Simulink.sdi.Run
Access run signals and metadata
Description
The Simulink.sdi.Run object contains run metadata and allows
you to access the Simulink.sdi.Signal objects that
contain data and metadata for the signals in the run. You can also use a
Simulink.sdi.Run object to import data into the Simulation Data
Inspector from the workspace or a file.
Creation
The Simulation Data Inspector creates Simulink.sdi.Run objects when
you import data or simulate a model that logs data. You can access a
Run object in the Simulation Data Inspector three ways:
When you want to access a run that corresponds to a specific run ID, use the
Simulink.sdi.getRunfunction.Tip
Use the
Simulink.sdi.getAllRunIDsfunction to get the run IDs for all the runs in the Simulation Data Inspector.When you want to access the most recently created run in the Simulation Data Inspector, use the
Simulink.sdi.Run.getLatestfunction.When you want to access the run that corresponds to the in-progress or most recently completed simulation of a model, use the
Simulink.sdi.getCurrentSimulationRunfunction.
You can also programmatically create a Simulink.sdi.Run object to
import data into the Simulation Data Inspector.
Create an empty run in the Simulation Data Inspector using the
Simulink.sdi.Run.createfunction.Create an empty run in the Simulation Data Inspector or import data into the Simulation Data Inspector using the
Simulink.sdi.createRun.
Tip
Use the add function or the Simulink.sdi.addToRun function
to import data into an empty Run object.
Properties
Identification Properties
This property is read-only.
Unique numerical identification for the run, returned as an integer.
Run name, specified as a character vector or string.
By default, the Name property is empty when you
use the Simulink.sdi.Run.create function to create
a run.
You can specify the run name when you use the
Simulink.sdi.createRun function to create a
run.
When you create a run by simulating a model that logs data, the run
name is generated according to the run-naming rule in the Simulation
Data Inspector. You can modify the run-naming rule in the Simulation
Data Inspector in the UI or by using the Simulink.sdi.setRunNamingRule function.
Example: 'Run 1: vdp'
Description of the run, specified as a character vector or string. By
default, Description is empty. Use the
Description property to add notes about the
significance of the data within the run, like the test or simulation
conditions used to create the data.
Example: 'Initial simulation'
Tag for additional run information, specified as a character vector or
string. By default, Tag is empty. You can use the
Tag property to attach additional information
to the Run object. For example, you could use the
Tag property to include parameter values used
for the simulation that created the run in the Run
object metadata.
Example: 'Gain = 2'
Date and time the run was created, returned as a datetime object.
Example: 07-Dec-2019 13:55:25
Data Types: datetime
This property is read-only.
Index of the run in the Simulation Data Inspector when the run was
created, returned as an integer. The RunIndex matches
the run number in the run name when you use the run index as part of the
run-naming rule.
If you delete runs from the Simulation Data Inspector, the value of
the RunIndex property may not match the index of the
run ID in the vector returned by the
Simulink.sdi.getAllRunIDs function.
This property is read-only.
Number of signals in the run, returned as an integer.
Simulation Information
Name of the model simulated to create the run, returned as a character
vector. The Model property is empty for runs
created by importing data into the Simulation Data Inspector.
Simulation mode used in the simulation that created the run, returned
as a character vector. The SimMode property is
empty for runs created by importing data into the Simulation Data
Inspector.
Version of Simulink® used for the simulation that created the run, returned as
a character vector. The SLVersion property is empty
for runs created by importing data into the Simulation Data
Inspector.
Version of the model that was simulated to create the run, returned as
a character vector. The version of a model is stored in its model
properties. The ModelVersion property is empty for
runs created by importing data into the Simulation Data
Inspector.
System account used to perform the simulation that created the run,
returned as a character vector. The UserID property
is empty for runs created by importing data into the Simulation Data
Inspector.
Name of the machine used to perform the simulation that created the
run, returned as a character vector. The
MachineName property is empty for runs created
by importing data into the Simulation Data Inspector.
Operating system on the machine used to perform the simulation,
returned as a character vector. The Platform
property is empty for runs that do not correspond to a
simulation.
Example: 'PCWIN64'
Name of the simulation task that corresponds to the run, returned as a
character vector. The TaskName property is empty
unless the run was created using Parallel Computing Toolbox™ workers.
Type of solver used in the simulation that created the run, returned
as 'Variable-Step' or
'Fixed-Step'. The SolverType
property is empty for runs created by importing data into the Simulation
Data Inspector.
Name of the solver used in the simulation that created the run,
returned as a character vector. The SolverName
property is empty for runs created by importing data into the Simulation
Data Inspector.
