise and fall mask. You can optimize the spectral occupancy of your design by
selecting the pulse length.
Previous releases used a static pulse length of 1 in the GMSK modulator and sine-shaped spectral rise and fall masks. The raised cosine roll-off shape and pulse length of 4, improves the out-of-channel and out-of-band spectral rejection.
See Also
Objects
Functions
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)