Create Custom YOLO v2 Object Detection Network
This example shows how to create a custom YOLO v2 object detection network by modifying a pretrained MobileNet v2 network.
The procedure to convert a pretrained network into a YOLO v2 network is similar to the transfer learning procedure for image classification:
Load the pretrained network.
Select a layer from the pretrained network to use for feature extraction.
Remove all layers after the feature extraction layer.
Add new layers to support the object detection task.
Load Pretrained Network
Load a pretrained MobileNet v2 network using the imagePretrainedNetwork function. This network requires the Deep Learning Toolbox Model for MobileNet v2 Network™ support package. If this support package is not installed, then the function provides a download link.
net = imagePretrainedNetwork("mobilenetv2")net =
dlnetwork with properties:
Layers: [153×1 nnet.cnn.layer.Layer]
Connections: [162×2 table]
Learnables: [210×3 table]
State: [104×3 table]
InputNames: {'input_1'}
OutputNames: {'Logits_softmax'}
Initialized: 1
View summary with summary.
Update Network Input Size
Update the network input size to meet the training data requirements. For example, assume the training data are 300-by-300 RGB images. Set the input size.
imageInputSize = [300 300 3];
Next, create a new image input layer with the same name as the original layer.
imgLayer = imageInputLayer(imageInputSize,Name="input_1")imgLayer =
ImageInputLayer with properties:
Name: 'input_1'
InputSize: [300 300 3]
SplitComplexInputs: 0
Hyperparameters
DataAugmentation: 'none'
Normalization: 'zerocenter'
NormalizationDimension: 'auto'
Mean: []
Replace the old image input layer with the new image input layer.
net = replaceLayer(net,"input_1",imgLayer);Display and inspect the layers in the network by using the analyzeNetwork function.
analyzeNetwork(net);
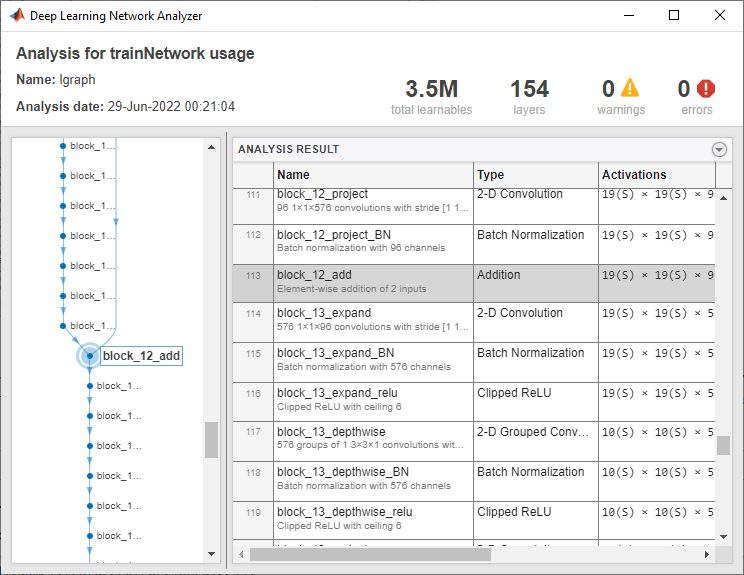
Select Feature Extraction Layer
A YOLO v2 feature extraction layer is most effective when the output feature width and height are between 8 and 16 times smaller than the input image. This amount of downsampling is a tradeoff between spatial resolution and output-feature quality. You can use the analyzeNetwork function or the Deep Network Designer app to determine the output sizes of layers within a network. Note that selecting an optimal feature extraction layer requires empirical evaluation.
Set the feature extraction layer to "block_12_add". The output size of this layer is about 16 times smaller than the input image size of 300-by-300.
featureExtractionLayer = "block_12_add";Remove Layers After Feature Extraction Layer
Remove all of the layers after the feature extraction layer by using the removeLayers function.
index = find(strcmp({net.Layers(1:end).Name},featureExtractionLayer));
net = removeLayers(net,{net.Layers(index+1:end).Name});Create YOLO v2 Detection Sub-Network
The detection subnetwork consists of groups of serially connected convolution, ReLU, and batch normalization layers. These layers are followed by a yolov2TransformLayer.
First, create two groups of serially connected convolution, ReLU, and batch normalization layers. Set the convolution layer filter size to 3-by-3 and the number of filters to match the number of channels in the feature extraction layer output. Specify "same" padding in the convolution layer to preserve the input size.
filterSize = [3 3];
numFilters = 96;
detectionLayers = [
convolution2dLayer(filterSize,numFilters,Name="yolov2Conv1", ...
Padding="same",WeightsInitializer=@(sz)randn(sz)*0.01)
batchNormalizationLayer(Name="yolov2Batch1")
reluLayer(Name="yolov2Relu1")
convolution2dLayer(filterSize,numFilters,Name="yolov2Conv2", ...
