resume
Resume training of Gaussian kernel regression model
Syntax
Description
UpdatedMdl = resume(Mdl,X,Y)Mdl,
including the training data (predictor data in X and
response data in Y) and the feature expansion. The training
starts at the current estimated parameters in Mdl. The
function returns a new Gaussian kernel regression model
UpdatedMdl.
UpdatedMdl = resume(Mdl,Tbl,ResponseVarName)Tbl and the
true responses in Tbl.ResponseVarName.
UpdatedMdl = resume(Mdl,Tbl,Y)Tbl and
the true responses in Y.
UpdatedMdl = resume(___,Name,Value)
[
also returns the fit information in the structure array
UpdatedMdl,FitInfo] = resume(___)FitInfo.
Examples
Resume training a Gaussian kernel regression model for more iterations to improve the regression loss.
Load the carbig data set.
load carbigSpecify the predictor variables (X) and the response variable (Y).
X = [Acceleration,Cylinders,Displacement,Horsepower,Weight]; Y = MPG;
Delete rows of X and Y where either array has NaN values. Removing rows with NaN values before passing data to fitrkernel can speed up training and reduce memory usage.
R = rmmissing([X Y]); % Data with missing entries removed
X = R(:,1:5);
Y = R(:,end); Reserve 10% of the observations as a holdout sample. Extract the training and test indices from the partition definition.
rng(10) % For reproducibility N = length(Y); cvp = cvpartition(N,'Holdout',0.1); idxTrn = training(cvp); % Training set indices idxTest = test(cvp); % Test set indices
Train a kernel regression model. Standardize the training data, set the iteration limit to 5, and specify 'Verbose',1 to display diagnostic information.
Xtrain = X(idxTrn,:); Ytrain = Y(idxTrn); Mdl = fitrkernel(Xtrain,Ytrain,'Standardize',true, ... 'IterationLimit',5,'Verbose',1)
|=================================================================================================================| | Solver | Pass | Iteration | Objective | Step | Gradient | Relative | sum(beta~=0) | | | | | | | magnitude | change in Beta | | |=================================================================================================================| | LBFGS | 1 | 0 | 5.691016e+00 | 0.000000e+00 | 5.852758e-02 | | 0 | | LBFGS | 1 | 1 | 5.086537e+00 | 8.000000e+00 | 5.220869e-02 | 9.846711e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 2 | 3.862301e+00 | 5.000000e-01 | 3.796034e-01 | 5.998808e-01 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 3 | 3.460613e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 3.257790e-01 | 1.615091e-01 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 4 | 3.136228e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.832861e-02 | 8.006254e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 5 | 3.063978e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 1.475038e-02 | 3.314455e-02 | 256 | |=================================================================================================================|
Mdl =
RegressionKernel
ResponseName: 'Y'
Learner: 'svm'
NumExpansionDimensions: 256
KernelScale: 1
Lambda: 0.0028
BoxConstraint: 1
Epsilon: 0.8617
Properties, Methods
Mdl is a RegressionKernel model.
Estimate the epsilon-insensitive error for the test set.
Xtest = X(idxTest,:); Ytest = Y(idxTest); L = loss(Mdl,Xtest,Ytest,'LossFun','epsiloninsensitive')
L = 2.0674
Continue training the model by using resume. This function continues training with the same options used for training Mdl.
