Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi® allows devices to connect to a local area network wirelessly. Based on IEEE® 802.11 standards, Wi-Fi is commonly used for providing internet access and enabling communication between devices without the need for physical cables.
Use Wi-Fi shields as an add-on to your Arduino® board to expand its Wi-Fi capabilities. These shields enable the boards to connect to wireless networks, allowing them to send and receive data over the internet or a local network.
Blocks
| WiFi TCP/IP Receive | Receive data over TCP/IP network from remote host on wireless network |
| WiFi TCP/IP Send | Send data over TCP/IP network to remote host over wireless network |
| WiFi UDP Receive | Receive data from UDP host on wireless network |
| WiFi UDP Send | Send data to UDP host on wireless network |
| WiFi ThingSpeak Read | Read data stored in a ThingSpeak channel on wireless network |
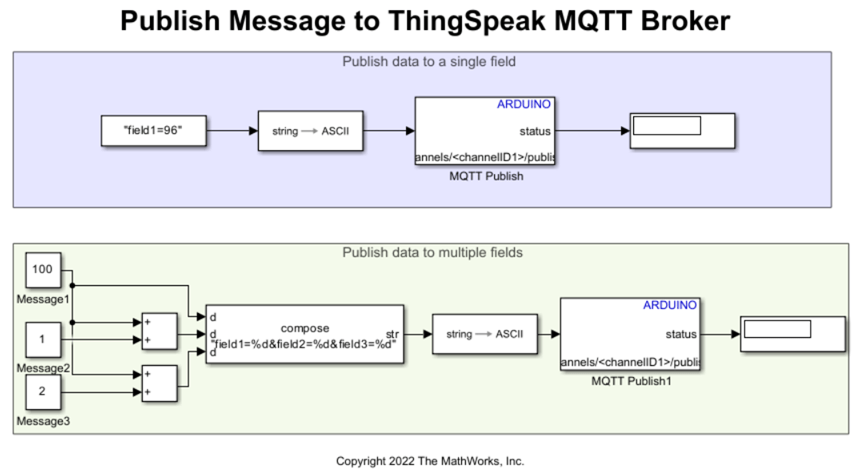
| WiFi ThingSpeak Write | Publish data to Internet of Things using ThingSpeak on wireless network |
| WebSocket Subscribe | Subscribe to the JSON data received by a WebSocket server |
| WebSocket Publish | Publish data to WebSocket server in JSON format |
| WiFi MQTT Publish | Publish messages to message queuing telemetry transport (MQTT) broker (Since R2022b) |
| WiFi MQTT Subscribe | Receive messages from message queuing telemetry transport (MQTT) broker (Since R2022b) |
| WiFi HTTP Client | Send and receive data from HTTP server over URL connection (Since R2023a) |
Topics
- Connect ESP8266 to Arduino Hardware
Pin mapping to connect ESP8266 to an Arduino board.
- Connect Arduino WiFi Shield to Arduino Hardware
Follow the steps to connect Arduino Wi-Fi Shield to an Arduino board.
- Connect Arduino MKR1000, Arduino MKR WIFI 1010, or Arduino MKR ZERO Hardware to Computer
Follow the steps to connect Arduino MKR1000, Arduino MKR WIFI 1010, or Arduino MKR ZERO hardware to a computer.
- Set Up a Wi-Fi TCP/IP Connection with Connected IO in Simulink
Establish a Wi-Fi TCP/IP connection and simulate model in the connected IO mode.
- Set Up a Wi-Fi UDP Connection with Connected IO in Simulink
Establish a Wi-Fi UDP connection and simulate model in connected IO mode.
- Configure Network Settings for Wi-Fi
Follow the steps to configure the Wi-Fi settings for an Arduino board.
- Configure Model to Run in External Mode over Wi-Fi or Serial
Simulate model in external mode using Wi-Fi or serial communication.
Troubleshooting
Unable to Deploy Code on an Arduino Board Connected to an ESP8266
No separate serial port is available on Arduino Uno board to deploy code.
Unable to Connect ESP8266 to Wi-Fi Network
Connection between ESP8266 and Wi-Fi network failed.
Unable to Assign IP Address to an Arduino Board Connected to ESP8266
Failed to assign IP address to Arduino board connected to ESP8266.
Unable to Assign IP Address to an Arduino MKR1000 Board
Failed to assign IP address to Arduino MKR WIFI 1010 board.
Unable to Assign IP Address to an Arduino MKR WIFI 1010 Board
Failed to assign IP address to Arduino MKR WIFI 1010 board.
Unable to Assign IP Address to an Arduino Board Connected to WiFi Shield
Failed to assign IP address to Arduino board connected to WiFi shield.
Expected Data Not Received on WiFi TCP or UDP Receive Block
Data received on the WiFi TCP Receive block or WiFi UDP Receive block is incorrect.
WiFi TCP/IP Send or Receive Server Block Is Unable to Communicate to TCP/IP Client
In server mode, the WiFi TCP/IP block is unable to communicate with TCP/IP client.
WiFi TCP/IP Send or Receive Client Block Is Unable to Communicate to TCP/IP Server
In client mode, the WiFi TCP/IP block is unable to communicate with TCP/IP server.
WiFi ThingSpeak Write Block Unable to Upload Data to a ThingSpeak Channel
Data is not uploaded on ThingSpeak™ channel.