fit
Description
Examples
Load the human activity dataset. Randomly shuffle the data.
load humanactivity; n = numel(actid); rng(1) % For reproducibility idx = randsample(n,n);
For details on the data set, enter Description at the command line.
Define the predictor and response variables.
X = feat(idx,:); Y = actid(idx);
Responses can be one of five classes: Sitting, Standing, Walking, Running, or Dancing.
Dichotomize the response by identifying whether the subject is moving (actid > 2).
Y = Y > 2;
Flip labels for the second half of the dataset to simulate drift.
Y(floor(numel(Y)/2):end,:) = ~Y(floor(numel(Y)/2):end,:);
Initiate a default incremental drift-aware model for classification as follows:
Create an incremental linear SVM model for binary classification. Specify an estimation period of 5000 observations and the SGD solver.
Initiate a default incremental drift-aware model using the incremental linear SVM model as the base learner. Specify a training period of 5000 observations.
baseMdl = incrementalClassificationLinear(EstimationPeriod=5000,Solver="sgd");
idaMdl = incrementalDriftAwareLearner(baseMdl,TrainingPeriod=5000);idaMdl is an incrementalDriftAwareLearner model. All its properties are read-only. By default, incrementalDriftAwareLearner uses the Hoeffding's Bound drift detection method based on moving averages ("hddma").
idaMdl must be fit to data before you can use it to perform any other operations.
Fit the incremental drift-aware model to the training data, in chunks of 50 observations at a time, by using the fit function. At each iteration:
Simulate a data stream by processing 50 observations.
Overwrite the previous incremental model with a new one fitted to the incoming observations.
Store the number of training observations, and the prior probability of whether the subject moved (Y = true) to see how they evolve during incremental training.
% Preallocation numObsPerChunk = 50; nchunk = floor(n/numObsPerChunk); beta1 = zeros(nchunk,1); numtrainobs = zeros(nchunk,1); dstatus = zeros(nchunk,1); statusname = strings(nchunk,1); driftTimes = []; ce = array2table(zeros(nchunk,2),VariableNames=["Cumulative" "Window"]); % Incremental fitting for j = 1:nchunk ibegin = min(n,numObsPerChunk*(j-1) + 1); iend = min(n,numObsPerChunk*j); idx = ibegin:iend; idaMdl = fit(idaMdl,X(idx,:),Y(idx)); idaMdl = updateMetrics(idaMdl,X(idx,:),Y(idx)); beta1(j) = idaMdl.BaseLearner.Beta(1); % Record drift status and classification error statusname(j) = string(idaMdl.DriftStatus); ce{j,:} = idaMdl.Metrics{"ClassificationError",:}; numtrainobs(j) = idaMdl.NumTrainingObservations; if idaMdl.DriftDetected dstatus(j) = 2; driftTimes(end+1) = j; elseif idaMdl.WarningDetected dstatus(j) = 1; else dstatus(j) = 0; end end
idaMdl is an incrementalDriftAwareLearner model object trained on all the data in the stream.
To see how the parameters evolve during incremental learning, plot them on separate tiles.
tiledlayout(2,1) set(groot,DefaultConstantLineLineWidth=1.5); nexttile plot(beta1) ylabel("\beta_1") xline(idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod/numObsPerChunk,"r-.","EstimationPeriod") xline(idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod/numObsPerChunk + driftTimes,"r-.") xlabel('Iteration') xline((idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod+idaMdl.TrainingPeriod)/numObsPerChunk, ... "b-.",{"Estimation +","Training Period"},LabelVerticalAlignment="middle") xline(floor(numel(Y)/2)/numObsPerChunk,"m--","Drift", ... LabelVerticalAlignment="middle") nexttile plot(numtrainobs) ylabel("Number of Training Observations") xline(idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod/numObsPerChunk,"r-.","EstimationPeriod") xline(idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod/numObsPerChunk + driftTimes,"r-.") xlabel("Iteration") xline((idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod+idaMdl.TrainingPeriod)/numObsPerChunk, ... "b-.",{"Estimation +","Training Period"},LabelVerticalAlignment="middle") xline(floor(numel(Y)/2)/numObsPerChunk,"m--","Drift", ... LabelVerticalAlignment="middle")
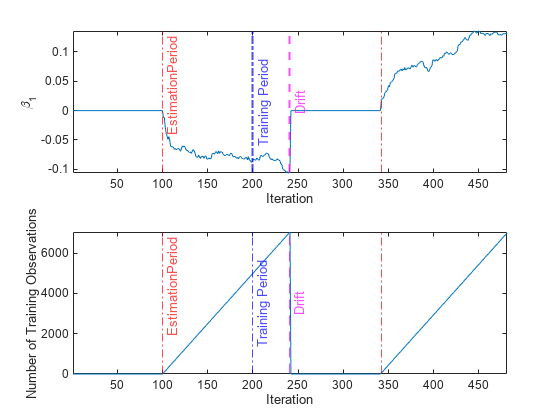
The plot suggests that fit does not fit the model to the data or update the parameters until after the estimation period. After a drift is detected, the function waits for another Mdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod number of observations to fit the new model to data.
