imhmin
Suppress regional minima in image using H-minima transform
Description
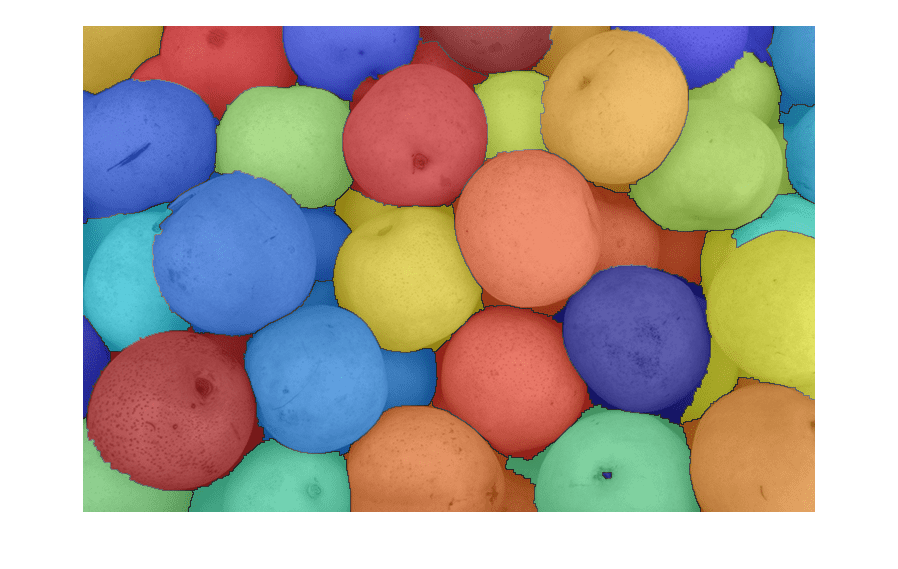
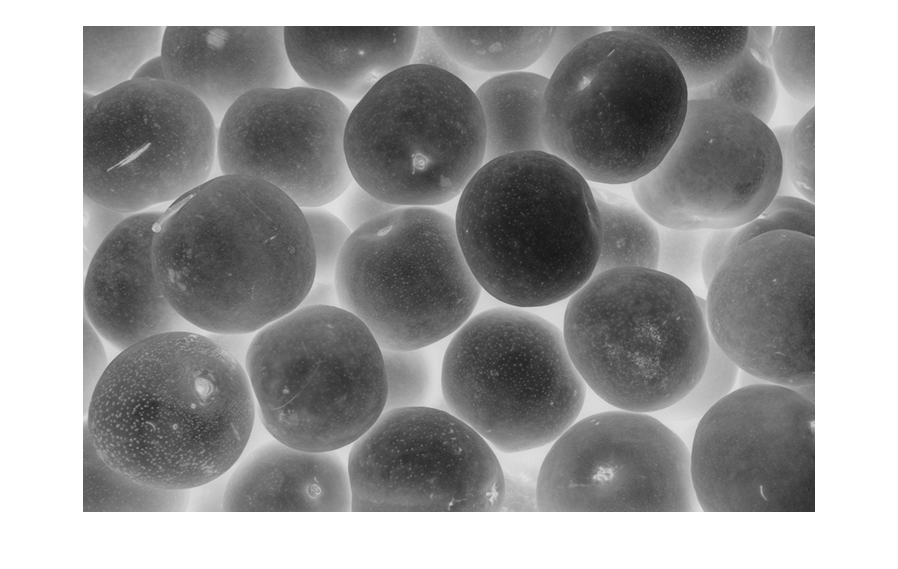
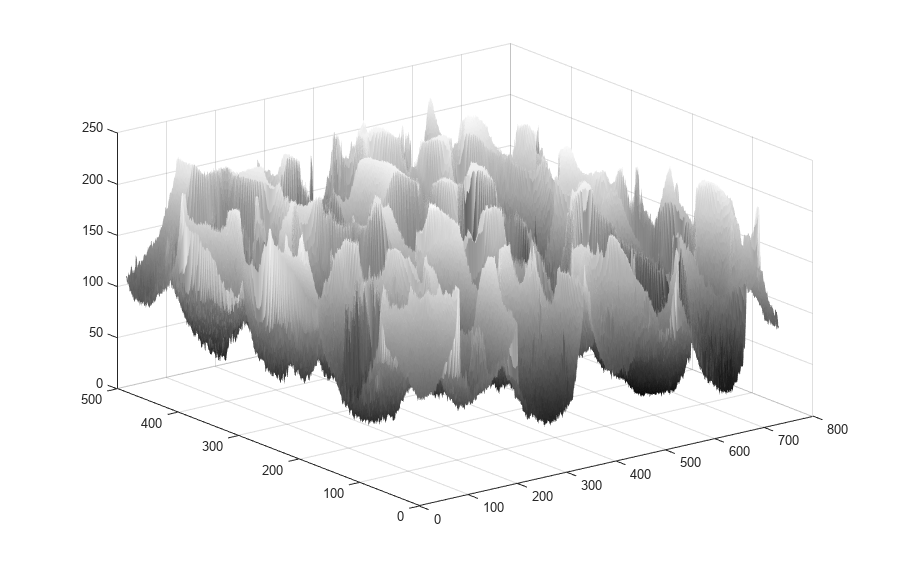
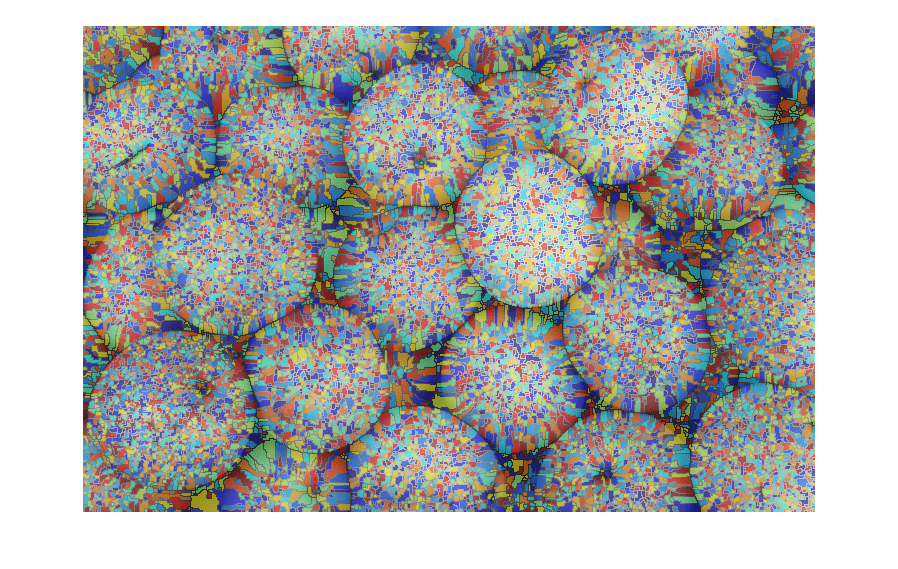
J = imhmin(I,H)I by using the
H-minima transform. The H-minima transform decreases the depth of all regional
minima by an amount up to H. As a result, the transform fully
suppresses regional minima whose depth is less than H.
Regional minima are connected pixels with the same
intensity value, t, that are surrounded by pixels with an
intensity value greater than t.
Examples
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
References
[1] Soille, P. Morphological Image Analysis: Principles and Applications. Springer-Verlag, 1999, pp. 170-171.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced before R2006a