Create and Use Code Generation Reports
HDL Coder™ generates and displays an HTML code generation report when you generate HDL code from a Simulink® model that has at least one of the report configuration parameters enabled. The report contains information about the generated code such as:
Resource utilization estimates
Timing estimates
The impact of HDL Coder optimizations
Links tracing code to Simulink blocks
Customize the code generation reports by using the model configuration parameters in the HDL Code Generation > Report settings of the Configuration Parameters dialog box.
Generate Reports
These tables list the sections you can add to your code generation reports. HDL Coder generates the Summary, Clock Summary, and Code Interface Report sections by default.
| Report Section | Description | Configuration Parameter | Dependencies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Summary | Contains information about the model, design under test (DUT), date of code generation, and non-default HDL Coder settings. | Enable at least one of the parameters in HDL Code Generation > Report section of the Configuration Parameters dialog box. | In the HDL Code Generation > Global Settings settings, enable Generate HDL code. |
| Clock Summary | Contains information about the:
The report also displays information based on the number of clocks in the model, including:
For more information, see Using Multiple Clocks in HDL Coder. | ||
| Code Interface report | Lists the names, data types, and bit lengths of the input and output ports to the DUT. The report displays links to each input port and output port in your Simulink model. |
Timing and Area Reports
| Report Section | Description | Configuration Parameter | Dependencies |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-level Resource Report | Summarizes the adders, subtractors, multipliers, registers, and other resources the DUT consumes. | Generate resource utilization report | In the HDL Code Generation > Global Settings settings, enable Generate HDL code. |
| Target-specific Report | Shows the resource utilization report when you generate target-specific code with an FPGA floating-point library mapping. |
| |
| Native Floating-Point Resource Report | Lists the floating-point operators that your Simulink blocks map to. |
| |
| Critical Path Estimation | Estimates the critical path and the propagation delay along the path. This section estimates the maximum frequency the DUT can run at. | Generate high-level timing critical path report |
|
Optimization Reports
| Report Section | Description | Configuration Parameter | Dependencies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delay Balancing | Provides detailed information on the:
For more information, see Delay Balancing Report. | Generate optimization report |
|
| Hierarchy Flattening | Displays the hierarchy flattening status, subsystems that
have FlattenHierarchy set to
on or
off, and the inline HDL files.
For more information, see Hierarchy Flattening Report. | ||
| Code Reuse | Summarizes where HDL Coder reused generated subsystem code. | ||
| Target Code Generation | Displays target device summary and target mapping status when the generated code uses floating-point types. | ||
| Streaming and Sharing | Summarizes information about the subsystems you specify sharing or streaming for. For more information, see Streaming Report and Resource Sharing Report. | ||
| Clock Rate Pipelining | Details how clock-rate pipelining performed in your model. For more information, see Clock-Rate Pipelining Report. | ||
| Distributed Pipelining | Displays comparative listings of the registers before and after you apply the distributed pipelining transform. For more information, see Distributed Pipelining Report. | ||
| Adaptive Pipelining | Displays the status of the adaptive pipelining optimization, blocks for which pipeline registers are inserted, and the number of pipeline registers. For more information, see Adaptive Pipelining Report. | ||
| Frame to Sample | Contains information about the:
|
Traceability Report and Model Web View
| Report Section | Description | Configuration Parameter | Dependencies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traceability Report | Links lines of the generated code to the corresponding blocks in the Simulink model when possible. Enable this report to use the code view in Simulink to trace between the code and model. For more information, see Navigate Between Simulink Model and HDL Code by Using Traceability. | Generate traceability report | In the HDL Code Generation > Global Settings settings, enable Generate HDL code. |
| Model Web View | Displays the Simulink model in the HTML code generation report. The model web view requires Simulink Report Generator™. For more information, see Generate Web View of Model in Code Generation Report. | Generate model Web view | In the HDL Code Generation > Global Settings settings, enable Generate HDL code. |
Alternatively, you can programmatically customize the code generation reports
by setting the properties in this table on or
off. Use hdlset_param or makehdl to set these properties.
| Report Section | makehdl Property | Dependencies |
|---|---|---|
| High-level Resource Report | ResourceReport | Set GenerateHDLCode to
on. |
| Target-specific Report | Set GenerateHDLCode to
on, and set
FloatingPointTargetConfiguration to a
vendor-specific floating point library. | |
| Native Floating-Point Resource Report | Set GenerateHDLCode and
UseFloatingPoint to
on. | |
| Critical Path Estimation | CriticalPathEstimation | Set GenerateHDLCode and
GenerateModel to
on. |
| Delay Balancing | OptimizationReport | Set GenerateHDLCode and
GenerateModel to
on. |
| Hierarchy Flattening | ||
| Code Reuse | ||
| Target Code Generation | ||
| Streaming and Sharing | ||
| Clock Rate Pipelining | ||
| Distributed Pipelining | ||
| Adaptive Pipelining | ||
| Frame to sample | ||
| Traceability Report | Traceability | Set GenerateHDLCode to
on. |
| Model Web View | HDLGenerateWebView | Set GenerateHDLCode to
on. |
Navigate the Code Generation Report
You can navigate to the code generation report from the Simulink model. For example, suppose you generate a report for the model
hdlcoderFocCurrentFixptHdl.slx. Open the model by using this
command:
openExample('hdlcoder/ClockRatePipeliningExample','supportingFile','hdlcoderFocCurrentFixptHdl.slx')
In this model, the configuration parameters Generate resource
utilization reports and Generate optimization
reports are enabled. Build HDL code from the subsystem
FOC_Current_Control by using this command:
makehdl('hdlcoderFocCurrentFixptHdl/FOC_Current_Control')After code generation, the report opens automatically. You can also open it
manually by clicking the link to
hdlcoderFoxCurrentFixptHdl_codegen_rpt.html in the
MATLAB® Command Window, or by selecting Open Report
in the HDL Coder app.
