Export Data to Parquet File Using Record Block
When you log data using a Record block, you can chose to log data to the workspace, a file, or both. One file type that you can record data to is a Parquet file. Parquet is an open-source file format with efficient compression and encoding of column-oriented data that is often used when processing big data.
Use the Record block to log scalar and multidimensional data from a signal, message, bus, or array of buses to a Parquet file. The Record block also supports logging variable-size signals, but does not support visualizing or logging variable-size signals to a Parquet file. Use the Record block to log real and complex data of any built-in data type or user-defined data types such as buses, enumerations, and fixed-point data.
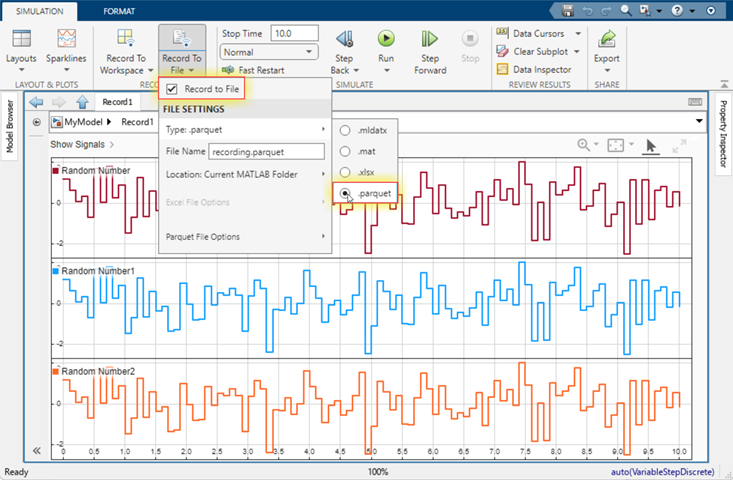
To log data to a Parquet file, double-click the Record block. Click the
Record To File button arrow. From this menu, select
Record to File and set the file type to
*.parquet. By default, the filename is
recording.parquet, and the file is saved in the local folder. You can
also select Parquet File Options to change other options specific
to Parquet files, such as the compression style, time column configuration, and row group
options.
You can also configure the Record block to log data to a Parquet file
programmatically using the set_param function. First, set the
Record block to record to a file. Then, specify the name of the Parquet file.
set_param("MyModel/Record","RecordToFile","on","FileName","myRecording.parquet")
set_param function to set other Parquet file options, such as the
compression
style.set_param("MyModel/Record","ParquetCompression","compact")
You can log data to a Parquet file using normal, accelerator, and rapid accelerator mode simulations. All signals connected to the Record block are written to the Parquet file when the simulation is paused or stopped. By default, when you record data to a Parquet file, the Record block stores all logged metadata associated with the Simulink® simulation in a JSON sidecar. The sidecar contains information such as the block path, port index, and sample time.
The Record block supports logging some data types that are not supported by
a Parquet file. Most data types, such as double, int, or
string, do not change when the Record block saves data to
a Parquet file. This table shows the data types supported by the Record block
and how that data is represented when saved to a Parquet file.
| Simulink Data Type | Parquet File Logical Data Type |
|---|---|
double | double |
single | single |
int8 | int8 |
int16 | int16 |
int32 | int32 |
int64 | int64 |
uint8 | uint8 |
uint16 | uint16 |
uint32 | uint32 |
uint64 | uint64 |
string | string |
Boolean | Boolean |
half | double |
fixed point | double (fixed-point data is stored in the JSON
sidecar) |
enum | int32 |
image | Data type of underlying image data |
datetime | double representation of epoch time |
For more information about Parquet file data types, see Apache Parquet Data Type Mappings.
