ArduPlane SITL Setup Tutorial
ArduPlane is a powerful open-source autopilot system designed for fixed-wing aircraft, widely used in research, hobby, and professional applications. This tutorial will guide you through setting up ArduPlane’s Software-In-The-Loop (SITL) simulation environment on Windows using WSL and Ubuntu 22.04. By following these steps, you’ll be able to simulate, control, and experiment with ArduPlane configurations before deploying them to real hardware. This setup is ideal for safe testing, development, and tuning of your plane’s autopilot features.
This tutorial helps you to:
Run an ArduPlane SITL simulation on your Windows PC.
Connect to the simulated plane using Mission Planner.
Manually control the plane and observe its behavior.
Tune parameters and verify servo output mappings.
Prerequisites
If you are new to Simulink, watch the Simulink Quick Start video.
If you have not performed the hardware setup, complete it before proceeding. For more information, see Install UAV Toolbox Support Package for ArduPilot Autopilots in Windows.
SITL Setup Steps
Perform these steps to set up Software-in-the-Loop (SITL) simulation for your ArduPilot hardware using Simulink.
Install or Verify if WSL is Installed.
If WSL is already installed, proceed to the next step.
If WSL is not installed, install WSL. For more information, see Install Ubuntu Distribution for Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL).
Note
If you have previously used ArduPilot® support package in your existing WSL distribution, it is recommended to install a fresh Ubuntu distribution to avoid conflicts.
Start the hardware setup screens and in the Install Ubuntu Distribution for WSL screen, select I have already installed Ubuntu 22.04.
Select
Ubuntu 22.04from the Ubuntu Distribution drop-down list and then click Next.Install Python.
In the Install Python 3.8.2 Software screen, select the required option.
If Python is not installed, select Automatically download and install option. This is a recommended option and will install Python and other required packages.
If required version Python is already installed, select I have already installed Python 3.7 or a later version and then click Next.
Python 3.8.2 or later is required to upload the ArduPilot executable to an ArduPilot device.
Specify the path for installing Python and other packages and click Install.
A message indicating successful installation is displayed.
In the Select and ArduPilot Vehicle Type screen, select ArduPlane and then click Next.
In the Download ArduPilot Code & Set Up Toolchain on WSL screen, download the ArduPilot source code and setup the toolchain. Click Next. For more information, see Download ArduPilot Source Code and Set Up Toolchain in Windows Subsystem for Linux.
Specify the folder where you downloaded the ArduPilot source code and then click Validate to check that the folder contains a valid ArduPilot installation.
Select SITL and ArduPlane.
In the Select and ArduPilot Board screen, select
ArduPilot Host Targetfor Autopilot name andsitlfor Board options.Click Next.
Download Mission Planner.
In the Download Mission Planner screen, download and install the mission planning software. For more information, see Download and Install Mission Planner
Click Next.
Build ArduPilot Firmware.
Click Build Firmware to start building the firmware. This might take a few minutes to complete.
After the firmware build is complete, click Next.
This completes the hardware setup process,
Click Finish.
Since this is a manual controller setup, try tuning the gains for roll, pitch, yaw, and throttle. Gains are parameters that determine how strongly the controller responds to your input or to changes in the system.
Lowering the gains can reduce sensitivity, resulting in smoother and more stable plane movements.
Configure and Control the Plane
After completing the hardware setup process, perform these steps in the example model.
Open the example model by entering the following command in the MATLAB Command Window:
apManualControlFixedWing
Monitor signals and tune parameters on the example model.
Open Mission Planner and perform these steps.
Select the Data tab, go to Actions tab, select Manual mode from the drop-down list, and then click Set Mode.