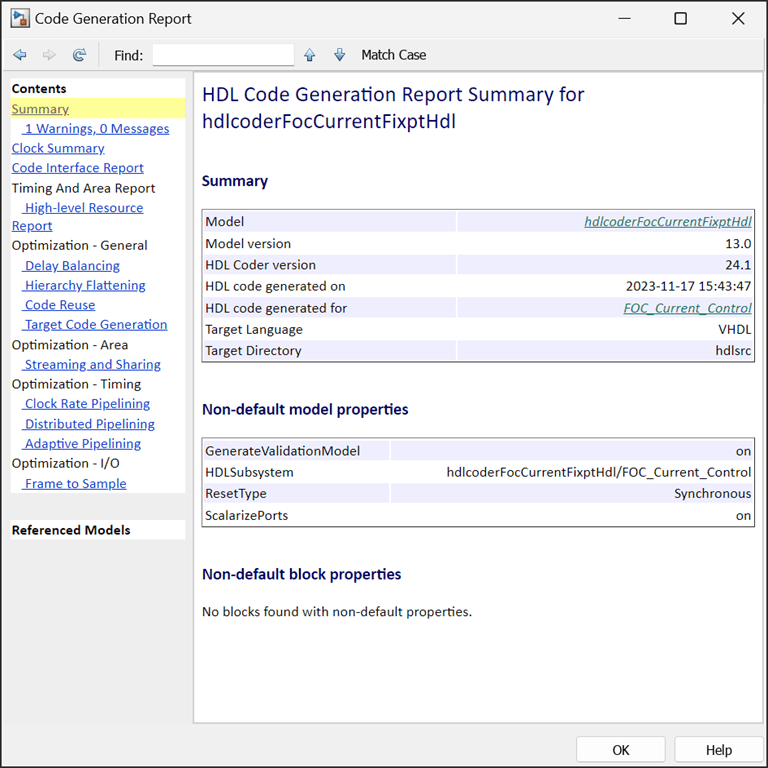
The code generation report for the model
hdlcoderFoxCurrentFixptHdl_codegen_rpt.html includes:
A Content pane with links to different sections of the report.
A High-level Resource Report section that shows resource utilization of the generated code.
Additional sections on clock-rate pipelining, distributed pipelining, and other optimizations applied by HDL Coder.
To navigate the report, click the corresponding links in the Content pane to view different sections.
You can customize the reports to include only the sections you need. For example,
to add a Critical Path Estimation section, enable the
CriticalPathEstimation property,
enter:
makehdl('hdlcoderFocCurrentFixptHdl/FOC_Current_Control', 'CriticalPathEstimation', 'on')
hdlcoderFocCurrentFixptHdl.slx with an added
Critical Path Estimation section.
You can also customize how the generated code appears in the report using the
configuration parameters button ![]() . In the Display
pane, you can apply the following filters:
. In the Display
pane, you can apply the following filters:
To include comments and empty lines in the generated code, select the Show comments and empty lines parameter. The report displays comments and empty lines in the code.
