var
Variance
Syntax
Description
V = var(A)A along the first array dimension whose size
does not equal 1. By default, the variance is normalized by N-1,
where N is the number of observations.
If
Ais a vector of observations, thenVis a scalar.If
Ais a matrix whose columns are random variables and whose rows are observations, thenVis a row vector containing the variance corresponding to each column.If
Ais a multidimensional array, thenvar(A)operates along the first array dimension whose size does not equal 1, treating the elements as vectors. The size ofVin this dimension becomes1, while the sizes of all other dimensions are the same as inA.If
Ais a scalar, thenVis0.If
Ais a0-by-0empty array, thenVisNaN.If
Ais a table or timetable, thenvar(A)returns a one-row table containing the variance of each variable. (since R2023a)
V = var(A,w)w = 0 (default), the variance
is normalized by N-1, where N is the number of
observations. When w = 1, the variance is normalized by the
number of observations. w can also be a weight vector containing
nonnegative elements. In this case, the length of w must equal
the length of the dimension over which var is operating.
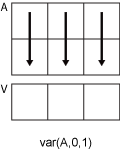
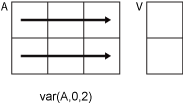
V = var(A,w,vecdim)vecdim when w is 0 or 1. For example, if
A is a matrix, then var(A,0,[1 2]) returns
the variance over all elements in A because every element of a
matrix is contained in the array slice defined by dimensions 1 and 2.
[
also returns the mean of the elements of V,M] = var(___)A used to calculate the
variance. If V is the weighted
variance, then M is the weighted
mean.