How the Record block formats data in the Parquet file depends on the type of signal being recorded. This table shows how each type of Simulink signal is recorded in the Parquet file.
| Simulink Signal Type | Parquet File Logging Format |
|---|---|
| Scalar signal |
Single column with a scalar value at each time step |
| Scalar signal with complex data | Single column with a |
| Nonscalar signal | The logging format of a nonscalar signal depends on how the signal is represented in the Record block.
|
| Nonscalar signal with complex data | The logging format of a nonscalar signal depends on how the signal is represented in the Record block.
|
| Virtual or nonvirtual bus | Separate columns for each element in the bus or bus hierarchy |
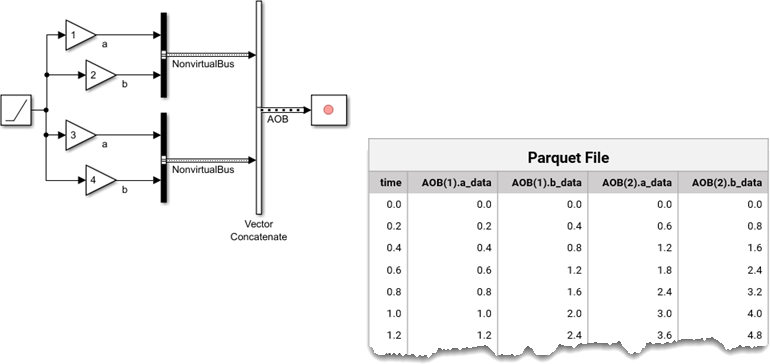
| Array of buses | Separate columns for each element in the array of buses |
Single-Rate and Multirate Data
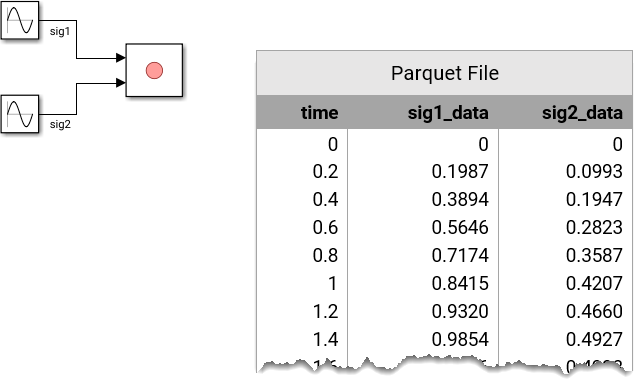
You can choose to save data to a Parquet file using shared or individual time columns. When you save single-rate data with a shared time column, the first column in the file contains time data, followed by columns containing signal data. The Record block logs data to a Parquet file using shared time columns by default.
When you save multirate data using shared time columns, data is grouped by shared time vectors. Time columns specify the sample times for signals to the right, up to the next time vector.
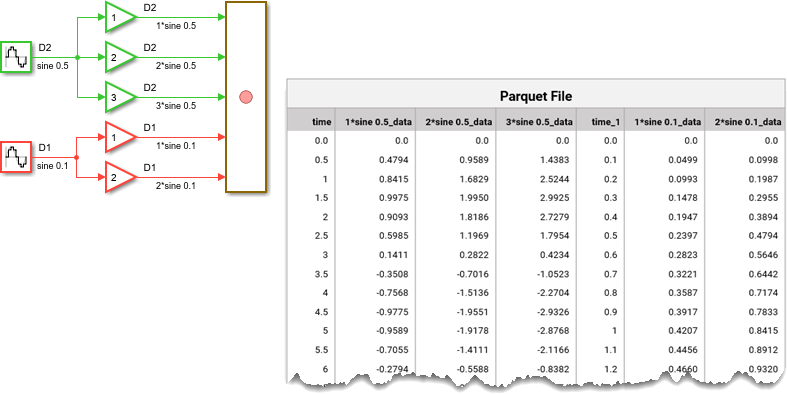
A Parquet file requires that all columns be of equal length. When you record signals
that are not of equal length to the same Parquet file, the Record block
appends NULL to any empty cells.
