GroundSurface
Description
The GroundSurface object defines a ground
surface object belonging to a trackingScenario
object. You can use the GroundSurface object to model
terrain in a scenario and query the occlusion status of line-of-sight between two points in
the scenario.
Creation
Create GroundSurface objects using the groundSurface
object function of the trackingScenario
object.
Properties
Terrain data for the surface, specified as an M-by-N real-valued matrix, or a string scalar specifying a Digital Terrain Elevation Data (DTED) file name.
M-by-N real-valued matrix — The matrix values represent the height data of an area defined by the
Boundaryproperty of the ground surface object. The object extends the height data in the matrix to the area. The object automatically fills heights of unspecified points using linear interpolation. M and N must both be greater than 3.String scalar or character vector specifying DTED file name — To use this option, you must specify the
IsEarthCenteredproperty of the tracking scenario astrue. In this case, the object specifies the terrain heights for the area using those defined in the DTED file. The ground surface object automatically fills unspecified data in the DTED file using linear interpolation. If you want to use only a part of the terrain defined in the DTED file, specify theBoundaryproperty as your desired subset of the terrain area defined in the DTED file. Otherwise, specify theBoundaryproperty as the whole area defined in the DTED file.
Data Types: single | double | char
Boundary of the surface, specified as a 2-by-2 matrix of real values with the form
[xmin xmax; ymin ymax]. When the
IsEarthCentered property of tracking scenario object is
specified as:
false— Specifyxmin,xmax,yminymax, in meters, as Cartesian coordinates in the reference frame of the scenario, wherexmin<xmax, andymin<ymaxtrue— Specifyxminandxmaxas the minimum and maximum latitudes of the geodetic frame in degrees, wherexmin<xmax. Specifyyminandymaxas the minimum and maximum longitudes of the geodetic frame in degrees. Ifymax<ymin, the object wrapsymaxtoymax+360.
Data Types: single | double
Reference height of the terrain data, specified as a scalar in meters. Specify the terrain data relative to this reference height.
Data Types: single | double
Object Functions
Examples
Create a mesh grid that spans from -1000 meters to 1000 meters in both the x- and y-directions.
[x,y] = meshgrid(linspace(-1000,1000,500));
Specify the height for each mesh grid point.
z = 200*cos(x*pi/2000).*cos(y*pi/2000);
Create a tracking scenario and add a ground surface object to the tracking scenario. Specify the boundary of the surface area.
scene = trackingScenario; surface = groundSurface(scene,Terrain=z,Boundary=[-1e3 1e3; -1e3 1e3])
surface =
GroundSurface with properties:
Terrain: [500×500 double]
ReferenceHeight: 0
Boundary: [2×2 double]
Note that the SurfaceManager property of the tracking scenario now contains the created GroundSurface object.
manager = scene.SurfaceManager
manager =
SurfaceManager with properties:
UseOcclusion: 1
Surfaces: [1×1 fusion.scenario.GroundSurface]
manager.Surfaces
ans =
GroundSurface with properties:
Terrain: [500×500 double]
ReferenceHeight: 0
Boundary: [2×2 double]
Visualize the surface using the helperGetTerrainMap helper function, attached to this example.
xSamples = linspace(-1e3,1e3,100); ySamples = linspace(-1e3,1e3,100); helperGetTerrainMap(surface,xSamples,ySamples); xlabel("x (m)") ylabel("y (m)") zlabel("Height (m)")
![]()
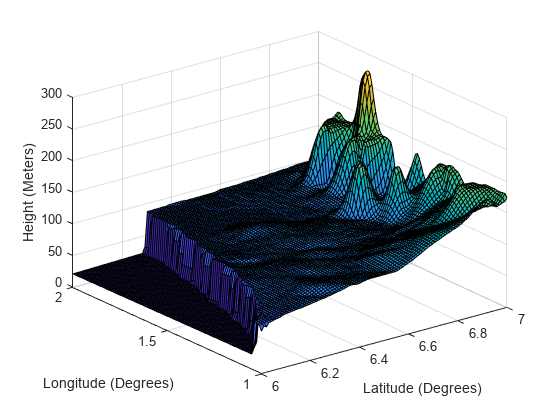
Create a tracking scenario and specify its IsEarthCentered property as true.
scene = trackingScenario(IsEarthCentered=true);
Add a ground surface based on a DTED file, covering from 6 to 7 degrees in latitude and from 1 to 2 degrees in longitude.
terrain = "n06.dt0"; boundary = [6 7; % Latitude in degrees 1 2]; % Longitude in degrees surface = groundSurface(scene,Terrain=terrain,Boundary=boundary);
Sample the area using a 100-by-100 grid map.
samples = 100; latitudes = linspace(6,7,samples); longitudes = linspace(1,2,samples); positions = [latitudes; longitudes];
Plot the terrain using the helperGetTerrrainMap helper function, attached to this example.
helperGetTerrainMap(surface,latitudes,longitudes); xlabel("Latitude (Degrees)"); ylabel("Longitude (Degrees)"); zlabel("Height (Meters)");
Create a tracking scenario object.
scene = trackingScenario;
Specify the terrain as magic(4) and define the boundary of the terrain as a square.
terrain = magic(4)
terrain = 4×4
16 2 3 13
5 11 10 8
9 7 6 12
4 14 15 1
boundary = [0 100; 0 100];
Create the ground surface and add it to the scenario.
surface = groundSurface(scene,Terrain=terrain,Boundary=boundary)
surface =
GroundSurface with properties:
Terrain: [4×4 double]
ReferenceHeight: 0
Boundary: [2×2 double]
Get the heights of the surface at the center and its four corners.
h0 = height(surface,[50 50]')
h0 = 8.5000
h1 = height(surface,[0 0]')
h1 = 16
h2 = height(surface,[100 0]')
h2 = 13
h3 = height(surface,[0 100]')
h3 = 4
h4 = height(surface,[100 100]')
h4 = 1
Create a tracking scenario object.
scene = trackingScenario;
Specify the terrain and define the boundary of the terrain as a square centered at the origin.
terrrain =[0 10 0;
0 10 0;
0 10 0];
boundary = [-100 100; -100 100];Create the ground surface and add it to the scenario.
surface = groundSurface(scene,Terrain=terrrain,Boundary=boundary)
surface =
GroundSurface with properties:
Terrain: [3×3 double]
ReferenceHeight: 0
Boundary: [2×2 double]
Query the occlusion status of the line-of-sight vector between the corner point (–100, –100, 0) and the other corner point (100, 100, 20). The ground surface occludes the line-of-sight.
occlusion(surface,[-100 -100 0],[100 100 20])
ans = logical
0
Raise the height of the first corner point. Now the ground surface no longer occludes the line-of-sight.
occlusion(surface,[-100 -100 10],[100 100 20])
ans = logical
0
Version History
Introduced in R2022a
See Also
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom (English)