UpdatedMdl = resume(Mdl,Xtrain,Ytrain);
|=================================================================================================================| | Solver | Pass | Iteration | Objective | Step | Gradient | Relative | sum(beta~=0) | | | | | | | magnitude | change in Beta | | |=================================================================================================================| | LBFGS | 1 | 0 | 3.063978e+00 | 0.000000e+00 | 1.475038e-02 | | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 1 | 3.007822e+00 | 8.000000e+00 | 1.391637e-02 | 2.603966e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 2 | 2.817171e+00 | 5.000000e-01 | 5.949008e-02 | 1.918084e-01 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 3 | 2.807294e+00 | 2.500000e-01 | 6.798867e-02 | 2.973097e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 4 | 2.791060e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.549575e-02 | 1.639328e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 5 | 2.767821e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 6.154419e-03 | 2.468903e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 6 | 2.738163e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 5.949008e-02 | 9.476263e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 7 | 2.719146e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 1.699717e-02 | 1.849972e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 8 | 2.705941e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 3.116147e-02 | 4.152590e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 9 | 2.701162e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 5.665722e-03 | 9.401466e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 10 | 2.695341e+00 | 5.000000e-01 | 3.116147e-02 | 4.968046e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 11 | 2.691277e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 8.498584e-03 | 1.017446e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 12 | 2.689972e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 1.983003e-02 | 9.938921e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 13 | 2.688979e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 1.416431e-02 | 6.606316e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 14 | 2.687787e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 1.621956e-03 | 7.089542e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 15 | 2.686539e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 1.699717e-02 | 1.169701e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 16 | 2.685356e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 1.133144e-02 | 1.069310e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 17 | 2.685021e+00 | 5.000000e-01 | 1.133144e-02 | 2.104248e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 18 | 2.684002e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.832861e-03 | 6.175231e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 19 | 2.683507e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 5.665722e-03 | 3.724026e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 20 | 2.683343e+00 | 5.000000e-01 | 5.665722e-03 | 9.549119e-03 | 256 | |=================================================================================================================| | Solver | Pass | Iteration | Objective | Step | Gradient | Relative | sum(beta~=0) | | | | | | | magnitude | change in Beta | | |=================================================================================================================| | LBFGS | 1 | 21 | 2.682897e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 5.665722e-03 | 7.172867e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 22 | 2.682682e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.832861e-03 | 2.587726e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 23 | 2.682485e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.832861e-03 | 2.953648e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 24 | 2.682326e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.832861e-03 | 7.777294e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 25 | 2.681914e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.832861e-03 | 2.778555e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 26 | 2.681867e+00 | 5.000000e-01 | 1.031085e-03 | 3.638352e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 27 | 2.681725e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 5.665722e-03 | 1.515199e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 28 | 2.681692e+00 | 5.000000e-01 | 1.314940e-03 | 1.850055e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 29 | 2.681625e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.832861e-03 | 1.456903e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 30 | 2.681594e+00 | 5.000000e-01 | 2.832861e-03 | 8.704875e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 31 | 2.681581e+00 | 5.000000e-01 | 8.498584e-03 | 3.934768e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 32 | 2.681579e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 8.498584e-03 | 1.847866e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 33 | 2.681553e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 9.857038e-04 | 6.509825e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 34 | 2.681541e+00 | 5.000000e-01 | 8.498584e-03 | 6.635528e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 35 | 2.681499e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 5.665722e-03 | 6.194735e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 36 | 2.681493e+00 | 5.000000e-01 | 1.133144e-02 | 1.617763e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 37 | 2.681473e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 9.869233e-04 | 8.418484e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 38 | 2.681469e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 5.665722e-03 | 1.069722e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 39 | 2.681432e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.832861e-03 | 8.501930e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 40 | 2.681423e+00 | 2.500000e-01 | 1.133144e-02 | 9.543716e-04 | 256 | |=================================================================================================================| | Solver | Pass | Iteration | Objective | Step | Gradient | Relative | sum(beta~=0) | | | | | | | magnitude | change in Beta | | |=================================================================================================================| | LBFGS | 1 | 41 | 2.681416e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.832861e-03 | 8.763251e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 42 | 2.681413e+00 | 5.000000e-01 | 2.832861e-03 | 4.101888e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 43 | 2.681403e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 5.665722e-03 | 2.713209e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 44 | 2.681392e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.832861e-03 | 2.115241e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 45 | 2.681383e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.832861e-03 | 2.872858e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 46 | 2.681374e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 8.498584e-03 | 5.771001e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 47 | 2.681353e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.832861e-03 | 3.160871e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 48 | 2.681334e+00 | 5.000000e-01 | 8.498584e-03 | 1.045502e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 49 | 2.681314e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 7.878714e-04 | 1.505118e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 50 | 2.681306e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.832861e-03 | 4.756894e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 51 | 2.681301e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 1.133144e-02 | 3.664873e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 52 | 2.681288e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.832861e-03 | 1.449821e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 53 | 2.681287e+00 | 2.500000e-01 | 1.699717e-02 | 2.357176e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 54 | 2.681282e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 5.665722e-03 | 2.046663e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 55 | 2.681278e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.832861e-03 | 2.546349e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 56 | 2.681276e+00 | 2.500000e-01 | 1.307940e-03 | 1.966786e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 57 | 2.681274e+00 | 5.000000e-01 | 1.416431e-02 | 1.005310e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 58 | 2.681271e+00 | 5.000000e-01 | 1.118892e-03 | 1.147324e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 59 | 2.681269e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.832861e-03 | 1.332914e-04 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 60 | 2.681268e+00 | 2.500000e-01 | 1.132045e-03 | 5.441369e-05 | 256 | |=================================================================================================================|
Estimate the epsilon-insensitive error for the test set using the updated model.
