movvar
Moving variance
Syntax
Description
M = movvar( returns the
local A,k)k-point variance values, where
each variance is calculated over a sliding window of length k
across neighboring elements of A. When k is
odd, the window is centered about the element in the current position. When
k is even, the window is centered about the current and
previous elements. The window size is automatically truncated at the endpoints when
there are not enough elements to fill the window. When the window is truncated, the
variance is taken over only the elements that fill the window. M
is the same size as A.
If
Ais a vector, thenmovvaroperates along the length of the vectorA.If
Ais a multidimensional array, thenmovvaroperates along the first dimension ofAwhose size does not equal 1.If
Ais a table or timetable, thenmovvaroperates along the variables ofA. (since R2025a)
M = movvar(___, specifies
a normalization factor for any of the previous syntaxes. When w)w
= 0 (default), M is normalized by k-1 for
window length k. When w = 1, M is
normalized by k.
M = movvar(___,
specifies the dimension of w,dim)A to operate along for any of the
previous syntaxes. Always specify the weight w from the previous
syntax when specifying dim. For example, if A
is a matrix, then movvar(A,k,0,2) operates along the columns of
A, computing the k-element sliding
variance for each row. The normalization factor is the default,
k-1.
M = movvar(___, specifies
whether to include or omit nanflag)NaN values in A.
For example, movvar(A,k,"omitnan") ignores NaN
values when computing each variance. By default, movvar
includes NaN values.
M = movvar(___, specifies
additional parameters for the variance using one or more name-value pair arguments.
For example, if Name,Value)x is a vector of time values, then
movvar(A,k,"SamplePoints",x) computes the moving variance
relative to the times in x.
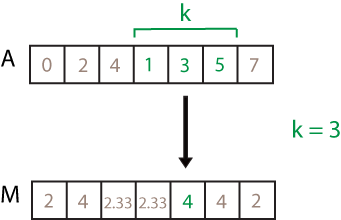
![movvar(A,[2 1]) computation. The elements in the sample window are 4, 1, 3, and 5, so the resulting local variance is 2.92.](movvar_windowing.png)