Detect Data Changes by Using Requirements Table Blocks
Requirements Table blocks can detect changes in the values of data between time steps. You can use change detection operators to determine when data changes to or from a value.
Change Detection Operators
To detect changes in data, use the operators listed in this table.
| Operator | Syntax | Description |
|---|---|---|
hasChanged | tf = hasChanged(data_name) | Returns 1 (true) if the value of
data_name at the beginning of the current time step is different
from the value of data_name at the beginning of the previous time
step. Otherwise, the operator returns 0
(false). |
hasChangedFrom | tf = hasChangedFrom(data_name,value) | Returns 1 (true) if the value of
data_name was equal to the specified value at
the beginning of the previous time step and is a different value at the beginning of
the current time step. Otherwise, the operator returns 0
(false). |
hasChangedTo | tf = hasChangedTo(data_name,value) | Returns 1 (true) if the value of
data_name was not equal to the specified value
at the beginning of the previous time step and is equal to value at
the beginning of the current time step. Otherwise, the operator returns
0 (false). |
The input argument data_name is data defined in the Requirements
Table block, specified as a:
Scalar
Matrix or an element of a matrix
Structure or a field in a structure
Valid combination of structure fields or matrix elements
For the hasChangedFrom and hasChangedTo
operators, the argument value must be an expression that resolves to a
value that is comparable with data_name. For example, if
data_name is a matrix, then value must resolve to a
matrix value with the same dimensions as data_name.
Example of Requirements Table Block with Change Detection
This example shows how the operators hasChanged, hasChangedFrom, and hasChangedTo detect specific changes in an input signal. In this example, a Ramp (Simulink) block sends a discrete, increasing time signal to a Requirements Table block.
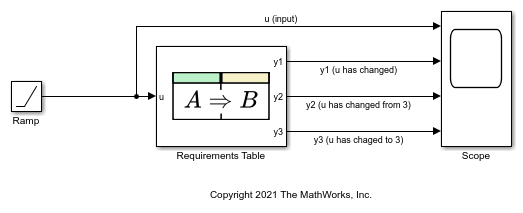
The model uses a fixed-step solver with a step size of 1. The signal increments by 1 every time step. The block checks the input u for these changes:
Changes from the previous time step
A change from the value
3A change to the value
3
To check the signal, the block calls three change detection operators and specifies six requirements. Each change detection operator determines the value of the output data y1, y2, and y3.
If
hasChanged(u)istrue,y1equals1. Otherwise,y1equals0.If
hasChangedFrom(u,3)istrue,y2equals1. Otherwise,y2equals0.If
hasChangedTo(u,3)istrue,y3equals1. Otherwise,y3equals0.
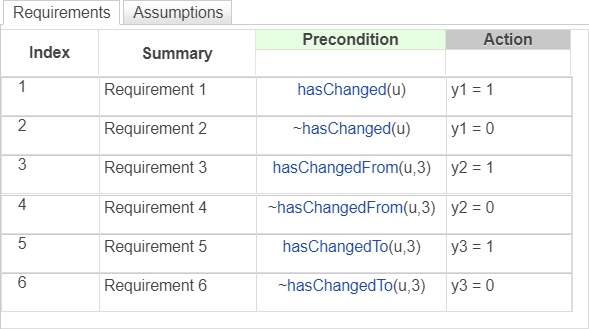
During simulation, the Scope (Simulink) block shows the input and output signals for the block.
The value of
uincreases by1every time step.The value of
y1changes from0to1at timet = 1. The value ofy1remains1becauseucontinues to change at each subsequent time step.The value of
y2changes from0to1at timet = 4when the value ofuchanges from3to4. The value ofy2returns to0after one time step.The value of
y3changes from0to1at timet = 3when the value ofuchanges from2to3. The value ofy3returns to0after one time step.