Example: ode45
Step size used by the solver during the simulation, returned as a
character vector. If the simulation used a fixed-step solver, the
SolverStepSize property indicates the fixed
step size used in the simulation. If the simulation used a variable-step
solver, the SolverStepSize property indicates the
maximum step size used in the simulation.
Example: '0.4'
User-specified string that corresponds to the simulation, returned as
a character vector. Often, the UserString provides
a brief description of the simulation. You specify the
UserString for a simulation in the Simulink.SimulationInput
object for the simulation.
Timing Properties
First time point shared by all signals in the run, returned as a scalar.
Last time point shared by all signals in the run, returned as a scalar.
Time required to initialize the model for the simulation that created
the run, returned as a double. The
ModelInitializationTime property is empty for
runs created by importing data into the Simulation Data
Inspector.
Execution time for the simulation that created the run, returned as a
double. The ModelExecutionTime property is empty
for runs created by importing data into the Simulation Data
Inspector.
Time to terminate the simulation that created the run, returned as a
double. The ModelTerminationTime property is empty
for runs created by importing data into the Simulation Data
Inspector.
Total simulation time for the simulation that created the run,
returned as a double. The ModelTotalElapsedTime
property is empty for runs created by importing data into the Simulation
Data Inspector.
Status Information
Simulation status, returned as a character vector. When the simulation
is running, the Status property is
'Running'. When a simulation is paused or
completes, the Status property takes the value from
the StopEvent field of the Simulink.SimulationMetadata object
StopEvent property. The
StopEvent property has one of these values:
ReachedStopTime— The simulation completed with no reported errors, not including errors reported in theStopFcncallback, which executes after the simulation stops.ModelStop— A block or solver stopped the simulation before the simulation stop time.StopCommand— A Stop button press orset_paramfunction call ended the simulation.DiagnosticError— A reported error ended the simulation.KeyboardControlC— ACtrl+Ckeyboard entry ended the simulation.PauseCommand— A Pause button press orset_paramfunction call paused the simulation.ConditionalPause— A conditional breakpoint paused the simulation.PauseTime— A specified pause time paused the simulation.StepForward— The simulation paused after stepping forward while stepping through a simulation.StepBackward— The simulation paused after stepping backward while stepping through a simulation.TimeOut— The simulation stopped after the simulation execution time exceeded the timeout time specified using the'TimeOut'name-value pair for thesimfunction.
Block that issued the stop event that stopped the simulation, returned
as a Simulink.SimulationData.BlockPath object.
Translated description of the simulation stop, returned as a character
vector. The StopEventDescription includes a
description of the stop event and the associated simulation time, if
applicable. The StopEventDescription property takes
its value from the StopEventDescription field of the
Simulink.SimulationMetadata object
ExecutionInfo property.
Example: 'Pause command issued at time 100'
Errors that occurred during simulation, returned as a character vector.
Warnings that occurred during simulation, returned as a character vector.
Object Functions
add | Import data into existing run in Simulation Data Inspector using
Simulink.sdi.Run object |
export | Export run to base workspace or file |
getAllSignalIDs | Get all signal IDs for signals in Simulink.sdi.Run
object |
getAllSignals | Get all signals in Simulink.sdi.Run object |
getDatasetRef | Create a Simulink.sdi.DatasetRef object for a
run |
getSignalByIndex | Get signal in Simulink.sdi.Run object by index |
getSignalIDByIndex | Get signal ID for signal at specified index in
Simulink.sdi.Run object |
getSignalIDsByName | Get signal IDs for signals inside Simulink.sdi.Run object using
signal name |
getSignalsByName | Access signals in a Simulink.sdi.Run object using signal
name |
isValidSignalID | Check whether signal ID corresponds to signal in
Simulink.sdi.Run object |
Examples
This example demonstrates how to access the Simulink.sdi.Run object for a Simulation Data Inspector run created by logging signals. From the Simulink.sdi.Run object you can get Simulink.sdi.Signal objects that contain the logged signal data and metadata. You can use the Signal objects and the plotOnSubPlot function to plot the data in the Simulation Data Inspector.
Create a Simulation Run and Access the Run Object
The vdp model logs two signals. To create a simulation run containing the logged data, simulate the model.
mdl = "vdp";
sim(mdl);The Simulation Data Inspector keeps track of runs by assigning a unique numeric run ID to each run created by simulation, importing data, or opening a session. To access the run object for the simulation you just performed, use the Simulink.sdi.getAllRunIDs function and take the last run ID in the returned vector.
runIDs = Simulink.sdi.getAllRunIDs; runID = runIDs(end);
Once you have the run ID for the run, you can use the Simulink.sdi.getRun function to get the Simulink.sdi.Run object that corresponds to the run. You can use the Run object to check the metadata associated with the run, including the number of signals in the run.
vdpRun = Simulink.sdi.getRun(runID); vdpRun.SignalCount
ans = int32
4
Plot Data Using Signal Objects
Use the getSignalByIndex function to access signals from the Run object, vdpRun.
signal1 = getSignalByIndex(vdpRun,1); signal2 = getSignalByIndex(vdpRun,2);
Use the Simulink.sdi.setSubPlotLayout function to specify a 2-by-1 layout.