Plot the cumulative and per window classification error. Mark the warmup and training periods, and where the drift was introduced.
figure() h = plot(ce.Variables); xlim([0 nchunk]) ylabel("Classification Error") xlabel("Iteration") xline((idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod+idaMdl.MetricsWarmupPeriod)/numObsPerChunk, ... "g-.","Estimation + Warmup Period") xline((idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod+idaMdl.MetricsWarmupPeriod)/numObsPerChunk+ ... driftTimes,"g-.","Estimation + Warmup Period") xline((idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod+idaMdl.TrainingPeriod)/numObsPerChunk, ... "b-.","Estimation + Training Period",LabelVerticalAlignment="middle") xline(driftTimes,"m--","Drift",LabelVerticalAlignment="middle") legend(h,ce.Properties.VariableNames) legend(h,Location="north")

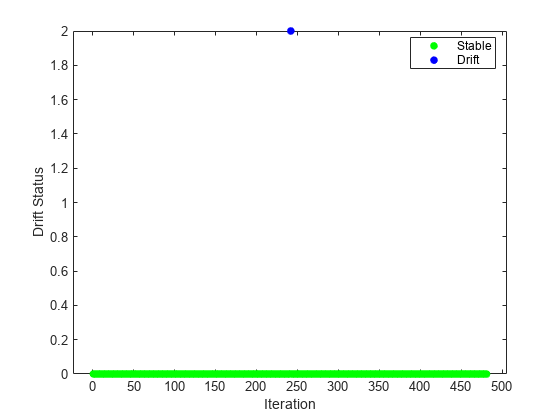
Plot the drift status versus the iteration number.
gscatter(1:nchunk,dstatus,statusname,"gbr","o",5,"on","Iteration","Drift Status","filled")
Predict labels for the second half of the data and check the accuracy of the model updated after the drift.
n = floor(numel(Y)/2); yhat = predict(idaMdl,X(n:end,:)); accuracy = sum(Y(n:end)==yhat)/n
accuracy = 0.9960
Load the robotarm data set. Obtain the sample size n and the number of predictor variables p.
load robotarm
n = numel(ytrain);
p = size(Xtrain,2);For details on the data set, enter Description at the command line.
Introduce an artificial drift to the response variable between observations 2500 and 5000.
Y=ytrain; j=1.25; for i=2500:1250:5000 idx=min(i+1250,5000); Y(i:idx)=ytrain(i:idx)*j; j=j+0.25; end
Initiate an incremental drift-aware model for regression as follows:
Create an incremental linear SVM model for regression. Specify an estimation period of 500 observations and the SGD solver.
Create an incremental drift detector for continuous data.
Initiate an incremental drift-aware model using the incremental linear SVM model as the base learner and the drift detector you created. Specify a training period of 2000.
baseMdl = incrementalRegressionLinear(EstimationPeriod=500,Solver="sgd",MetricsWarmUpPeriod=750); ddetector = incrementalConceptDriftDetector("hddma",InputType="continuous",Alternative="greater"); idaMdl = incrementalDriftAwareLearner(baseMdl,DriftDetector=ddetector,TrainingPeriod=2000);
idaMdl is an incrementalDriftAwareLearner model. All its properties are read-only.
Preallocate the number of variables in each chunk and number of iterations for creating a stream of data.
numObsPerChunk = 10; nchunk = floor(n/numObsPerChunk);
Preallocate the variables for tracking the drift status and drift time, and storing the regression error and number of training observations.
dstatus = zeros(nchunk,1); statusname = strings(nchunk,1); driftTimes = []; ei = array2table(nan(nchunk,2),VariableNames=["Cumulative","Window"]); numtrainobs = zeros(nchunk,1);
Perform incremental learning on the rest of the data by using the updateMetrics and fit functions. At each iteration:
Simulate a data stream by processing 10 observations at a time.
