Model Complex Objects in Activity Diagrams Using MATLAB Class Tokens
This example shows how to model an activity diagram representation of a system that processes tokens containing complex objects. In activity diagrams, you can model complex objects, which contain specialized data structures or large number of functions using MATLAB class tokens. The class can either be a value class or a handle class. For information on this, see Comparison of Handle and Value Classes.
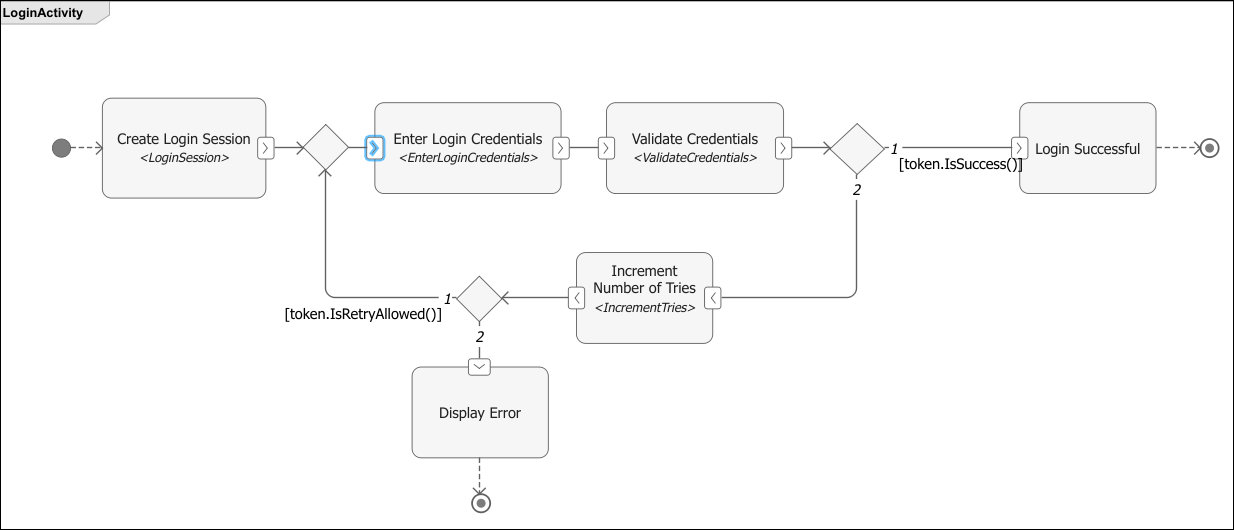
This example models a login authentication system using login credentials that are stored as MATLAB classes. The activity diagram has the following nodes:
Enter Login Credentialsaction node, which accepts login credentials from the user.Validate Credentialsaction node, which verifies whether the entered pin is an even number with at least four digits.Decision node, which checks whether the login succeeded or not.
If the
IsSuccessfunction returns aTruevalue, the token flows towards theLoginSuccesfulaction node.If the
IsSuccessfunction returns afalsevalue, the token flows towardsIncrement number of triesaction node.
Increment number of triesaction node, which counts the number of failed login attempts.
For more information about activity diagrams, see Describe System Behavior Using Activity Diagrams.
Open Activity Diagram for Login Session
From the example file, open the activity diagram.
open("LoginActivity.slx")
Define LoginSession Class
Create a custom MATLAB class called LoginSession and define its
associated properties and methods. To use a MATLAB class, it has to be on the file
path.
The LoginSession class defines public properties such as the user
name, date of birth, and pin number, along with private properties such as the number of
login attempts and login status.
The class method defines the constructor that initializes login credentials and the functions that are necessary for the activity diagram to simulate a login session.
classdef LoginSession % Example MATLAB class that defines a login session object with % internal logic for validating credentials and allowing retries. properties UserName = "" DateOfBirth = datetime([0 0 0]) PinNumber = 0 end properties (Access = private) NumTries = 0 Success = false end properties (Constant) MaxTries = 3; end methods % Constructor function obj = LoginSession() % Create a LoginSession object with default property values end % Validate credentials function obj = ValidateCredentials(obj) % Pin must an even number with at least 4 digits obj.Success = (obj.PinNumber > 999) && (mod(obj.PinNumber, 2) == 0); end % Increase number of tries function obj = IncrementTries(obj) obj.NumTries = obj.NumTries + 1; end % Whether login is successful function result = IsSuccess(obj) result = obj.Success; end % Whether retry is allowed function result = IsRetryAllowed(obj) result = (obj.NumTries <= obj.MaxTries); end end end
Note these considerations and limitations when you use MATLAB class tokens.
Signal logging and breakpoints are not supported with flows that contain MATLAB class tokens.
Port value labels are inaccessible for flows that use MATLAB class tokens.
When you step back during a simulation, restoring tokens containing handle objects is not supported.
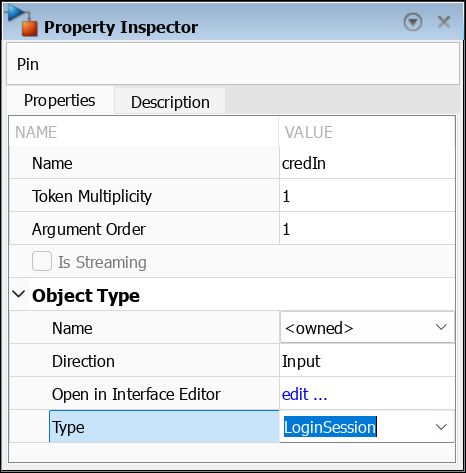
Configure Pins to Accept MATLAB Class Tokens
To enable MATLAB class tokens to flow through a pin, configure each pin to accept or generate a MATLAB class token.
In the activity diagram, open the Property Inspector and select the pin.
In the Name list, select owned. In the Type
field, enter LoginSession.
For example, input pin of the Enter Login Credentials action node
now expects a token with the MATLAB class LoginSession.
Create Conditional Flow with MATLAB Class Function
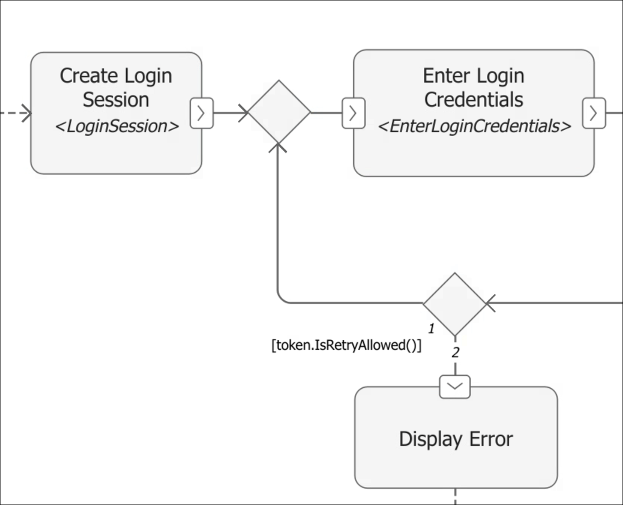
To access a function of the LoginSession class for the decision
node, use the built-in keyword token followed by the method name.
In this example, when the IsRetryAllowed function of the class
returns a True value, the token flows back to the Enter
Login Credentials action node. Otherwise, the token is routed to the
Display Error action node.
See Also
Functions
Tools
Blocks
- Initial Node | Action Node | Decision or Merge Node | Join or Fork Node | Flow Final Node | Activity Final Node