Decode LIN Data from BLF Files
This example shows you how to import and decode LIN data from BLF files in MATLAB® for analysis. The BLF file used in this example was generated from Vector CANoe™. This example also uses the LIN Description file (LDF), ExteriorLight_LIN_CH4.ldf, to decode LIN network information.
Open the LDF File
Open the database file describing the source LIN network using the linDatabase function.
ldb = linDatabase("ExteriorLight_LIN_CH4.ldf")ldb =
Database with properties:
File Information
Name: "ExteriorLight_LIN_CH4.ldf"
Path: "/tmp/Bdoc25b_3175293_1383481/tp798ae7c5/vnt-ex26110327/ExteriorLight_LIN_CH4.ldf"
ProtocolVersion: 2.2000
LanguageVersion: 2.2000
BusSpeed: 19.2000
Network Information
Nodes: [6×3 table]
Frames: [7×5 table]
Signals: [19×5 table]
Investigate the BLF File
Retrieve and view information about the BLF file. The blfinfo function parses general information about the format and contents of the Vector Binary Logging Format BLF file and returns the information as a structure. The channel details are organized primarily by protocol, with CAN and CAN FD grouped together, followed by the LIN protocol, and then sorted by ChannelID. In this example, there are 7 channels displayed for CAN/CAN FD, as the highest detected channel is 7; any channels lacking data will show 0 objects. Additionally, there are 6 LIN channels listed, as the highest channel with LIN data detected is 6.
info = blfinfo("Logging.blf")info = struct with fields:
Name: "Logging.blf"
Path: "/tmp/Bdoc25b_3175293_1383481/tp798ae7c5/vnt-ex26110327/Logging.blf"
Application: "CANoe"
ApplicationVersion: "18.2.65"
Objects: 3568
StartTime: 16-Jan-2025 14:44:41.936
EndTime: 16-Jan-2025 14:44:59.137
ChannelList: [13×3 table]
info.ChannelList
ans=13×3 table
ChannelID Protocol Objects
_________ ________ _______
1 "CAN FD" 314
2 "CAN" 0
3 "CAN" 258
4 "CAN FD" 314
5 "CAN" 0
6 "CAN" 0
7 "CAN" 86
1 "LIN" 0
2 "LIN" 0
3 "LIN" 1281
4 "LIN" 939
5 "LIN" 0
6 "LIN" 285
Read Data from BLF File
The LIN data of interest was stored in channel 4 of the BLF file. According to the output from the blfinfo function, channel 4 for the LIN protocol contains 939 LIN messages. Read the LIN data using the blfread function. To access LIN data specify "ProtocolMode" NV pair value as "LIN". Additionally, provide LIN database object to the function call which will enable message name lookup and signal value decoding.
blfData = blfread("Logging.blf", ChannelID = 4, ProtocolMode ="LIN", Database = ldb)
blfData=939×8 timetable
Time ID Name Data Length Signals ErrorType ChecksumType Checksum
___________ __ ___________ ____________________________________________________ ______ ____________ _________ ____________ ________
0.10573 sec 21 DLFLeft_01 255 0 255 206 255 255 0 0 6 {1×1 struct} None Enhanced 219
0.1125 sec 22 DLFRight_01 254 0 255 255 255 255 161 255 8 {1×1 struct} None Enhanced 136
0.11875 sec 25 GWE_01 224 0 255 247 255 255 203 0 7 {1×1 struct} None Enhanced 193
0.12187 sec 26 GWE_02 244 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 {1×1 struct} None Enhanced 240
0.20625 sec 23 DLRLeft_01 0 254 34 255 255 255 255 0 7 {1×1 struct} None Enhanced 71
0.21146 sec 24 DLRRight_01 16 254 55 255 255 0 0 0 5 {1×1 struct} None Enhanced 224
0.21562 sec 27 WWS_01 253 4 170 0 0 0 0 0 3 {1×1 struct} None Enhanced 247
0.22135 sec 21 DLFLeft_01 255 0 255 235 255 255 0 0 6 {1×1 struct} None Enhanced 190
0.22812 sec 22 DLFRight_01 253 0 255 255 255 255 52 255 8 {1×1 struct} None Enhanced 246
0.23437 sec 25 GWE_01 224 0 255 247 255 255 122 0 7 {1×1 struct} None Enhanced 19
0.2375 sec 26 GWE_02 236 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 {1×1 struct} None Enhanced 248
0.30573 sec 21 DLFLeft_01 252 0 255 36 255 255 0 0 6 {1×1 struct} None Enhanced 137
0.3125 sec 22 DLFRight_01 253 0 255 255 255 255 116 255 8 {1×1 struct} None Enhanced 182
0.31875 sec 25 GWE_01 224 0 255 247 255 255 108 0 7 {1×1 struct} None Enhanced 33
0.32187 sec 26 GWE_02 236 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 {1×1 struct} None Enhanced 248
0.40625 sec 23 DLRLeft_01 0 254 128 255 255 255 255 0 7 {1×1 struct} None Enhanced 232
⋮
View signals from the first "GWE_01" message.
blfData.Signals{3}ans = struct with fields:
GWE_TurnIndicationLeft: 0
GWE_TurnIndicationRight: 0
GWE_WarningLight: 0
GWE_DrivingLight: 1
GWE_Reserved: 203
Repackage and Visualize Signal Values of Interest
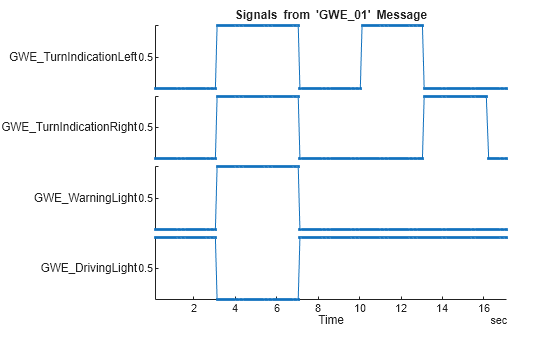
To organize signal data from each unique message on the bus into a signal timetable, use the hLINSignalTimetable helper function. This example demonstrates how to create signal timetables for the specific message of interest, "GWI_01," from the LIN message timetable. The "GWI_01" message includes the following signals: left turn, right turn, warning/hazard light, and driving light.
signalTimetable = hLINSignalTimetable(blfData,'GWE_01')signalTimetable=171×5 timetable
Time GWE_TurnIndicationLeft GWE_TurnIndicationRight GWE_WarningLight GWE_DrivingLight GWE_Reserved
___________ ______________________ _______________________ ________________ ________________ ____________
0.11875 sec 0 0 0 1 203
0.23437 sec 0 0 0 1 122
0.31875 sec 0 0 0 1 108
0.43437 sec 0 0 0 1 248
0.51875 sec 0 0 0 1 199
0.63437 sec 0 0 0 1 197
0.71875 sec 0 0 0 1 245
0.83437 sec 0 0 0 1 119
0.91875 sec 0 0 0 1 67
1.0344 sec 0 0 0 1 198
1.1187 sec 0 0 0 1 86
1.2344 sec 0 0 0 1 14
1.3187 sec 0 0 0 1 134
1.4344 sec 0 0 0 1 233
1.5187 sec 0 0 0 1 153
1.6344 sec 0 0 0 1 26
⋮
To visualize the signals of interest, columns from the signal timetables can be plotted over time for further analysis.
stackedplot(signalTimetable,{"GWE_TurnIndicationLeft","GWE_TurnIndicationRight","GWE_WarningLight","GWE_DrivingLight"},marker=".")
title("Signals from 'GWE\_01' Message")