Simulink.sdi.setSubPlotLayout(2,1)
Before plotting the data, use the Simulink.sdi.clearAllSubPlots function to clear any data that is already plotted.
Simulink.sdi.clearAllSubPlots
Plot one signal on each subplot. To plot signals on the first subplot, you can set the checked property for the signal. To plot signals on subplots other than the first subplot, use the plotOnSubPlot function.
signal1.Checked = true; plotOnSubPlot(signal2,2,1,true);
View the Plotted Data
To view the plots you just created, open the Simulation Data Inspector using the Simulink.sdi.view function.
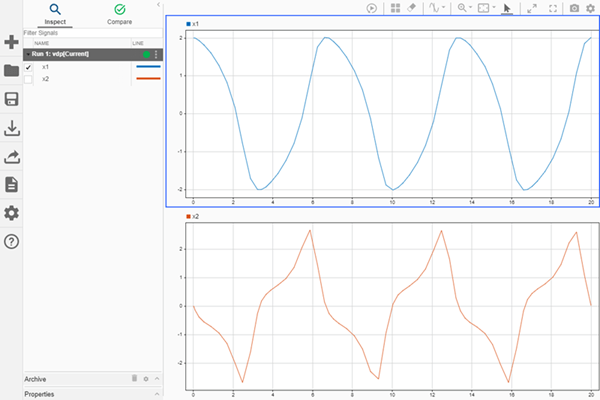
Create a run, add data to it, and then view the data in the Simulation Data Inspector.
Create Data for Run
Create two timeseries objects to contain data for a sine signal and a cosine signal. Give each timeseries object a descriptive name.
time = linspace(0,20,100); sine_vals = sin(2*pi/5*time); sine_ts = timeseries(sine_vals,time); sine_ts.Name = "Sine, T=5"; cos_vals = cos(2*pi/8*time); cos_ts = timeseries(cos_vals,time); cos_ts.Name = "Cosine, T=8";
Create Run and Add Data
Use the Simulink.sdi.view function to open the Simulation Data Inspector.
Simulink.sdi.view
To import data into the Simulation Data Inspector from the workspace, create a Simulink.sdi.Run object using the Simulink.sdi.Run.create function. Add information about the run to its metadata using the Name and Description properties of the Run object.
sinusoidsRun = Simulink.sdi.Run.create; sinusoidsRun.Name = "Sinusoids"; sinusoidsRun.Description = "Sine and cosine signals with different frequencies";
Use the add function to add the data you created in the workspace to the empty run.
add(sinusoidsRun,"vars",sine_ts,cos_ts);Plot Data in Simulation Data Inspector
Use the getSignalByIndex function to access Simulink.sdi.Signal objects that contain the signal data. You can use the Simulink.sdi.Signal object properties to specify the line style and color for the signal and plot the signal in the Simulation Data Inspector. Specify the LineColor and LineDashed properties for each signal.
sine_sig = getSignalByIndex(sinusoidsRun,1); sine_sig.LineColor = [0 0 1]; sine_sig.LineDashed = "-."; cos_sig = sinusoidsRun.getSignalByIndex(2); cos_sig.LineColor = [1 0 0]; cos_sig.LineDashed = "--";
Use the Simulink.sdi.setSubPlotLayout function to configure a 2-by-1 subplot layout in the Simulation Data Inspector plotting area. Then, use the plotOnSubplot function to plot the sine signal on the top subplot and the cosine signal on the lower subplot.
Simulink.sdi.setSubPlotLayout(2,1); plotOnSubPlot(sine_sig,1,1,true); plotOnSubPlot(cos_sig,2,1,true);

Close Simulation Data Inspector and Save Data
When you finish inspecting the plotted signal data, you can close the Simulation Data Inspector and save the session to an MLDATX file.
Simulink.sdi.close("sinusoids.mldatx")Execute parallel simulations of the model slexAircraftExample with different input filter time constants and access the data in different ways using the Simulation Data Inspector programmatic interface.
Setup
Check that the Simulation Data Inspector is empty and that Parallel Computing Toolbox support is configured to import runs created on local workers automatically. Then, create a vector of filter parameter values to use in each simulation.
