Differential (Tank) Drive
Add-On Required: This feature requires the Simulink Coder Support Package for VEX EDR V5 Robot Brain add-on.
Libraries:
Simulink Coder Support Package for VEX EDR V5 Robot Brain /
Drivetrain
Description
Use the Differential (Tank) Drive block to control pose (position and heading) of VEX® V5 robot drivetrain.
Provide the position and final heading waypoints as input to move the robot to the specified position and turn it toward the final heading.
This block also allows you configure drive parameters such as track width or wheel size and change controller parameters such as drive speed and accuracy.
This block requires Stateflow® license.
Note
To study or modify the block algorithm, click anywhere in the block. On the Block tab that appears on the Simulink toolstrip, click Disable Link, and then click Look inside mask.
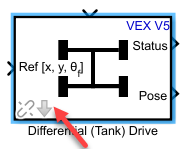
Ports
Input
Final pose or waypoint specified as a three-element vector of
[x y θ], where x and y corresponds to position
and θ corresponds to the orientation angle. Positive
angles are measured counterclockwise from the positive
x-axis relative to starting pose.
Since the differential drive robot cannot move sideways, position (x, y) and angle θ references are controlled one after the other. First the robot moves to the specified position and then turns towards the specified angle.
Output
This port outputs if the drive block is active or not. Use this output to determine if the current waypoint is reached. The status is active when:
The drive is moving or turning.
The sensors (inertial sensor or gyroscope) are being calibrated.
The port returns 1 when the drive is
active and 0 otherwise.
Data Types: Boolean
This port outputs the target wheel speed from right to left order measured in radians per second. This block contains controller logic that provides wheel speed commands, which corresponds to motor commands sent to Smart Motor write blocks.
You can use this output to monitor the wheel speed commands or to add additional Smart Motors.
Dependencies
To enable this port select Target wheel speeds in right, left order (rad/s) parameter.
Data Types: double
Current vehicle pose, specified as a three-element vector of
[x y θ], where x and y corresponds to position
and θ corresponds to orientation angle. Positive
angles are measured counterclockwise from the positive
x-axis.
Use this block to monitor the robot’s current position and heading.
Dependencies
To enable this port select Current Pose parameter.
Optional outputs
Parameters
Drive
Select the drivetrain configuration based on the number of smart
motors present. If the robot drivetrain is driven by two motors, select
2-Motor Differential (Tank) Drive. If it
is driven by four motors, select 4-Motor Differential
(Tank) Drive.
This parameter flips or reverses the direction of all smart motors (left and right) used in the drivetrain. The default value works for configurations where there is no direction reversal between motors and wheels (for example, a V5 speed bot).
When there are gears between motor and wheel, the motor and wheel might move in opposite directions. In such cases, select this option. Selecting this parameter incorrectly will destabilize the heading control.
Select the smart port to which the left motor is connected. There are 21 smart ports on V5 Robot Brain. Assign a unique port number to each motor.
Select the smart port to which the left motor is connected. There are 21 smart ports on V5 Robot Brain. Assign a unique port number to each motor.
Dependencies
To enable this port set the Configuration
parameter to 4-Motor Differential (Tank)
Drive.
Select the smart port to which the right motor is connected. There are 21 smart ports on V5 Robot Brain. Assign a unique port number to each motor.
Select the smart port to which the right motor is connected. There are 21 smart ports on V5 Robot Brain. Assign a unique port number to each motor.
Dependencies
The port is available only when you select the
4-Motor Differential (Tank) Drive
parameter.
Select the internal gear ratio for smart motors used in the drivetrain.
Enter the value for motor to wheel gear ratio for VEX V5 Differential (Tank) Drive.
If the motors are connected directly to wheels without any gear reduction (direct drive), Gear ratio (motor to wheel) is 1, else set the gear ratio. For example, if wheels turn once for every two rotations of motor, then the ratio is 2/1 or 2.
Select the wheel diameter in inches. If your wheel diameter is not
listed, select other and then enter the wheel
diameter.
Enter the wheel diameter in meters.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, select other
in VEX wheel diameter parameter.
Enter the track width in meters.
Sensors
Select the sensor to provide heading feedback.
For best results, select Inertial sensor.
Gyroscopes tend to drift over time and smart motor
encoders are susceptible to wheel slippage and might
lead to inaccurate heading.
Select the smart port to which the motor is connected. There are 21 smart ports on V5 Robot Brain. Assign a unique port number to each motor.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, select Inertial
sensor in Heading sensor
parameter.
If you are using a 3-Wire Expander, specify the smart port on VEX EDR V5 Robot Brain to which the expander is connected.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, select
Gyroscope in Heading
sensor parameter.
Select the port on the robot to which the block is connected.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, select
Gyroscope in Heading
sensor parameter.
Set the scale factor value for the gyroscope. For more information see, Monitoring Signals for Gyroscope Calibration Using the VEX V5 Touch Screen
Data Types: double
Specify how the gyroscope is mounted. This parameter indicates the orientation of the gyroscope.
Controller parameters
Distance
Set the linear speed of the robot in meters per second.
Set the deadband in meters. This parameter sets the accuracy of position control. The robot stops once the distance error (between current and reference position) falls below deadband value.
Setting a very low value might destabilize the robot motion.
Set the hysteresis distance in meters. As the robot uses an on-off type controller, the motor speeds may switch many times when the robot is near target. Hysteresis prevents the controller from switching too much.
Angle
Set the angular speed or turn rate of the robot.
Set the accuracy of angle control.
Since, heading angle is controlled even when the robot moves towards reference position, setting a low deadband can lead to oscillatory movement. Setting a high Deadband can compromise angle accuracy.
Set the hysteresis angle in degrees. Since the robot uses an on-off type heading controller, motor may switch on and off many times. Hysteresis prevents the controller from switching on-off too much.
Sample time
Specify a sample time by entering a positive scalar value, such as 0.1. The discrete sample time of -1 means that the block inherits its sample time from upstream blocks.
If you set the sample time to a high value, robot motion might not be stable.
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using Simulink® Coder™.
Version History
Introduced in R2021a
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)