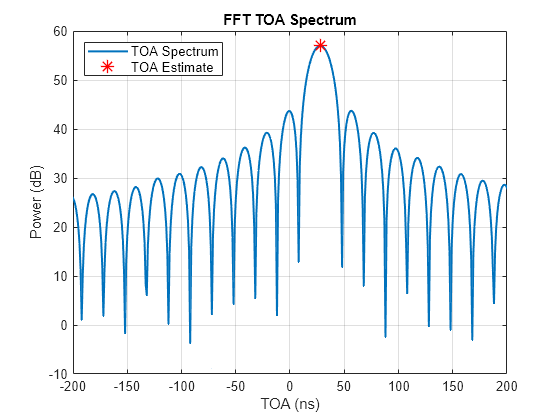
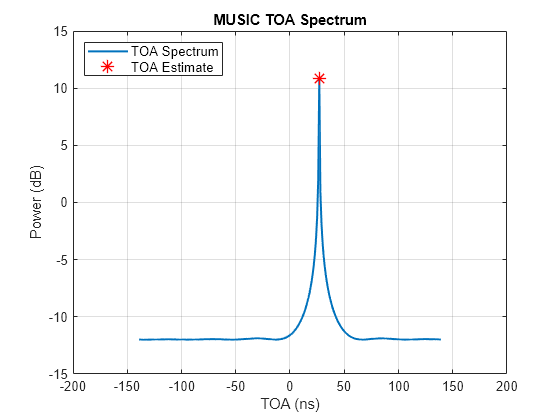
phased.TOAEstimator
Description
The phased.TOAEstimator
System object™ estimates times of arrival (TOAs) or time differences of arrival (TDOAs) of
signals at known anchor points. The System object uses time estimates to perform 2-D or 3-D target positioning of objects. Anchors
can encompass receivers or transmitters, such as cellular base stations, Wi-Fi® access points, ground radar stations, or sonobuoys with known positions and
targets with having unknown positions.
To estimate TOA or TDOA and estimate target positions:
Create the
phased.TOAEstimatorobject and set its properties.Call the object with arguments, as if it were a function.
To learn more about how System objects work, see What Are System Objects?
Creation
Description
estim = phased.TOAEstimatorestim.
estim = phased.TOAEstimator(Name=Value)estim
System object with each specified property Name set to the specified
Value. Specify optional pairs of arguments as
(Name1=Value1,...,NameN=ValueN)
where Name is the argument name and Value is the
corresponding value. Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order
of the pairs does not matter.
Properties
Usage
Syntax
Description
Y = estim(X,freqspacing)Y of signals at anchors from the channel estimation matrix
X. This syntax assumes that the anchors and the target are
synchronized in time.
If the
Measurementproperty is set to"TOA", the object estimates the TOA between each anchor and the target.If the
Measurementproperty is set to"TDOA", the object performs TOA estimation first and then uses the TOA measurements to calculate TDOA.
The freqspacing argument represents the channel
frequency spacing.
Y = estim(X,freqspacing,delayoffset)Y by the
specified delayoffset argument. To enable this syntax, set the
DelayOffsetInputPort property to true.
[
returns the measurement variances Y,var] = estim(X,freqspacing,delayoffset)var. To enable this syntax, set the
VarianceOutputPort property to true.
[
returns the measurement variances Y,var] = estim(X,freqspacing,npow)var for input Gaussian white noise
power npow. To enable this syntax, set the
NoisePowerSource to true.
[
returns the estimated target position Y,___,tgtposest,tgtposcov] = estim(X,freqspacing,___,anchorpos)tgtposest and the estimated
target position covariance tgtposcov. This syntax also accepts the
anchor positions anchorpos as input. To enable this syntax, set the
TargetPositionOutputPort property to
true.
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
Object Functions
To use an object function, specify the
System object as the first input argument. For
example, to release system resources of a System object named obj, use
this syntax:
release(obj)
Examples
Algorithms
References
[1] Zekavat, Seyed A., and R. Michael Buehrer, eds. Handbook of Position Location: Theory, Practice, and Advances. IEEE Series on Mobile & Digital Communication. Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley-IEEE Press, 2019.
[2] Molisch, Andreas F. Wireless Communications: From Fundamentals to Beyond 5G. Third edition. IEEE Press. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-IEEE Press, 2023.
[3] Chan, Y.T., and K.C. Ho. “A Simple and Efficient Estimator for Hyperbolic Location.” IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 42, no. 8 (August 1994): 1905–15. https://doi.org/10.1109/78.301830.
[4] Stoica, P., and Arye Nehorai. “MUSIC, Maximum Likelihood, and Cramer-Rao Bound.” IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing 37, no. 5 (May 1989): 720–41. https://doi.org/10.1109/29.17564.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2024a
See Also
spsmooth | toaposest | tdoaposest | plotTOASpectrum | plotTDOASpectrum | phased.TDOAEstimator