Call
updateMetricsto update the cumulative and window classification error of the model given the incoming chunk of observations. Overwrite the previous incremental model to update the losses in theMetricsproperty. Note that the function does not fit the model to the chunk of new data. Specify the observation orientation.Call
fitto fit the model to the incoming chunk of observations. Overwrite the previous incremental model to update the model parameters. Specify the observation orientation.Store the regression error and number of training observations.
rng(123) % For reproducibility for j = 1:nchunk ibegin = min(n,numObsPerChunk*(j-1) + 1); iend = min(n,numObsPerChunk*j); idx = ibegin:iend; idaMdl = updateMetrics(idaMdl,Xtrain(idx,:),Y(idx),ObservationsIn="rows"); ei{j,:} = idaMdl.Metrics{"EpsilonInsensitiveLoss",:}; idaMdl = fit(idaMdl,Xtrain(idx,:),Y(idx),ObservationsIn="rows"); numtrainobs(j) = idaMdl.NumTrainingObservations; statusname(j) = string(idaMdl.DriftStatus); if idaMdl.DriftDetected dstatus(j) = 2; driftTimes(end+1) = j; elseif idaMdl.WarningDetected dstatus(j) = 1; else dstatus(j) = 0; end end
idaMdl is an incrementalDriftAwareModel object trained on all the data in the stream.
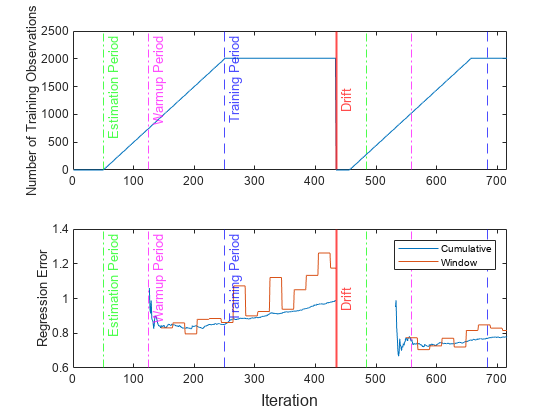
Plot a trace plot of the number of training observations and the performance metrics. Mark the times for estimation period, warm up metric period, and training period.
t = tiledlayout(2,1); nexttile plot(numtrainobs) xline(idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod/numObsPerChunk,"g-.","Estimation Period") xline((idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod+idaMdl.MetricsWarmupPeriod)/numObsPerChunk,"m-.","Warmup Period") xline((idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod+idaMdl.TrainingPeriod)/numObsPerChunk,"b--","Training Period") xline(idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod/numObsPerChunk+driftTimes,"g-.") xline((idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod+idaMdl.MetricsWarmupPeriod)/numObsPerChunk+driftTimes,"m-.") xline((idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod+idaMdl.TrainingPeriod)/numObsPerChunk+driftTimes,"b--") xline(driftTimes,"r","Drift",LabelVerticalAlignment="middle",LineWidth=1.5) xlim([0 nchunk]) ylabel("Number of Training Observations") nexttile plot(ei.Variables) xline(idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod/numObsPerChunk,"g-.","Estimation Period") xline((idaMdl.MetricsWarmupPeriod+idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod)/numObsPerChunk,"m-.","Warmup Period") xline((idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod+idaMdl.TrainingPeriod)/numObsPerChunk,"b--","Training Period") xline(idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod/numObsPerChunk+driftTimes,"g-.") xline((idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod+idaMdl.MetricsWarmupPeriod)/numObsPerChunk+driftTimes,"m-.") xline((idaMdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod+idaMdl.TrainingPeriod)/numObsPerChunk+driftTimes,"b--") xline(driftTimes,"r","Drift",LabelVerticalAlignment="middle",LineWidth=1.5) xlim([0 nchunk]) legend(ei.Properties.VariableNames,Location="northeast") ylabel("Regression Error") xlabel(t,"Iteration")
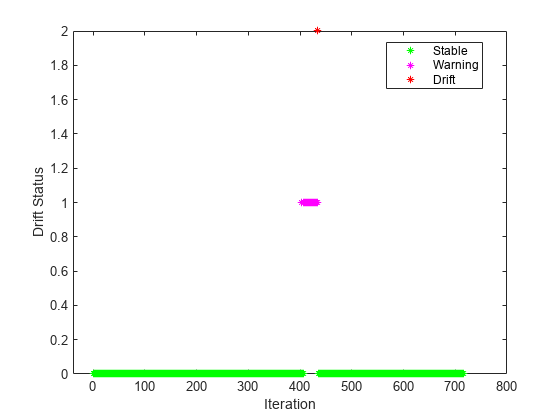
Plot the drift status versus the iteration number.
figure() gscatter(1:nchunk,dstatus,statusname,'gmr','*',5,'on',"Iteration","Drift Status")
Input Arguments
Incremental drift-aware learning model fit to streaming data, specified as an incrementalDriftAwareLearner model object. You can create
Mdl using the incrementalDriftAwareLearner
function. For more details, see the object reference page.
