cgsl_0411: Access nonvolatile memory
| ID: Title | cgsl_0411: Access nonvolatile memory | |
|---|---|---|
| Description | To access target platform nonvolatile memory, use one of these approaches: | |
| A | Use a persistency service interface for asynchronous or synchronous memory access:
| |
| B | Use Initialize Function and Terminate Function blocks and the Direct Access data communication method for synchronous memory access:
| |
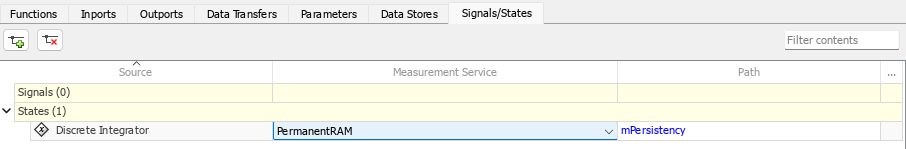
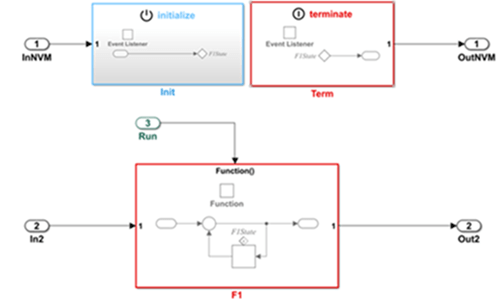
| Notes | Memory access using a persistency service interface For accessing nonvolatile memory by using a service provided by the target environment, map internal states and data stores to a measurement service interface for persistent data. For more information, see cgsl_0414: Configure service interface for component model. Alternatively, you can use a client-server interface approach for modeling the service interface. With this approach, you represent the target environment service that provides access to nonvolatile memory by using a Simulink Function block and access the service by using the Function Caller block. For more information, see Nonvolatile Memory Interfaces (Embedded Coder). Memory access by using Initialize Function and Terminate Function blocks For synchronous accesses of nonvolatile memory during function execution, see guidelines cgsl_0406: Data send for component deployment and cgsl_0405: Data receive for component deployment. | |
| Rationale | A | Memory access using a persistency service interface:
|
| B | Memory access using Initialize Function and Terminate Function blocks:
| |
| Model Advisor Check | A Model Advisor check is not provided for this guideline. | |
| Examples | Memory access using a persistency service interface
Example of generated
#include "PersistencyServiceExample_types.h" #include "services.h" . . . /* Storage class 'PersistentMemory' */ extern double DiscreteIntegrator; . . . #include "PersistencyServiceExample.h"
/* Storage class 'PersistentMemory' */
double DiscreteIntegrator; /* '<Root>/Discrete Integrator' */
.
.
.
void PersistencyServiceExample_step(void)
{
double EstimatedPosition;
EstimatedPosition = DiscreteIntegrator;
DiscreteIntegrator++;
.
.
.
}Memory access using Initialize Function and Terminate Function blocks
Example of generated
void CD_initialize(void)
.
.
.
&(get_CD_initialize_input())[0]
.
.
.
void CD_terminate(void)
{
memcpy(&(getref_CD_terminate_OutBus_NVM()))[0]...
} | |
See Also
Code Interfaces and Code Interface Specification (Embedded Coder)
Service Interfaces (Embedded Coder)
Client-Server Interface (Embedded Coder)
Using Initialize, Reinitialize, Reset, and Terminate Functions