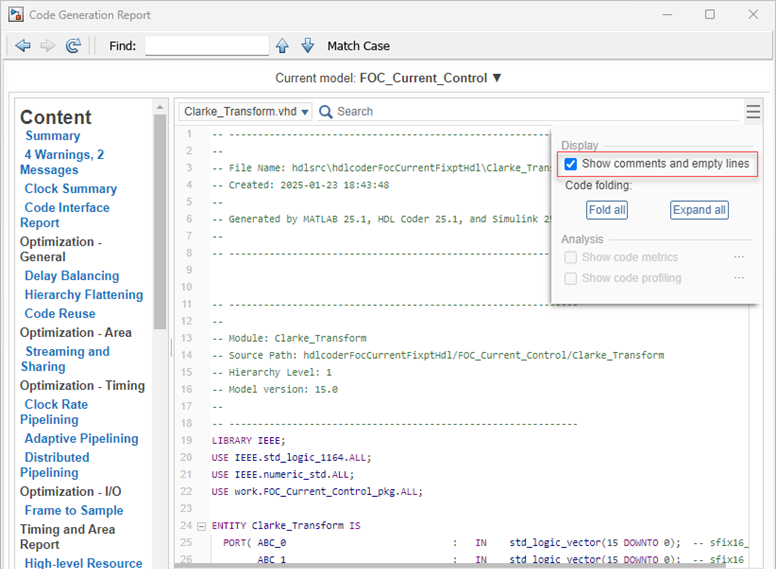
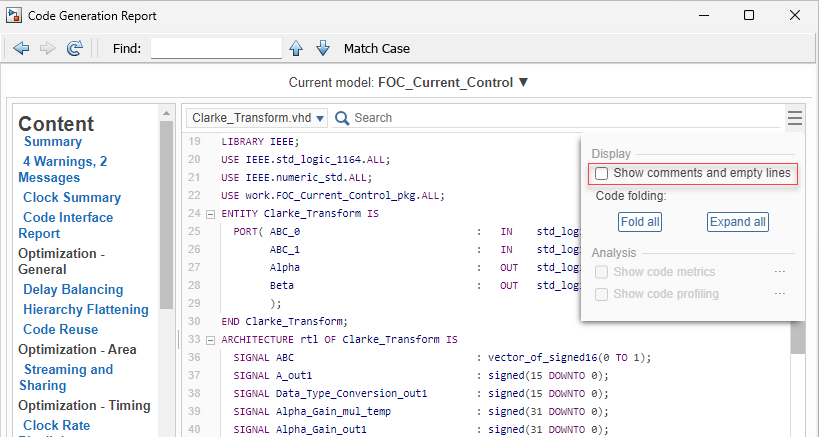
To exclude comments and empty lines from the generated code, clear the Show comments and empty lines parameter. The report hides comments and empty lines.
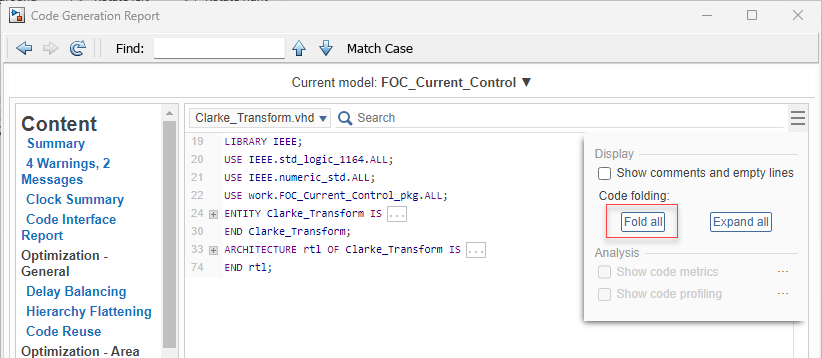
To collapse all code sections in the generated code, click the Fold all button. The report shows all code sections in a collapsed state.
To expand all code sections in the generated code, click the Expand all button. The report shows all code sections expanded.
Use Code Generation Reports to Evaluate Code Before Synthesis
When you select the Generate resource utilization report or Generate high-level timing critical path report parameters, HDL Coder adds a Timing and Area Report section to the code generation report. You can use the timing and area report to evaluate whether the generated code can run with the frequency and resources your hardware requires.
Assess the Area of the Generated Code
The Summary section of the high-level resource report estimates the usage of:
Multipliers
Adders and subtractors
1-bit registers
RAMs
Multiplexors
I/O bits
Static shift operators
Dynamic shift operators
Use the resource report to track and reduce the estimated resource usage of the generated HDL code.
The High-Level Resource Report section also contains the following sections:
The Registers section displays the total number of 1-bit registers. The total is the sum of products over the bit widths of the registers and their frequency of occurrence.
Static Shift Operators and Dynamic Shift operators sections. A static shift is a shift value that is a mask constant. The shift logic does not change. A dynamic shift is a shift value specified as an input to a block. Dynamic shifts are more resource expensive than static shifts.
If the resource usage in the reports exceeds what is available on your hardware, consider applying area optimizations such as resource sharing and streaming to the DUT. Resource sharing and streaming optimize the generated code to use shared hardware resources that reduce the area. For more information, see Area Optimizations.
Assess the Timing of the Generated Code
The Critical Path Estimation section includes an estimate
of the combinatorial path in the model with the longest timing delay.
HDL Coder uses target-specific timing databases to estimate the critical
path of the generated code. If HDL Coder does not have a timing database for your target configuration,
generate a target-specific timing database using the genhdltdb
function. For more information, see Critical Path Estimation Without Running Synthesis.
The propagation delay of the critical path limits the frequency that the
generated code can run at on the target. If the estimated delay of the critical
path estimation is too long for the DUT to run at your target frequency,
consider optimizing the estimated critical path. The critical path estimation
links to a criticalPathEstimated script that highlights the
critical path in the generated model. Use this script to identify the estimated
critical path in your generated model, and then add delays in your original
Simulink model to break the critical path.
Additionally, HDL Coder optimizations can optimize the timing of the critical path and increase the maximum frequency of the DUT. For more information, see Speed Optimizations.
Assess the Impact of Optimizations
If the reported timing or area usage do not meet requirements, you can optimize the original model and generate code from it again before synthesis. After generating code, use optimization reports to understand how HDL Coder optimized the DUT or why it did not apply specific optimizations. Use the optimization reports to identify obstacles to optimization and improve the timing and area of the DUT.