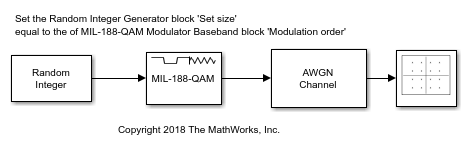
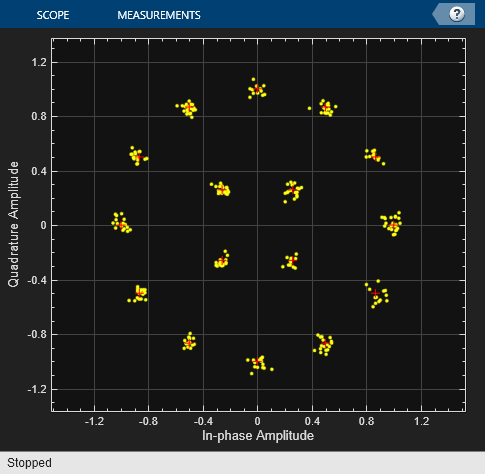
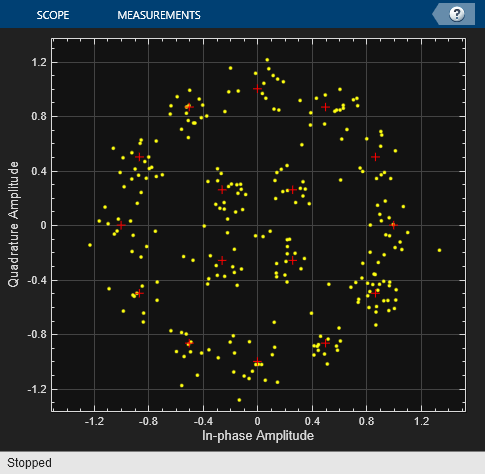
MIL-188 QAM Modulator Baseband
MIL-STD-188-110 B/C standard-specific quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM)
Libraries:
Communications Toolbox /
Modulation /
Digital Baseband Modulation /
AM
Communications Toolbox /
Modulation /
Digital Baseband Modulation /
Standard-Compliant
Description
The MIL-188 QAM Modulator Baseband block modulates the input signal using MIL-STD-188-110 standard-specific quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM).
Examples
Ports
Input
Output
Parameters
Block Characteristics
Data Types |
|
Multidimensional Signals |
|
Variable-Size Signals |
|
More About
References
[1] MIL-STD-188-110B & C: "Interoperability and Performance Standards for Data Modems." Department of Defense Interface Standard, USA.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2018b