Geometry from polyshape
This example shows how to create a polygonal geometry using the MATLAB® polyshape function. Then use the triangulated representation of the geometry to create an fegeometry object.
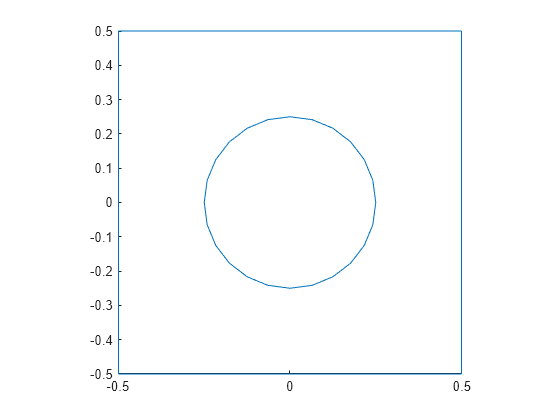
Create and plot a polyshape object of a square with a hole.
t = pi/12:pi/12:2*pi;
pgon = polyshape({[-0.5 -0.5 0.5 0.5], 0.25*cos(t)}, ...
{[0.5 -0.5 -0.5 0.5], 0.25*sin(t)})pgon =
polyshape with properties:
Vertices: [29×2 double]
NumRegions: 1
NumHoles: 1
plot(pgon)
axis equal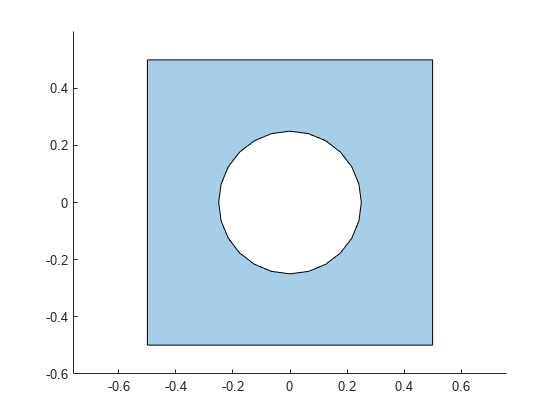
Create a triangulation representation of this object.
tr = triangulation(pgon);
Create a geometry by using the triangulation data.
gm = fegeometry(tr)
gm =
fegeometry with properties:
NumCells: 0
NumFaces: 1
NumEdges: 5
NumVertices: 5
Vertices: [5×3 double]
Mesh: [1×1 FEMesh]
Plot the geometry.
pdegplot(gm);
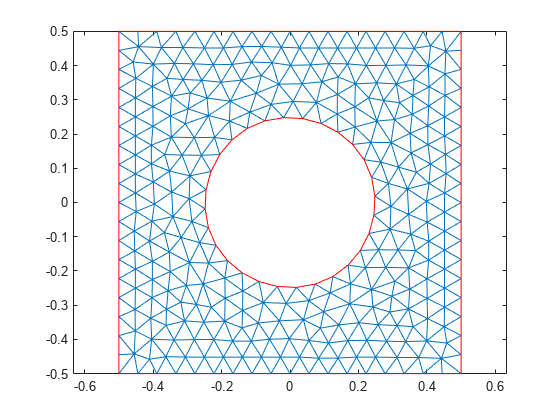
Because the triangulation data results in a low-quality linear mesh, generate a new finer mesh for further analysis.
gm = generateMesh(gm); gm.Mesh
ans =
FEMesh with properties:
Nodes: [2×1244 double]
Elements: [6×572 double]
MaxElementSize: 0.0566
MinElementSize: 0.0283
MeshGradation: 1.5000
GeometricOrder: 'quadratic'
Plot the mesh.
pdemesh(gm);