Simulink.sdi.clear
Simulink.sdi.enablePCTSupport("local")
Ts_vals = [0.01, 0.02, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1]; Initialize Parallel Workers
Use the gcp function to create a pool of local workers to run parallel simulations if you don't already have one. In an spmd code block, load the slexAircraftExample model and select signals to log. To avoid data concurrency issues using sim in parfor, create a temporary directory for each worker to use during simulations.
p = gcp;
Starting parallel pool (parpool) using the 'Processes' profile ... 21-Aug-2024 13:35:54: Job Queued. Waiting for parallel pool job with ID 1 to start ... 21-Aug-2024 13:36:55: Job Queued. Waiting for parallel pool job with ID 1 to start ... 21-Aug-2024 13:37:55: Job Running. Waiting for parallel pool workers to connect ... Connected to parallel pool with 6 workers.
spmd % Load system and select signals to log load_system("slexAircraftExample") Simulink.sdi.markSignalForStreaming("slexAircraftExample/Pilot", 1, "on") Simulink.sdi.markSignalForStreaming("slexAircraftExample/Aircraft Dynamics Model", 4, "on") % Create temporary directory on each worker workDir = pwd; addpath(workDir) tempDir = tempname; mkdir(tempDir) cd(tempDir) end
Run Parallel Simulations
Use parfor to run the seven simulations in parallel. Select the value for Ts for each simulation, and modify the value of Ts in the model workspace. Then, run the simulation and build an array of Simulink.sdi.WorkerRun objects to access the data with the Simulation Data Inspector. After the parfor loop, use another spmd segment to remove the temporary directories from the workers.
parfor index = 1:7 % Select value for Ts Ts_val = Ts_vals(index); % Change the filter time constant and simulate modelWorkspace = get_param("slexAircraftExample","modelworkspace"); assignin(modelWorkspace,"Ts",Ts_val) sim("slexAircraftExample"); % Create a worker run for each simulation workerRun(index) = Simulink.sdi.WorkerRun.getLatest end spmd % Remove temporary directories cd(workDir) rmdir(tempDir, "s") rmpath(workDir) end
Get Dataset Objects from Parallel Simulation Output
The getDataset function puts the data from a WorkerRun object into a Dataset object so you can easily post-process.
ds(7) = Simulink.SimulationData.Dataset; for a = 1:7 ds(a) = getDataset(workerRun(a)); end ds(1)
ans =
Simulink.SimulationData.Dataset '' with 12 elements
Name BlockPath
__________ ________________________________________
1 [1x1 State ] '' slexAircraftExample/Actuator Model
2 [1x1 Signal] alpha, rad ...rcraftExample/Aircraft Dynamics Model
3 [1x1 State ] '' ...cs Model/Pitch Channel/Integrate qdot
4 [1x1 State ] '' ...mics Model/Vertical Channel/Integrate
5 [1x1 State ] '' ...ntroller/Alpha-sensor Low-pass Filter
6 [1x1 State ] '' ...ller/Integrator/Continuous/Integrator
7 [1x1 State ] '' ...ple/Controller/Pitch Rate Lead Filter
8 [1x1 State ] '' ...aftExample/Controller/Stick Prefilter
9 [1x1 State ] '' .../Dryden Wind Gust Models/Q-gust model
10 [1x1 State ] '' .../Dryden Wind Gust Models/W-gust model
11 [1x1 Signal] Stick slexAircraftExample/Pilot
12 [1x1 Signal] alpha, rad slexAircraftExample/alpha, rad
- Use braces { } to access, modify, or add elements using index.
Get DatasetRef Objects from Parallel Simulation Output
For big data workflows, use the getDatasetRef function to reference the data associated with the WorkerRun.
for b = 1:7 datasetRef(b) = getDatasetRef(workerRun(b)); end datasetRef(1)
ans =
DatasetRef with properties:
Name: 'Run <run_index>: <model_name>'
Run: [1×1 Simulink.sdi.Run]
numElements: 12
Process Parallel Simulation Data in the Simulation Data Inspector
You can also create local Simulink.sdi.Run objects to analyze and visualize your data using the Simulation Data Inspector programmatic interface. This example shows a tag indicating the filter time constant value for each run.
for c = 1:7 Runs(c) = getLocalRun(workerRun(c)); Ts_val_str = num2str(Ts_vals(c)); desc = strcat("Ts = ", Ts_val_str); Runs(c).Description = desc; Runs(c).Name = strcat("slexAircraftExample run Ts=", Ts_val_str); end
Clean Up Worker Repositories
Clean up the files used by the workers to free up disk space for other simulations you want to run on your worker pool.
Simulink.sdi.cleanupWorkerResources
Alternatives
You can view run metadata and import data using the Simulation Data Inspector UI. For more information, see View Simulation Data in Simulation Data Inspector.
Version History
Introduced in R2012b
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)