Induction Machine Direct Torque Control (Single-Phase)
Single-phase induction machine direct torque control
Libraries:
Simscape /
Electrical /
Control /
Induction Machine Control
Description
The Induction Machine Direct Torque Control (Single-Phase) block implements a single-phase induction machine direct torque control structure.
Equations
This diagram shows the direct torque control architecture for single-phase machines

The torque and flux estimation is based on machine voltage equations. The discrete-time voltage equations using the backward Euler discretization method, are:
where:
Ras and Rbs are the main winding resistance and the auxiliary winding resistance, respectively.
ia and ib are the main winding current and the auxiliary winding current, respectively.
va and vb are the main and auxiliary winding voltage, respectively.
ψa and ψb are the main and auxiliary winding flux, respectively.
The torque and flux are obtained from:
where:
pis the number of pole pairs.ais the auxiliary to main windings turn ratio.
Employing simple hysteresis comparators detects the status of flux and torque errors. The following figures illustrate the hysteresis comparators and the switching sectors.
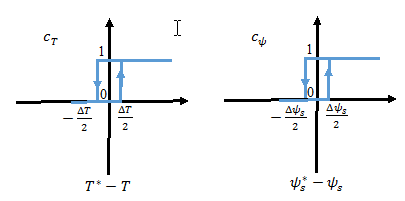
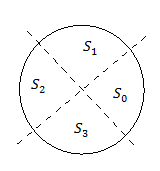
The table shows the optimum switching table (inverter high side).
| cψ, cT, S(θ) | S0 | S1 | S2 | S3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
cψ =
1 | cT = 1 | 1, 0 | 1, 1 | 0, 1 | 0, 0 |
cT = 0 | 1, 1 | 0, 1 | 0, 0 | 1, 0 | |
cψ =
0 | cT = 1 | 0, 0 | 1, 0 | 1, 1 | 0, 1 |
cT = 0 | 0, 1 | 0, 0 | 1, 0 | 1, 1 | |
The torque reference can be provided as an input, or, in the case of speed control, be generated internally using a PI speed controller.
The flux reference is generated internally using:
where,
ωr is the rotor angular mechanical speed in rad/s.
fn is the rated frequency.
ψn is the rated flux.
Limitations
The power inverter dead-times are not considered in this block. For hardware implementation, add the dead-time externally.
Ports
Input
Output
Parameters
References
[1] Takahashi, I., and T. Noguchi. "A New Quick-Response and High-Efficiency Control Strategy of an Induction Motor." IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications. Vol. IA-22, Number 5, 1986, pp. 820 - 827.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2018b
See Also
Blocks
- Induction Machine Current Controller | Induction Machine Direct Torque Control | Induction Machine Direct Torque Control with Space Vector Modulator | Induction Machine Field-Oriented Control | Induction Machine Field-Oriented Control (Single-Phase) | Induction Machine Flux Observer | Induction Machine Scalar Control