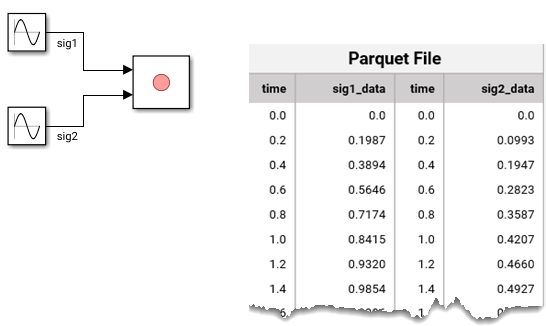
To save data to a Parquet file using individual time columns, select Record To File > Parquet File Options > Individual Time Columns. Alternatively, you can configure the Record block to log data to the Parquet file using individual time columns programmatically using the Time parameter. To specify how to log time data, first set the block to record data to a Parquet file.
set_param("MyModel/Record","RecordToFile","on","FileName","myRecording.parquet","SharedTimeColumn","off")
When you save data using individual time columns, the software saves data in pairs of time and signal data columns.
Complex Signals
The Record block exports complex sample values to a Parquet file as a
1×2 vector, where the first element is the real part
and the second element is the imaginary part of the complex value.
![A model that logs complex data to a Record block, with the Parquet file storing real and imaginary parts as a two-element vector. For example, at time 0.2, the signal value 0.3973 + 0.5960i is saved as [0.3973, 0.5960].](record-parquet-complex.png)
Multidimensional Signal Data
Multidimensional signal data with fixed dimensions can be represented in the Record block in two ways:
A single signal with multidimensional sample values
A set of signals with scalar sample values: one signal, called a channel, for each element of the multidimensional data
When multidimensional signal data is represented as a single signal with multidimensional sample points, the data for each time step is stored in the Parquet file as vectors for one-dimensional arrays, a list of column vectors for two-dimensional arrays, or as a nested list of column vectors for arrays with more than two dimensions.
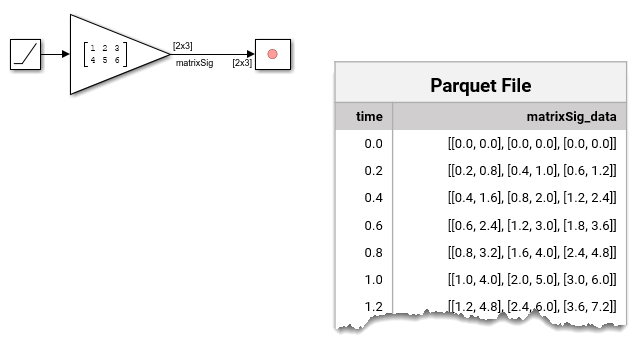
By default, signals with samples that contain fewer than five elements are represented as channels. When multidimensional signal data is represented as channels in the Record block, the Parquet file allocates a separate column for each channel.
You can control how multidimensional signal data is saved to a Parquet file using the
expand
function, the collapse
function, or the signal table in the Record block or the Simulation Data
Inspector. When you change the representation of a multidimensional signal in the
Record block, the change is reflected in the Simulation Data Inspector and
vice versa. For more information, see Analyze Multidimensional Signal Data.
When you save multidimensional signals that contain complex data to a Parquet file, each
sample element is a nested 1×2 vector, where the first
element is the real part and the second element is the imaginary part of the complex value.
For real values, the second element is 0.
![A model logs a 2 by 3 matrix signal containing complex data using a Record block. In the saved Parquet file, there are two columns: time and signal data grouped into three 1 by 2 column-wise vectors of the 2 by 3 matrix signal at each sample time. Each element of the sample values is represented as a pair of real and imaginary components in the form ([real, imaginary]).](record-parquet-matrix-complex.png)
The Record block does not support saving variable-sized signals to a Parquet file.