Chunk of predictor data to which the model is fit, specified as a floating-point matrix of n observations and Mdl.BaseLearner.NumPredictors predictor variables.
When Mdl.BaseLearner accepts the ObservationsIn name-value argument, the value of ObservationsIn determines the orientation of the variables and observations. The default ObservationsIn value is "rows", which indicates that observations in the predictor data are oriented along the rows of X.
The length of the observation responses (or labels) Y and the number of observations in X must be equal; Y( is the response (or label) of observation j (row or column) in j)X.
Note
If
Mdl.BaseLearner.NumPredictors= 0,fitinfers the number of predictors fromX, and sets the corresponding property of the output model. Otherwise, if the number of predictor variables in the streaming data changes fromMdl.BaseLearner.NumPredictors,fitissues an error.fitsupports only floating-point input predictor data. If your input data includes categorical data, you must prepare an encoded version of the categorical data. Usedummyvarto convert each categorical variable to a numeric matrix of dummy variables. Then, concatenate all dummy variable matrices and any other numeric predictors. For more details, see Dummy Variables.
Data Types: single | double
Chunk of responses (or labels) to which the model is fit, specified as one of the following:
Floating-point vector of n elements for regression models, where n is the number of rows in
X.Categorical, character, or string array, logical vector, or cell array of character vectors for classification models. If
Yis a character array, it must have one class label per row. Otherwise,Ymust be a vector with n elements.
The length of Y and the number of observations in
X must be equal;
Y( is the response (or label) of
observation j (row or column) in j)X.
For classification problems:
When
Mdl.BaseLearner.ClassNamesis nonempty, the following conditions apply:If
Ycontains a label that is not a member ofMdl.BaseLearner.ClassNames,fitissues an error.The data type of
YandMdl.BaseLearner.ClassNamesmust be the same.
When
Mdl.BaseLearner.ClassNamesis empty,fitinfersMdl.BaseLearner.ClassNamesfrom data.
Data Types: single | double | categorical | char | string | logical | cell
Name-Value Arguments
Specify optional pairs of arguments as
Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN, where Name is
the argument name and Value is the corresponding value.
Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the
pairs does not matter.
Example: ObservationsIn="columns",Weights=W specifies that the columns
of the predictor matrix correspond to observations, and the vector W
contains observation weights to apply during incremental learning.
Predictor data observation dimension, specified as "columns" or
"rows".
fit supports ObservationsIn only if
Mdl.BaseLearner supports the ObservationsIn
name-value argument.
Example: ObservationsIn="columns"
Data Types: char | string
Chunk of observation weights, specified as a floating-point vector of positive values. fit weighs the observations in X with the corresponding values in Weights. The size of Weights must equal n, which is the number of observations in X.
By default, Weights is ones(.n,1)
Example: Weights=w
Data Types: double | single
Output Arguments
Updated incremental drift-aware learning model, returned as an incremental
drift-aware learning model object of the same data type as the input model
Mdl, incrementalDriftAwareLearner.
If Mdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod > 0, the incremental
fitting functions updateMetricsAndFit and fit
estimate hyperparameters using the first
Mdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod observations passed to either
function; they do not train the input model to the data. However, if an incoming chunk
of n observations is greater than or equal to the number of
observations remaining in the estimation period m,
fit estimates hyperparameters using the first
n – m observations, and fits the input model to
the remaining m observations.
For classification problems, if the ClassNames property of the
input model Mdl.BaseLearner is an empty array,
fit sets the ClassNames property of
the output model Mdl.BaseLearner to
unique(Y).
Algorithms
Incremental learning, or online learning, is a branch of machine learning concerned with processing incoming data from a data stream, possibly given little to no knowledge of the distribution of the predictor variables, aspects of the prediction or objective function (including tuning parameter values), or whether the observations are labeled. Incremental learning differs from traditional machine learning, where enough labeled data is available to fit to a model, perform cross-validation to tune hyperparameters, and infer the predictor distribution. For more details, see Incremental Learning Overview.