UpdatedL = loss(UpdatedMdl,Xtest,Ytest,'LossFun','epsiloninsensitive')
UpdatedL = 1.8933
The regression error decreases by a factor of about 0.08 after resume updates the regression model with more iterations.
Load the carbig data set.
load carbigSpecify the predictor variables (X) and the response variable (Y).
X = [Acceleration,Cylinders,Displacement,Horsepower,Weight]; Y = MPG;
Delete rows of X and Y where either array has NaN values. Removing rows with NaN values before passing data to fitrkernel can speed up training and reduce memory usage.
R = rmmissing([X Y]); % Data with missing entries removed
X = R(:,1:5);
Y = R(:,end); Reserve 10% of the observations as a holdout sample. Extract the training and test indices from the partition definition.
rng(10) % For reproducibility N = length(Y); cvp = cvpartition(N,'Holdout',0.1); idxTrn = training(cvp); % Training set indices idxTest = test(cvp); % Test set indices
Train a kernel regression model with relaxed convergence control training options by using the name-value arguments 'BetaTolerance' and 'GradientTolerance'. Standardize the training data, and specify 'Verbose',1 to display diagnostic information.
Xtrain = X(idxTrn,:); Ytrain = Y(idxTrn); [Mdl,FitInfo] = fitrkernel(Xtrain,Ytrain,'Standardize',true,'Verbose',1, ... 'BetaTolerance',2e-2,'GradientTolerance',2e-2);
|=================================================================================================================| | Solver | Pass | Iteration | Objective | Step | Gradient | Relative | sum(beta~=0) | | | | | | | magnitude | change in Beta | | |=================================================================================================================| | LBFGS | 1 | 0 | 5.691016e+00 | 0.000000e+00 | 5.852758e-02 | | 0 | | LBFGS | 1 | 1 | 5.086537e+00 | 8.000000e+00 | 5.220869e-02 | 9.846711e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 2 | 3.862301e+00 | 5.000000e-01 | 3.796034e-01 | 5.998808e-01 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 3 | 3.460613e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 3.257790e-01 | 1.615091e-01 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 4 | 3.136228e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.832861e-02 | 8.006254e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 5 | 3.063978e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 1.475038e-02 | 3.314455e-02 | 256 | |=================================================================================================================|
Mdl is a RegressionKernel model.
Estimate the epsilon-insensitive error for the test set.
Xtest = X(idxTest,:); Ytest = Y(idxTest); L = loss(Mdl,Xtest,Ytest,'LossFun','epsiloninsensitive')
L = 2.0674
Continue training the model by using resume with modified convergence control options.
[UpdatedMdl,UpdatedFitInfo] = resume(Mdl,Xtrain,Ytrain, ... 'BetaTolerance',2e-3,'GradientTolerance',2e-3);
|=================================================================================================================| | Solver | Pass | Iteration | Objective | Step | Gradient | Relative | sum(beta~=0) | | | | | | | magnitude | change in Beta | | |=================================================================================================================| | LBFGS | 1 | 0 | 3.063978e+00 | 0.000000e+00 | 1.475038e-02 | | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 1 | 3.007822e+00 | 8.000000e+00 | 1.391637e-02 | 2.603966e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 2 | 2.817171e+00 | 5.000000e-01 | 5.949008e-02 | 1.918084e-01 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 3 | 2.807294e+00 | 2.500000e-01 | 6.798867e-02 | 2.973097e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 4 | 2.791060e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 2.549575e-02 | 1.639328e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 5 | 2.767821e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 6.154419e-03 | 2.468903e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 6 | 2.738163e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 5.949008e-02 | 9.476263e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 7 | 2.719146e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 1.699717e-02 | 1.849972e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 8 | 2.705941e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 3.116147e-02 | 4.152590e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 9 | 2.701162e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 5.665722e-03 | 9.401466e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 10 | 2.695341e+00 | 5.000000e-01 | 3.116147e-02 | 4.968046e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 11 | 2.691277e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 8.498584e-03 | 1.017446e-02 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 12 | 2.689972e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 1.983003e-02 | 9.938921e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 13 | 2.688979e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 1.416431e-02 | 6.606316e-03 | 256 | | LBFGS | 1 | 14 | 2.687787e+00 | 1.000000e+00 | 1.621956e-03 | 7.089542e-03 | 256 | |=================================================================================================================|
Estimate the epsilon-insensitive error for the test set using the updated model.
UpdatedL = loss(UpdatedMdl,Xtest,Ytest,'LossFun','epsiloninsensitive')
UpdatedL = 1.8891
The regression error decreases after resume updates the regression model with smaller convergence tolerances.
Display the outputs FitInfo and UpdatedFitInfo.
