Call Custom C Functions in Simulink Using C Caller Block
This example shows how to map custom C functions into Simulink® using C Caller blocks. In this example, three C Caller blocks call three different custom C functions that perform various arithmetic operations and follow different mapping strategies. The example model CCallerExample is divided into three components:
Map C function argument to Simulink (Pass-by-value type)
Map C function argument to Parameter
Map pointer variable from C Function to Simulink (Pass-by-pointer type)
Open the model that contains the C Caller blocks.
mdl= "CCallerExample.slx";
open_system(mdl)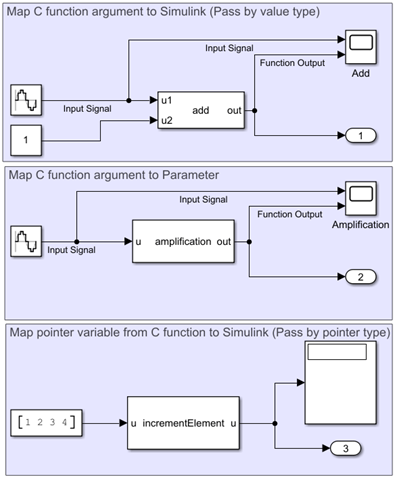
C Caller Block Configuration to Call Custom C Function
In this example, the C functions are declared in the header file arithmeticops.h and the operations are defined in the source file arithmeticops.c. In the CCallerExample model, each C Caller block is configured to call one function at a time.
To observe the configuration of the C Caller block that calls the add function, follow the steps mentioned below. You can apply the same procedure to observe the C Caller block configurations for the other two functions, amplification and incrementElement.
Open the In the C Caller Block Parameters dialog box and observe that the Function name field specifies
add.In the dialog box, click
 . This opens the Configuration Parameters dialog box.
. This opens the Configuration Parameters dialog box. In the Configuration Parameters dialog box, navigate to the Code information tab under Simulation Target pane. Observe that Include headers field specifies
"arithmeticops.h"and Source files field specifiesarithmeticops.c.
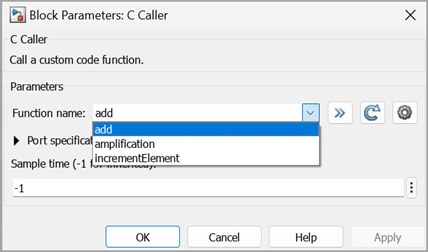
C Caller Block Parameter Settings to Map C Function Arguments
To observe mapping of C functions into Simulink®, open the Port specification table in the Block Parameters dialog box. This table maps the arguments specified in the C functions into Simulink® using different parameters. The parameters and their functionalities are mentioned below:
Name Demonstrates the variable name inferred from the source code.
Scope Indicates role of each function argument in the C Caller block source code.
Label Labels the input or output variable of the Simulink® model. For function arguments scoped as Input, Output or InputOutput, the Label values are the corresponding block port names. For arguments scoped as Parameter, the Label value is the parameter prompt text. If the Scope is constant, then the Label value is a constant value expression.
Type Indicates the data types coming from the ports.
Size Indicates the size of the input and output data.
The following components describe each function and how they are mapped. Observe the functionality of each function by looking at their corresponding block dialog box and the Port specification tables.
Map C function argument to Simulink (Pass-by-value type)
add Adds a scalar value (u2) to the input sine wave (u1). The prototype of the function is: double add(double u1, double u2)
After parsing the code, the block populates Scope values of the input arguments (u1 and u2) as Input and function return (out) as Output. Since the arguments are scoped as input and output, the Label values are the corresponding block port names.
Map C function argument to Parameter
amplification Amplifies the input sine wave (u) by a scalar value indicated by the parameter AmplificationFactor. The prototype of the function is: double amplification(double u, double AmplificationFactor)
After parsing the code, the block populates Scope values for the amplification factor (Amplification Factor) and the input argument (u) as Input, and the Scope value for the function return (out) as Output. For this example, Scope of AmplificationFactor is changed to Parameter.
Since the arguments are primarily scoped as input and output, the Label values are the corresponding block port names. For this example, Label of the amplification factor is changed to Amplification Factor.
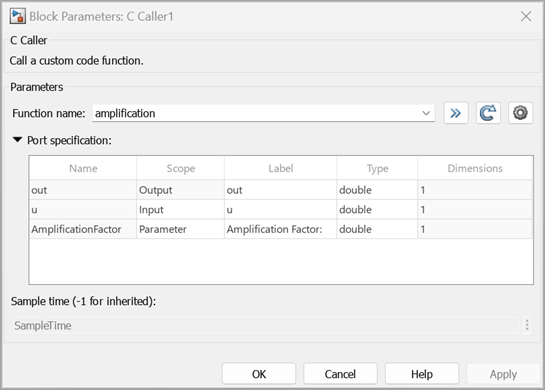
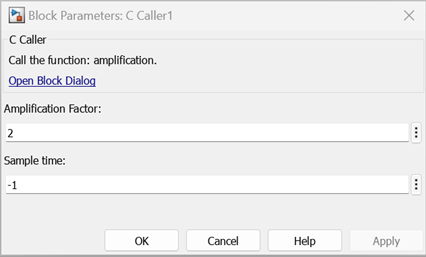
When AmplificationFactor is scoped as parameter, Simulink® generates a mask with a prompt text (Amplification Factor) same as the Label value.
Map pointer variable from C function to Simulink (Pass-by-pointer type)
incrementElement Increases the value of an element of the input array. The index of the array element is indicated by a scalar value assigned to the parameter elementIndex. The value increases when the index value is less than the array size indicated by size. Simulink® uses the size function to compute the array size. The prototype of the incrementElement function is: void incrementElement(int* u, unsigned int size, unsigned int elementIndex).
After parsing the code, the block populates Scope values for elementIndex and size as Input. Subsequently, the block populates Scope value for the input argument u as InputOutput since the function returns the same array as the input array with updated value of an element of the array. For this example, Scope of elementIndex and size are changed to Parameter and Constant, respectively.
Since the arguments are primarily scoped as input and output, the Label values are the corresponding block port names. For this example, Label value for array size (size) is changed to a constant expression size(u,1). Similarly, Label value of elementIndex is changed to Element Index.
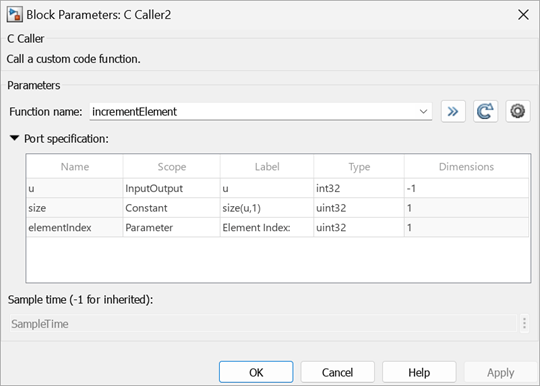
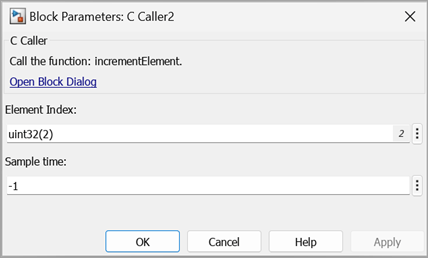
Similar to the amplification function, Simulink® generates a mask with the prompt text (Element Index) same as the Label value.
Simulate and Visualize Results
Simulate the model and visualize the results using Display blocks.
out = sim(mdl);