Example
Suppose that you are packing four signals into a vector of data type uint8
or uint16, and the signals have these attributes.
| Dimension | Size | Type |
|---|
| Vector | 3 | int8 |
| Vector | 2 | int16 |
| Scalar | 1 | uint8 |
| Scalar | 1 | uint32 |
To pack the signals:
Set . This
example compares uint8 and
uint16.
Set
to:
{'int8’, ‘int16’, ‘uint8’, ‘uint32’}The block creates four input ports that match the order of the incoming
signal data types specified in the cell array.
Set the required byte alignment value. The byte alignment value specifies
the number of bytes after which a new byte starts from the previous
boundary.
The size of the output is based on the packed vector size, the byte
alignment value, and the smallest memory cell size of the processor.
Depending on the byte alignment value, input values are padded with zeros
before the next signal is packed. The smallest addressable memory cell
indicates the number of bits occupied by the char or
uint8 data type for a processor and determines the
structure of packets.
Connect incoming signals to the input port of the Byte Pack
block.
For processors with a smallest addressable memory cell of 8 bits per char,
consider these values for input signals.
| Unpacked
Signals |
|---|
| Dimension | Size | Data Type | Dec Value | Hex Value |
|---|
| Vector | 3 | int8 | 35 | 23 |
| 4 | 04 |
| –3 | FD |
| Vector | 2 | int16 | 218 | 00DA |
| –12 | FFF4 |
| Scalar | 1 | uint8 | 112 | 70 |
| Scalar | 1 | uint32 | 5000 | 00001388 |
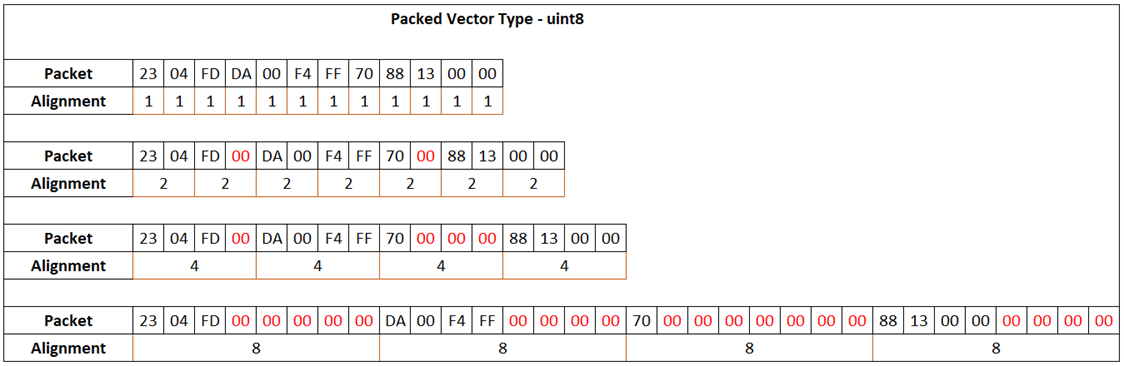
The packed output vector data type uint8 is:
Red zeros represent padded empty memory cells.
For a packed output vector of data type uint8 and byte
alignment value 2, the int8 data value (23 04 FD) occupies the
first three memory cells, with each cell occupying 8 bits. Because three is not a
multiple of the byte alignment value 2, the next input signal of
int16 data value (00DA FFF4) is allocated the next four cells
(fifth through eighth), leaving the fourth cell empty. The block fills the empty
cell with zero. The rest of the input signals are packed in a similar way.
After packing all input signals, the Byte Pack block calculates the
total packets allocated and outputs a uint8 vector of size 4 + 4
+ 2 + 4 = 14. Here, the int8 signal occupies the first 4 cells,
the int16 signal occupies the second 4 cells, the
uint16 signal occupies the third 2 cells, and the
uint32 signal occupies the fourth 4 cells.