FitInfo
FitInfo = struct with fields:
Solver: 'LBFGS-fast'
LossFunction: 'epsiloninsensitive'
Lambda: 0.0028
BetaTolerance: 0.0200
GradientTolerance: 0.0200
ObjectiveValue: 3.0640
GradientMagnitude: 0.0148
RelativeChangeInBeta: 0.0331
FitTime: 0.0088
History: [1×1 struct]
UpdatedFitInfo
UpdatedFitInfo = struct with fields:
Solver: 'LBFGS-fast'
LossFunction: 'epsiloninsensitive'
Lambda: 0.0028
BetaTolerance: 0.0020
GradientTolerance: 0.0020
ObjectiveValue: 2.6878
GradientMagnitude: 0.0016
RelativeChangeInBeta: 0.0071
FitTime: 0.0049
History: [1×1 struct]
Both trainings terminate because the software satisfies the absolute gradient tolerance.
Plot the gradient magnitude versus the number of iterations by using UpdatedFitInfo.History.GradientMagnitude. Note that the History field of UpdatedFitInfo includes the information in the History field of FitInfo.
semilogy(UpdatedFitInfo.History.GradientMagnitude,'o-') ax = gca; ax.XTick = 1:21; ax.XTickLabel = UpdatedFitInfo.History.IterationNumber; grid on xlabel('Number of Iterations') ylabel('Gradient Magnitude')
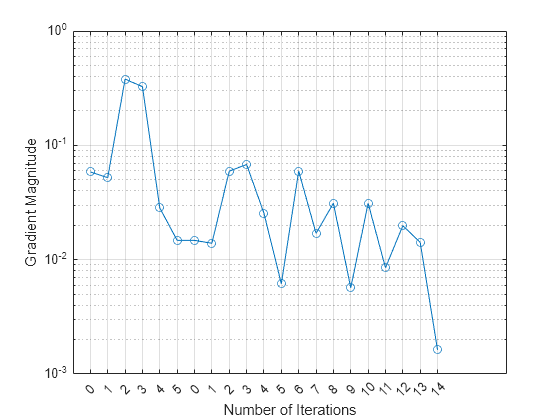
The first training terminates after five iterations because the gradient magnitude becomes less than 2e-2. The second training terminates after 14 iterations because the gradient magnitude becomes less than 2e-3.
Input Arguments
Kernel regression model, specified as a RegressionKernel model object. You can create a
RegressionKernel model object using fitrkernel.
Predictor data used to train Mdl, specified as an
n-by-p numeric matrix, where
n is the number of observations and
p is the number of predictors.
Data Types: single | double
Response data used to train Mdl, specified as a
numeric vector.
Data Types: double | single
Sample data used to train Mdl, specified as a table.
Each row of Tbl corresponds to one observation, and
each column corresponds to one predictor variable. Optionally,
Tbl can contain additional columns for the response
variable and observation weights. Tbl must contain all
of the predictors used to train Mdl. Multicolumn
variables and cell arrays other than cell arrays of character vectors are
not allowed.
If you trained Mdl using sample data contained in a
table, then the input data for resume must also be in a
table.
Note
resume should run only on the same training data and
observation weights (Weights) used to train
Mdl. The resume function uses the same
training options, such as feature expansion, used to train
Mdl.
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose
Name in quotes.
Example: UpdatedMdl = resume(Mdl,X,Y,'BetaTolerance',1e-3)
resumes training with the same options used to train Mdl, except
the relative tolerance on the linear coefficients and the bias term.
Observation weights used to train Mdl, specified
as the comma-separated pair consisting of 'Weights'
and a numeric vector or the name of a variable in
Tbl.
If
Weightsis a numeric vector, then the size ofWeightsmust be equal to the number of rows inXorTbl.If
Weightsis the name of a variable inTbl, you must specifyWeightsas a character vector or string scalar. For example, if the weights are stored asTbl.W, then specifyWeightsas'W'. Otherwise, the software treats all columns ofTbl, includingTbl.W, as predictors.
If you supply the observation weights, resume
normalizes Weights to sum to 1.
Data Types: double | single | char | string
Relative tolerance on the linear coefficients and the bias term (intercept), specified as a nonnegative scalar.
Let , that is, the vector of the coefficients and the bias term at optimization iteration t. If , then optimization terminates.
If you also specify GradientTolerance, then optimization terminates when the software satisfies either stopping criterion.
By default, the value is the same BetaTolerance
value used to train Mdl.
Example: 'BetaTolerance',1e-6
Data Types: single | double
Absolute gradient tolerance, specified as a nonnegative scalar.
