Creating an IRFunctionCurve Object
To create an IRFunctionCurve object, see the following
options:
Fitting IRFunctionCurve Object Using a Function Handle
You can use IRFunctionCurve with a MATLAB® function handle to define an interest-rate curve. For more information
on defining a function handle, see the MATLAB Programming Fundamentals documentation.
Example
This example uses a FunctionHandle argument with a value
@(t) t.^2 to create an interest-rate curve.
rr = IRFunctionCurve('Zero',today,@(t) t.^2)
rr =
Properties:
FunctionHandle: @(t)t.^2
Type: 'Zero'
Settle: 733600
Compounding: 2
Basis: 0Fitting IRFunctionCurve Object Using Nelson-Siegel Method
This example shows how to use the function, fitNelsonSiegel, for the Nelson-Siegel model that fits the empirical form of the yield curve with a prespecified functional form of the spot rates which is a function of the time to maturity of the bonds.
The Nelson-Siegel model represents a dynamic three-factor model: level, slope, and curvature. However, the Nelson-Siegel factors are unobserved, or latent, which allows for measurement error, and the associated loadings have economic restrictions (forward rates are always positive, and the discount factor approaches zero as maturity increases). For more information, see "Zero-Coupon Yield Curves: Technical Documentation," BIS Papers, Bank for International Settlements, Number 25, October 2005.
This example uses IRFunctionCurve to model the default-free term structure of interest rates in the United Kingdom.
Load the data.
load ukdata20080430Convert repo rates to be equivalent zero-coupon bonds.
RepoCouponRate = repmat(0,size(RepoRates)); RepoPrice = bndprice(RepoRates, RepoCouponRate, RepoSettle, RepoMaturity);
Aggregate the data.
Settle = [RepoSettle;BondSettle]; Maturity = [RepoMaturity;BondMaturity]; CleanPrice = [RepoPrice;BondCleanPrice]; CouponRate = [RepoCouponRate;BondCouponRate]; Instruments = [Settle Maturity CleanPrice CouponRate]; InstrumentPeriod = [repmat(0,6,1);repmat(2,31,1)]; CurveSettle = datetime(2008,4,30);
The IRFunctionCurve object provides the capability to fit a Nelson-Siegel curve to observed market data with the fitNelsonSiegel function. The fitting is done by calling the function lsqnonlin. The fitNelsonSiegel function has required inputs of Type, Settle, and a matrix of instrument data.
NSModel = IRFunctionCurve.fitNelsonSiegel('Zero',CurveSettle,... Instruments,'Compounding',-1,'InstrumentPeriod',InstrumentPeriod);
Plot the Nelson-Siegel interest-rate curve for forward rates.
PlottingDates = CurveSettle+20:30:CurveSettle+365*25;
TimeToMaturity = yearfrac(CurveSettle,PlottingDates);
NSForwardRates = getForwardRates(NSModel, PlottingDates);
plot(TimeToMaturity,NSForwardRates)
title('Nelson Siegel Model of UK Instantaneous Nominal Forward Curve')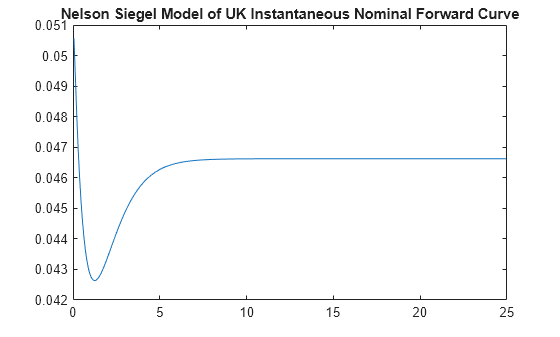
Fitting IRFunctionCurve Object Using Svensson Method
This example shows how to use the function, fitSvensson, for the Svensson model to improve the flexibility of the curves and the fit for a Nelson-Siegel model. In 1994, Svensson extended Nelson and Siegel's function by adding a further term that allows for a second "hump." The extra precision is achieved at the cost of adding two more parameters, amd , which have to be estimated.