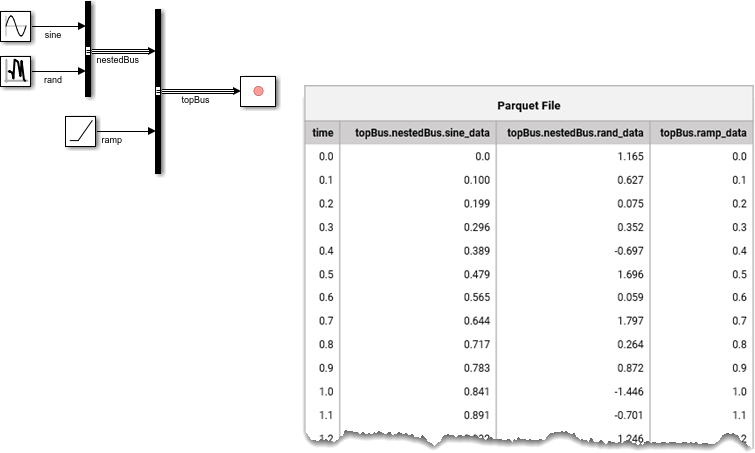
Buses
You can export data logged from virtual or nonvirtual buses to a Parquet file. In the Parquet file, dots in signal names specify the bus hierarchy.
You can also use the Record block to save arrays of buses to a Parquet file. The Record block saves each element in the array of buses as a column in the Parquet file.
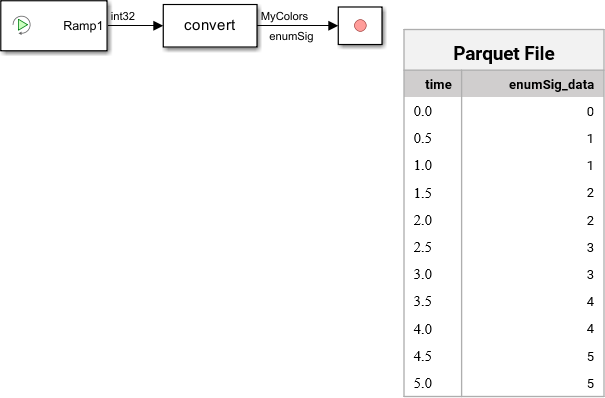
Enumerated Data
The Record block supports logging enumerated data. When you save
enumerated data to a Parquet file, the Record block exports only the
underlying integer data as int32 values.
For example, the MyColors class in this model defines a set of
enumerated values consisting of six colors, each associated with an integer value between
0 and 5.
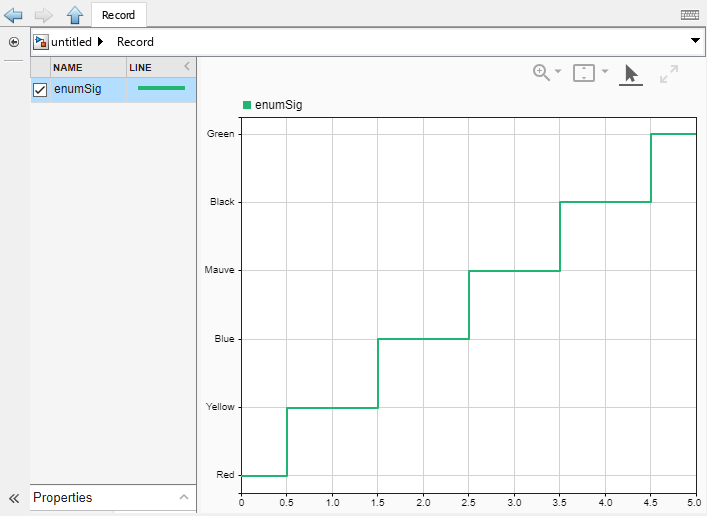
When you save the enumerated data to a Parquet file, only the underlying integer values associated with each enumerated value are saved in the file.
See Also
Record | Playback | parquetread | parquetinfo