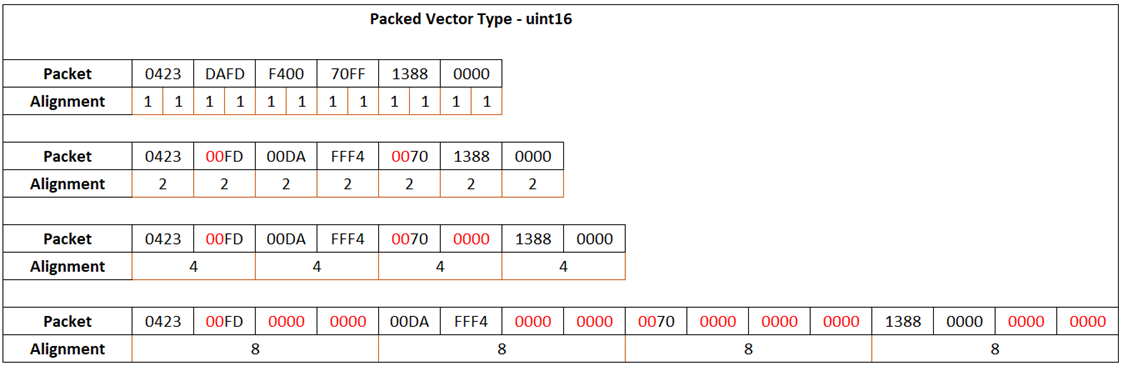
The packed output vector of data type uint16 is:
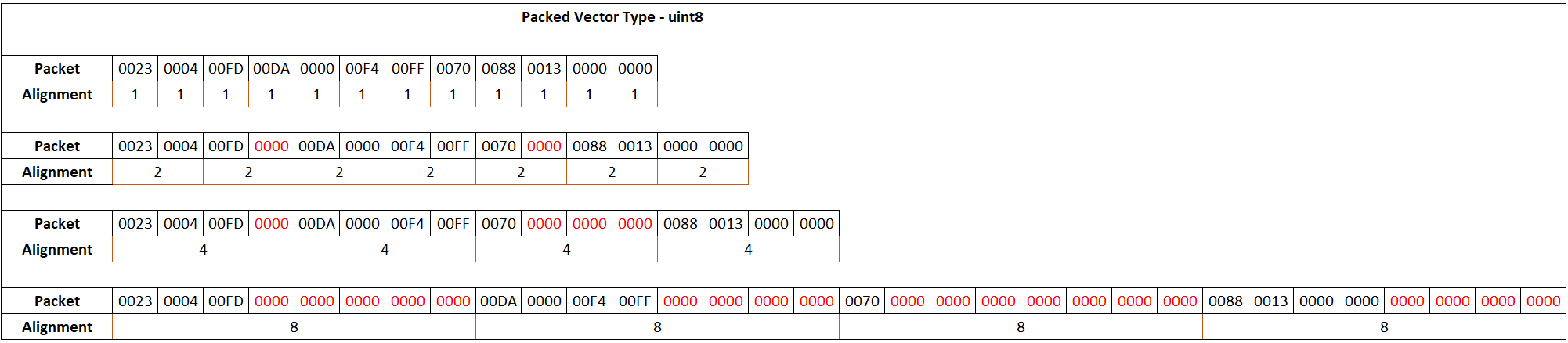
For processors such as Texas Instruments®
C2000™, with the smallest addressable memory cell of 16 bits per char,
consider these values for input signals. The int8 and
uint8 data values occupy 16 bits, as indicated by the hex value.
| Unpacked
Signals |
|---|
| Dimension | Size | Data Type | Dec Value | Hex Value |
|---|
| Vector | 3 | int8 | 35 | 0023 |
| 4 | 0004 |
| –3 | FFFD |
| Vector | 2 | int16 | 218 | 00DA |
| –12 | FFF4 |
| Scalar | 1 | uint8 | 112 | 0070 |
| Scalar | 1 | uint32 | 5000 | 00001388 |
For the packed output vector of data type uint8, the output
packet occupies 16 bits, although the data value the packet represents is 8 bits.
The byte alignment values are calculated with respect to the16-bit addressable
memory.
For a packed output vector of data type uint8 and byte
alignment value 2, the int8 data value (0023 0004 00FD) occupies
the first three memory cells, with each cell occupying 16 bits. Because three is not
a multiple of byte alignment value 2, the next signal of data type
int16 (00DA 0000 00F4 00FF) is allocated the next four cells
(fifth through eighth), leaving the fourth cell empty. The block fills the empty
cell with zero. The rest of the input signals are packed in a similar way. After
packing all input signals, the Byte Pack block calculates total
packets allocated and outputs a uint8 vector of size 4 + 4 + 2 +
4 = 14.
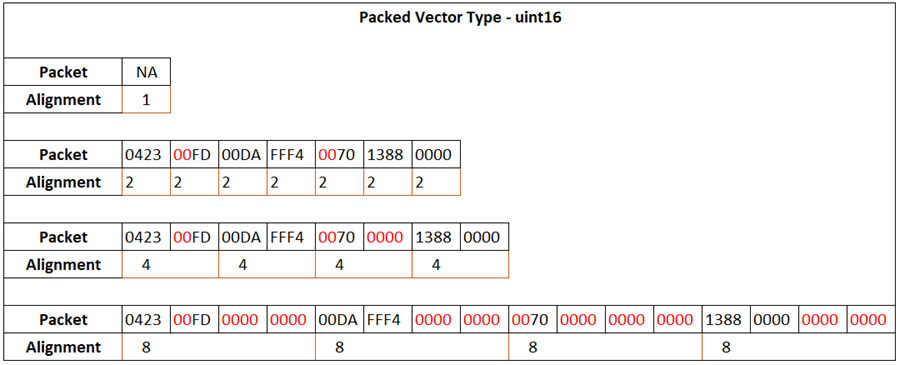
For the packed output vector of data type uint16, the output
packet occupies 16 bits, and the data value the packet represents is also 16 bits.
For a packet size of 16 and larger, the byte alignment is calculated with respect to
the number of bytes the data values are packed into. Therefore, in this case, 1-byte
alignment is not allowed.
For a packed output of data type uint16 and byte alignment
value 2, the three int8 data values (0423 FD) are packed together
as two words in the first two memory cells. The fourth byte in the second memory
cell is empty and filled with zero. The int16 data value (00DA
FFF4) is allocated the next two memory cells (third and fourth). The rest of the
input signals are packed in a similar way. After packing all signals, the
Byte Pack block calculates total packets allocated and outputs a
uint16 vector of size 2 + 2 + 1 + 2 = 7.