Padding="same",WeightsInitializer=@(sz)randn(sz)*0.01)
batchNormalizationLayer(Name="yolov2Batch2")
reluLayer(Name="yolov2Relu2")
]detectionLayers =
6×1 Layer array with layers:
1 'yolov2Conv1' 2-D Convolution 96 3×3 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding 'same'
2 'yolov2Batch1' Batch Normalization Batch normalization
3 'yolov2Relu1' ReLU ReLU
4 'yolov2Conv2' 2-D Convolution 96 3×3 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding 'same'
5 'yolov2Batch2' Batch Normalization Batch normalization
6 'yolov2Relu2' ReLU ReLU
Next, create the final portion of the detection subnetwork, which has a convolution layer followed by a yolov2TransformLayer. The output of the convolution layer predicts the following for each anchor box:
The object class probabilities.
The x and y location offset.
The width and height offset.
Specify the anchor boxes and number of classes and compute the number of filters for the convolution layer.
numClasses = 5; anchorBoxes = [16 16; 32 16]; numAnchors = size(anchorBoxes,1); numPredictionsPerAnchor = 5; numFiltersInLastConvLayer = numAnchors*(numClasses+numPredictionsPerAnchor);
Add the convolution2dLayer and yolov2TransformLayer to the detection subnetwork.
detectionLayers = [
detectionLayers
convolution2dLayer(1,numFiltersInLastConvLayer, ...
Name="yolov2ClassConv",WeightsInitializer=@(sz)randn(sz)*0.01)
yolov2TransformLayer(numAnchors,Name="yolov2Transform")
]detectionLayers =
8×1 Layer array with layers:
1 'yolov2Conv1' 2-D Convolution 96 3×3 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding 'same'
2 'yolov2Batch1' Batch Normalization Batch normalization
3 'yolov2Relu1' ReLU ReLU
4 'yolov2Conv2' 2-D Convolution 96 3×3 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding 'same'
5 'yolov2Batch2' Batch Normalization Batch normalization
6 'yolov2Relu2' ReLU ReLU
7 'yolov2ClassConv' 2-D Convolution 20 1×1 convolutions with stride [1 1] and padding [0 0 0 0]
8 'yolov2Transform' YOLO v2 Transform Layer YOLO v2 Transform Layer with 2 anchors
Complete YOLO v2 Detection Network
Attach the detection subnetwork to the feature extraction network.
net = addLayers(net,detectionLayers);
net = connectLayers(net,featureExtractionLayer,"yolov2Conv1");Use analyzeNetwork function to check the network.
analyzeNetwork(net)
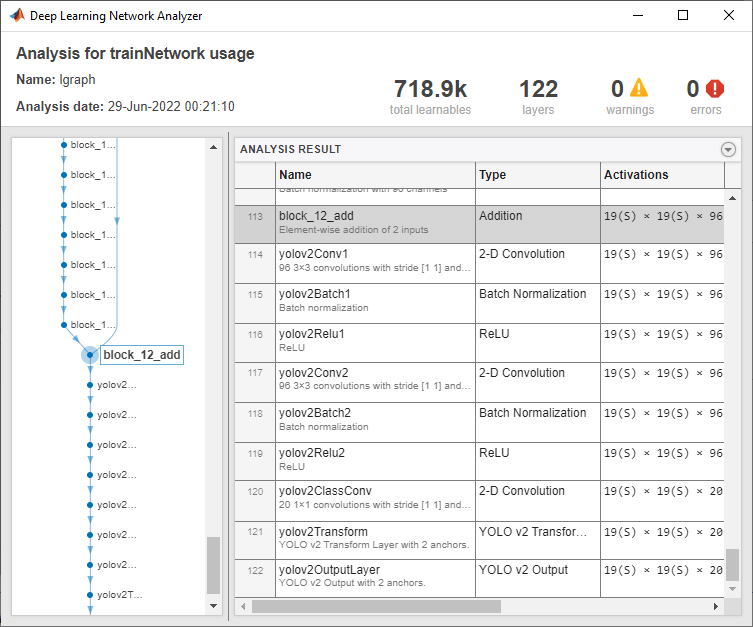
Create a yolov2ObjectDetector object from the network. You can then train the network by using the trainYOLOv2ObjectDetector function.
classNames = ["person" "bicycle" "car" "bus" "truck"]; detector = yolov2ObjectDetector(net,classNames,anchorBoxes)
detector =
yolov2ObjectDetector with properties:
Network: [1×1 dlnetwork]
InputSize: [300 300 3]
TrainingImageSize: [300 300]
AnchorBoxes: [2×2 double]
ClassNames: [5×1 categorical]
ReorganizeLayerSource: ''
LossFactors: [5 1 1 1]
ModelName: ''
See Also
yolov2ObjectDetector |
trainYOLOv2ObjectDetector