Unlike other incremental learning functionality offered by Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox™, fit model object combines incremental learning and
concept drift detection.
After creating an incrementalDriftAwareLearner object, use updateMetrics
to update model performance metrics and fit to fit the
base model to incoming chunk of data, check for potential drift in the model performance
(concept drift), and update or reset the incremental drift-aware learner, if necessary. You
can also use updateMetricsAndFit. The fit function
implements the Reactive Drift Detection Method (RDDM) [1] as follows:
After
Mdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod(if necessary) andMetricsWarmupPeriod, the function trains the incremental drift-aware model up toNumTrainingObservationsobservations until it reachesTrainingPeriod. (If theTrainingPeriodvalue is smaller than theMdl.BaseLearner.MetricsWarmupPeriodvalue, thenincrementalDriftAwareLearnersets theTrainingPeriodvalue asMdl.BaseLearner.MetricsWarmupPeriod.)When
NumTrainingObservations > TrainingPeriod, the software starts tracking the model loss. The software computes the per observation loss using theperObservationLossfunction. While computing the per observation loss, the software uses the"classiferror"loss metric for classification models and"squarederror"for regression models. The function then appends the loss values computed using the last chunk of data to the existing buffer loss values.Next, the software checks to see if any concept drift occurred by using the
detectdriftfunction and updatesDriftStatusaccordingly.
Based on the drift status, fit performs the following procedure:
DriftStatusis'Warning'– The software first increases the consecutive'Warning'status count by 1.If the consecutive
'Warning'status count is less than theWarningCountLimitvalue and thePreviousDriftStatusvalue isStable, then the software trains a temporary incremental learner (if one does not exist) and sets it (or the existing one) toBaseLearner.Then the software resets the temporary incremental learner using the learner's
resetfunction.If the consecutive
'Warning'status count is less than theWarningCountLimitvalue and thePreviousDriftStatusvalue is'Warning', then the software trains the existing temporary incremental model using the latest chunk of data.If the consecutive
'Warning'status count is more than theWarningCountLimitvalue, then the software sets theDriftStatusvalue to'Drift'.
DriftStatusis'Drift'– The software performs the following steps.Sets the consecutive
'Warning'status count to 0.Resets
DriftDetectorusing theresetfunction.Empties the buffer loss values and appends the loss values for the latest chunk of data to buffer loss values.
If the temporary incremental model is not empty, then the software sets the current
BaseLearnervalue to the temporary incremental model and empties the temporary incremental model.If the temporary incremental model is empty, then the software resets the
BaseLearnervalue by using the learner'sresetfunction.
DriftStatusis'Stable'– The software first increases the consecutive'Stable'status count by 1.If the consecutive
'Stable'status count is less than theStableCountLimitand thePreviousDriftStatusvalue is'Warning', then the software sets the number of warnings to zero and empties the temporary model.If the consecutive
'Stable'status count is more than theStableCountLimitvalue, then the software resets theDriftDetectorusing theresetfunction. Then the software tests all of the saved loss values in the buffer for concept drift by using thedetectdriftfunction.
Once DriftStatus is set to 'Drift', and the
BaseLearner and DriftDetector are reset, the
software waits until Mdl.BaseLearner.EstimationPeriod +
Mdl.BaseLearner.MetricsWarmupPeriod before it starts computing the
performance metrics.
For classification problems, if the prior class probability distribution is known (in other words, the prior distribution is not empirical), fit normalizes observation weights to sum to the prior class probabilities in the respective classes. This action implies that observation weights are the respective prior class probabilities by default.
For regression problems or if the prior class probability distribution is empirical, the software normalizes the specified observation weights to sum to 1 each time you call fit.
References
[1] Barros, Roberto S.M. , et al. "RDDM: Reactive drift detection method." Expert Systems with Applications. vol. 90, Dec. 2017, pp. 344-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2017.08.023.
[2] Bifet, Albert, et al. "New Ensemble Methods for Evolving Data Streams." Proceedings of the 15th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. ACM Press, 2009, p. 139. https://doi.org/10.1145/1557019.1557041.
[3] Gama, João, et al. "Learning with drift detection". Advances in Artificial Intelligence – SBIA 2004, edited by Ana L. C. Bazzan and Sofiane Labidi, vol. 3171, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2004, pp. 286–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-28645-5_29.
Version History
Introduced in R2022b
See Also
predict | perObservationLoss | incrementalDriftAwareLearner | updateMetrics | updateMetricsAndFit | loss
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)