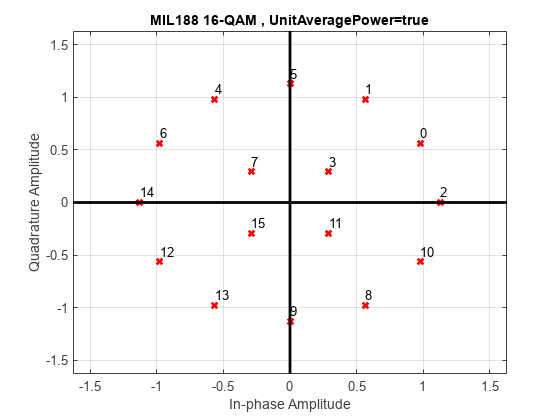
mil188qammod
MIL-STD-188-110 B/C standard-specific quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM)
Description
Y = mil188qammod(X,M)X, in accordance
with MIL-STD-188-110 and the modulation order, M. For more
information, see MIL-STD-188-110.
Y = mil188qammod(X,M,Name=Value)mil188qammod(Y,M,PlotConstellation=true) specifies modulation
order M and plots the constellation. Specify name-value
arguments after all other input arguments.
Examples
Input Arguments
Name-Value Arguments
Output Arguments
More About
References
[1] MIL-STD-188-110B & C: "Interoperability and Performance Standards for Data Modems." Department of Defense Interface Standard, USA.
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2018a