Let be the gradient vector of the objective function with respect to the coefficients and bias term at optimization iteration t. If , then optimization terminates.
If you also specify BetaTolerance, then optimization terminates when the
software satisfies either stopping criterion.
By default, the value is the same GradientTolerance
value used to train Mdl.
Example: 'GradientTolerance',1e-5
Data Types: single | double
Maximum number of additional optimization iterations, specified as the
comma-separated pair consisting of 'IterationLimit'
and a positive integer.
The default value is 1000 if the transformed data fits in memory
(Mdl.ModelParameters.BlockSize), which you
specify by using the 'BlockSize' name-value pair argument when training
Mdl with fitrkernel. Otherwise, the default value is 100.
Note that the default value is not the value used to train
Mdl.
Example: 'IterationLimit',500
Data Types: single | double
Output Arguments
Updated kernel regression model, returned as a RegressionKernel model object.
Optimization details, returned as a structure array including fields described in this table. The fields contain final values or name-value pair argument specifications.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Solver |
Objective function minimization technique:
|
LossFunction | Loss function. Either mean squared error (MSE) or
epsilon-insensitive, depending on the type of linear
regression model. See Learner of
fitrkernel. |
Lambda | Regularization term strength. See Lambda of
fitrkernel. |
BetaTolerance | Relative tolerance on the linear coefficients and the
bias term. See BetaTolerance. |
GradientTolerance | Absolute gradient tolerance. See
GradientTolerance. |
ObjectiveValue | Value of the objective function when optimization terminates. The regression loss plus the regularization term compose the objective function. |
GradientMagnitude | Infinite norm of the gradient vector of the objective
function when optimization terminates. See
GradientTolerance. |
RelativeChangeInBeta | Relative changes in the linear coefficients and the bias
term when optimization terminates. See
BetaTolerance. |
FitTime | Elapsed, wall-clock time (in seconds) required to fit the model to the data. |
History | History of optimization information. This field also
includes the optimization information from training
Mdl. This field is empty
([]) if you specify
'Verbose',0 when training
Mdl. For details, see Verbose and the Algorithms section of fitrkernel. |
To access fields, use dot notation. For example, to access the vector of
objective function values for each iteration, enter
FitInfo.ObjectiveValue in the Command Window.
Examine the information provided by FitInfo to assess
whether convergence is satisfactory.
More About
Random feature expansion, such as Random Kitchen Sinks [1] or Fastfood [2], is a scheme to approximate Gaussian kernels of the kernel regression algorithm for big data in a computationally efficient way. Random feature expansion is more practical for big data applications that have large training sets, but can also be applied to smaller data sets that fit in memory.
After mapping the predictor data into a high-dimensional space, the kernel regression algorithm searches for an optimal function that deviates from each response data point (yi) by values no greater than the epsilon margin (ε).
Some regression problems cannot be described adequately using a linear model. In such cases, obtain a nonlinear regression model by replacing the dot product x1x2′ with a nonlinear kernel function , where xi is the ith observation (row vector) and φ(xi) is a transformation that maps xi to a high-dimensional space (called the “kernel trick”). However, evaluating G(x1,x2), the Gram matrix, for each pair of observations is computationally expensive for a large data set (large n).
The random feature expansion scheme finds a random transformation so that its dot product approximates the Gaussian kernel. That is,
where T(x) maps x in to a high-dimensional space (). The Random Kitchen Sinks [1] scheme uses the random transformation
where is a sample drawn from and σ is a kernel scale. This scheme requires O(mp) computation and storage. The Fastfood [2] scheme introduces
another random basis V instead of Z using Hadamard
matrices combined with Gaussian scaling matrices. This random basis reduces computation cost
to O(mlogp) and reduces storage to O(m).
You can specify values for m and σ, using the
NumExpansionDimensions and KernelScale
name-value pair arguments of fitrkernel, respectively.
The fitrkernel function uses the Fastfood scheme for random feature
expansion and uses linear regression to train a Gaussian kernel regression model. Unlike
solvers in the fitrsvm function, which require computation of the
n-by-n Gram matrix, the solver in
fitrkernel only needs to form a matrix of size
n-by-m, with m typically much
less than n for big data.
Extended Capabilities
The
resume function supports tall arrays with the following usage
notes and limitations:
resumedoes not support talltabledata.The default value for the
'IterationLimit'name-value pair argument is relaxed to 20 when you work with tall arrays.resumeuses a block-wise strategy. For details, see the Algorithms section offitrkernel.
For more information, see Tall Arrays.
This function fully supports GPU arrays. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions on a GPU (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Version History
Introduced in R2018aresume fully supports GPU arrays.
See Also
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)