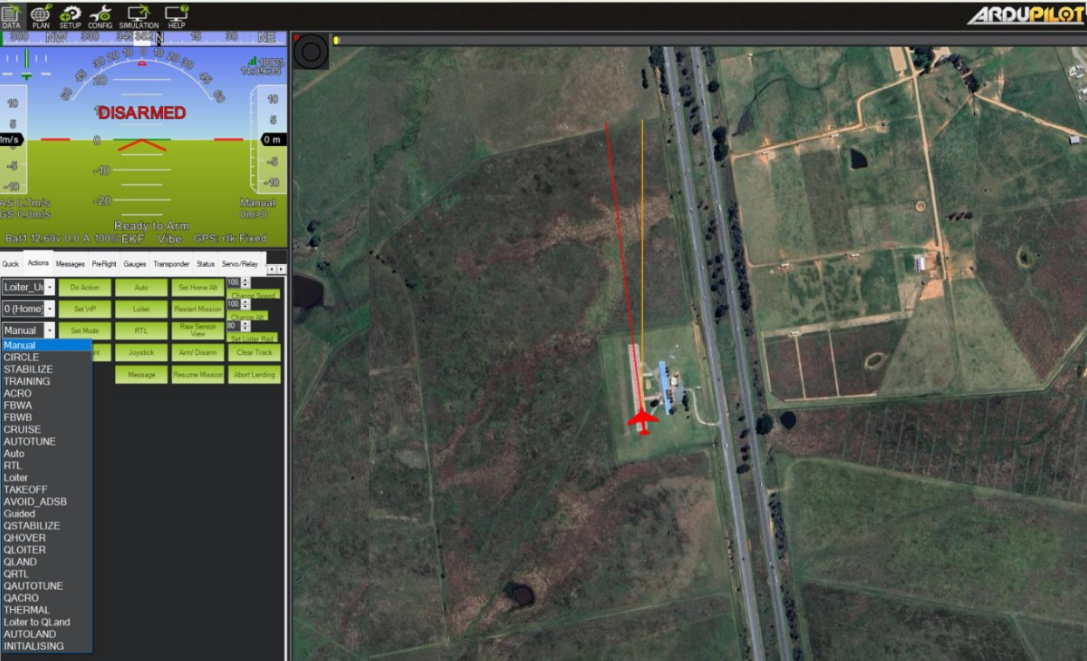
From the Flight Mode drop-down list, usually labeled Set Mode, select
Manualand then click Set Mode.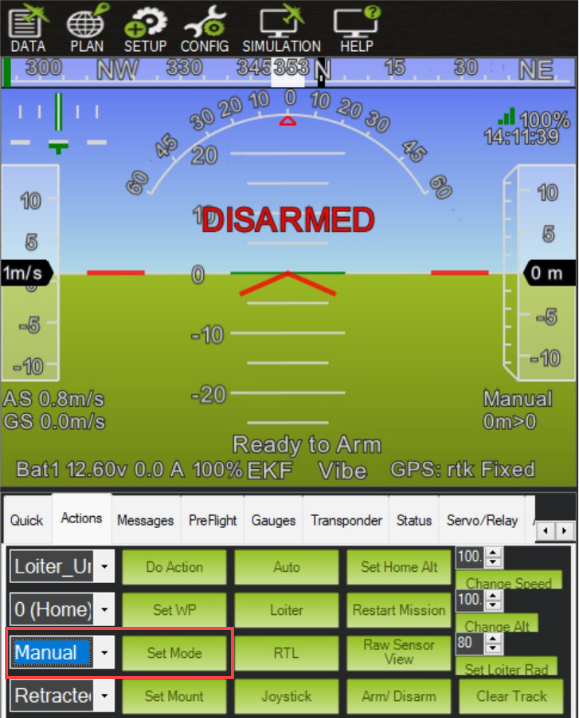
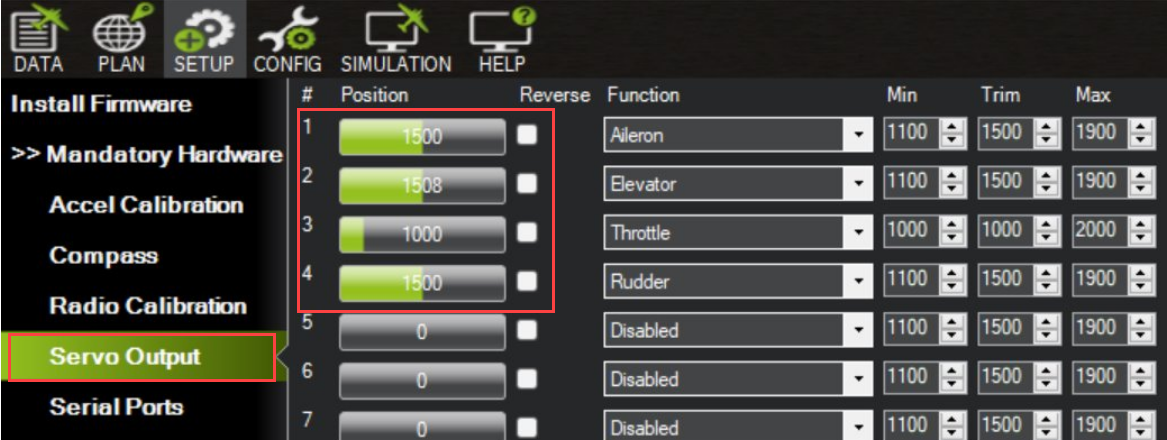
Verify Servo configuration.
Go to Setup > Mandatory Hardware > Servo Output and check that the servos are configured correctly.
Default mapping for a plane:
Servo 1: Aileron
Servo 2: Elevator
Servo 3: Throttle
Servo 4: Rudder
Arm the plane.
From the Data tab, go to Actions tab, and then click Arm/Disarm to arm the plane. The display changes from Disarmed to Armed.

Use the throttle control to increase or decrease the engine power.
Adjust the sliders for roll, pitch, and yaw.
Observe the plane's movement in the Launch Map console as you change the controls You can find the Launch Map console in the main Mission Planner window, typically located under the Flight Data or Simulation tab. It displays a real-time map view of your plane’s position and movement during simulation or flight..
Since this is a manual controller setup, try tuning the gains for roll, pitch, yaw, and throttle.
Lowering the gains can reduce sensitivity, resulting in smoother and more stable plane movements.
See Also
SITL Simulation | Create Your First Model with Software-In-The-Loop Simulation