Simulink Function Blocks in Referenced Models
You can place Simulink Function blocks and function callers (such as Function Caller blocks and Stateflow® charts) in a referenced model, but doing so requires some special considerations:
The referenced model must follow export-function model rules and be designated as an export-function model. See Export-Function Models Overview.
Sometimes, you must explicitly define the argument data types for a Function Caller block.
These examples show four relationships between Function Caller blocks, Simulink Function blocks, and referenced models. To visually display the connections between the Simulink® functions and their callers with lines, on the Debug tab, under Information Overlays, the Function Connectors button is selected.
Simulink Function Block in Referenced Model
This example shows a parent model that contains a Function Caller block and a referenced model that contains a Simulink Function block. The referenced model must follow export-function model requirements.
Open the model named ex_referenced_model_with_simulink_function_block.
open_system("ex_referenced_model_with_simulink_function_block");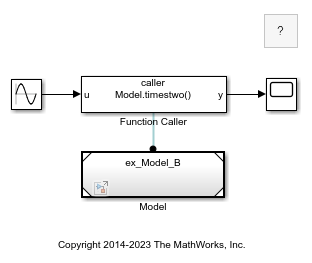
The Function Caller block can determine the argument data types of the function. You do not need to define the Input argument specifications and Output argument specifications parameters of the Function Caller block.
By default, the Simulink Function block is scoped to the model. Therefore, you must qualify a call to the function name with the Model block name.
Open referenced model ex_Model_B.
open_system('ex_Model_B');
Open the Simulink Function block.
open_system('ex_Model_B/Simulink Function');
Referenced model ex_Model_B contains a Simulink Function block that defines a function for multiplying the input by 2. This model satisfies export-function model requirements and is configured as an export-function model. For more information, see Export-Function Models Overview.
When the Trigger block in the Simulink Function block has its Function visibility block parameter set to global, you can reference the model that contains the Simulink Function block anywhere in the model hierarchy. For example, you can place a Model block that references model ex_Model_B in a subsystem.
Function Caller Block in Referenced Model
This example shows a parent model that contains a Simulink Function block and a referenced model that contains a Function Caller block. To use this modeling pattern, the Function visibility parameter of the Trigger block in the Simulink Function block must be set to global.
Open the parent model named ex_referenced_model_with_function_caller_block.
open_system("ex_referenced_model_with_function_caller_block");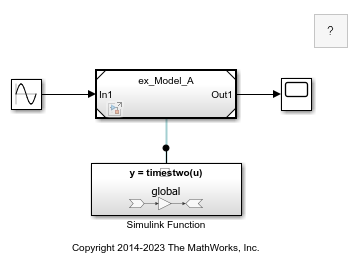
For the parent model, set the solver type to Variable-step or Fixed-step.
The referenced model, named ex_Model_A, contains a Function Caller block.
open_system('ex_Model_A');
For the Function Caller block to find the function in ex_Model_A, set the Function visibility parameter of the Trigger block in the Simulink Function block to global and specify the Function Caller block argument parameters:
Input argument specifications: Specify to match the Simulink Function block input argument data types, for example,
double(1.0).Output argument specifications: Specify to match the Simulink Function block output argument data types, for example,
double(1.0).
For the Simulink Function block, specify the argument specification with the Data type parameter of the Input Argument and Output Argument blocks.
Function and Function Caller Blocks in Separate Referenced Models
This example shows a parent model that contains two referenced models. One referenced model has a Function Caller block, while the other referenced model has a Simulink Function block that specifies a global function.
Open the parent model named ex_referenced_model_with_simulink_function_and_function_caller.
open_system('ex_referenced_model_with_simulink_function_and_function_caller');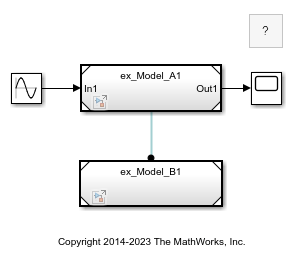
Referenced model ex_Model_B1 contains a Simulink Function block.
open_system('ex_Model_B1');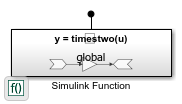
The Simulink Function block defines a global function named timestwo, which multiples input by 2. To specify that the function is global, in the Simulink Function block, the Trigger block sets Function visibility to global.
Referenced model ex_Model_B1 satisfies export-function model requirements and is configured as an export-function model. For more information, see Export-Function Models Overview.
Referenced model ex_Model_A1 contains a Function Caller block.
open_system('ex_Model_A1');
The Function Caller block calls the global timestwo function without qualifying the call to the function. The Function Caller block specifies a Function prototype of y = timestwo(u). The Function Caller block also specifies the Input argument specifications and Output argument specifications parameters.
Suppose you want to call a function that is scoped to a separate referenced model. For example, in ex_Model_B1, set Function visibility of the Trigger block to scoped.
When the function is scoped to a separate referenced model, the Function Caller block must qualify the call to the function with the file name, not the block name, of the model where the function is expected to be resolved. For example, set the Function prototype parameter of the Function Caller block to y = ex_Model_B1.timestwo(u).

You can also use function ports to call a Simulink function in a referenced model from another referenced model. For more information, see Model Client and Server Components Using Function Ports.
Function and Function Caller in Same Model
This example shows a parent model that contains one referenced model. The referenced model contains both a Function Caller block and a scoped Simulink Function block.
Open the model named FunctionAndFunctionCaller.
open_system("FunctionAndFunctionCaller");
Open the referenced model named ex_Model_C.
open_system('ex_Model_C');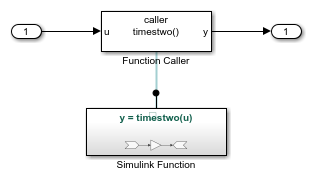
When the referenced model is not configured as an export-function model, it does not need to follow export-function model rules. Export-function model rules do not allow a Function Caller block at the top level of an export-function model. For more information, see Export-Function Models Overview.
When the Simulink Function block specifies a scoped function, as in ex_Model_C, a model hierarchy supports multiple instances of the referenced model.
When the Simulink Function block specifies a global function, a model hierarchy supports only one instance of the referenced model. Otherwise, multiple Model blocks attempt to define functions with the same name and the software throws an error.
See Also
Simulink Function | Argument Inport | Argument Outport | Function Caller | MATLAB Function