This example of uses the fitSvensson function and an IRFitOptions structure, defined using IRFitOptions. Thus, you must specify FitType, InitialGuess, UpperBound, LowerBound, and the OptOptions optimization parameters for lsqnonlin.
Load the data.
load ukdata20080430Convert repo rates to be equivalent zero coupon bonds.
RepoCouponRate = repmat(0,size(RepoRates)); RepoPrice = bndprice(RepoRates, RepoCouponRate, RepoSettle, RepoMaturity);
Aggregate the data.
Settle = [RepoSettle;BondSettle]; Maturity = [RepoMaturity;BondMaturity]; CleanPrice = [RepoPrice;BondCleanPrice]; CouponRate = [RepoCouponRate;BondCouponRate]; Instruments = [Settle Maturity CleanPrice CouponRate]; InstrumentPeriod = [repmat(0,6,1);repmat(2,31,1)]; CurveSettle = datetime(2008,4,30);
Define OptOptions for IRFitOptions.
OptOptions = optimoptions('lsqnonlin','MaxFunEvals',1000); fIRFitOptions = IRFitOptions([5.82 -2.55 -.87 0.45 3.9 0.44],... 'FitType','durationweightedprice','OptOptions',OptOptions,... 'LowerBound',[0 -Inf -Inf -Inf 0 0],'UpperBound',[Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf]);
Fit the interest-rate curve using a Svensson model.
SvenssonModel = IRFunctionCurve.fitSvensson('Zero',CurveSettle,... Instruments,'IRFitOptions', fIRFitOptions, 'Compounding',-1,... 'InstrumentPeriod',InstrumentPeriod)
Local minimum possible. lsqnonlin stopped because the final change in the sum of squares relative to its initial value is less than the value of the function tolerance. <stopping criteria details>
SvenssonModel = Type: Zero Settle: 733528 (30-Apr-2008) Compounding: -1 Basis: 0 (actual/actual)
The status message, output from lsqnonlin, indicates that the optimization to find parameters for the Svensson equation terminated successfully.
Plot the Svensson interest-rate curve for forward rates.
PlottingDates = CurveSettle+20:30:CurveSettle+365*25;
TimeToMaturity = yearfrac(CurveSettle,PlottingDates);
SvenssonForwardRates = getForwardRates(SvenssonModel, PlottingDates);
plot(TimeToMaturity,SvenssonForwardRates)
title('Svensson Model of UK Instantaneous Nominal Forward Curve')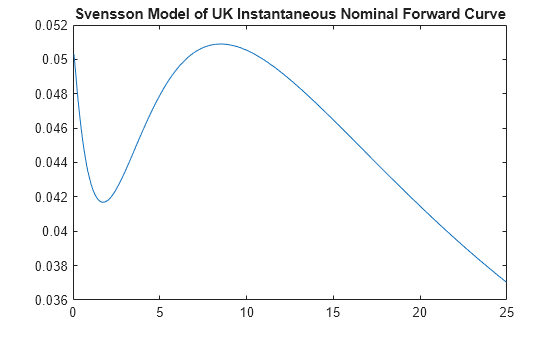
Fitting IRFunctionCurve Object Using Smoothing Spline Method
This example shows how to use fitSmoothingSpline to model the term structure with a spline, where the term structure represents the forward curve with a cubic spline.
Note: You must have a license for Curve Fitting Toolbox™ software to use the fitSmoothingSpline function.
The IRFunctionCurve object is used to fit a smoothing spline representation of the forward curve with a penalty function. Required inputs for fitSmoothingSpline are Type, Settle, the matrix of Instruments, and Lambdafun, a function handle containing the penalty function.
Load the data.
load ukdata20080430Convert repo rates to be equivalent zero coupon bonds.
RepoCouponRate = repmat(0,size(RepoRates)); RepoPrice = bndprice(RepoRates, RepoCouponRate, RepoSettle, RepoMaturity);
Aggregate the data.
Settle = [RepoSettle;BondSettle];
Maturity = [RepoMaturity;BondMaturity];
CleanPrice = [RepoPrice;BondCleanPrice];
CouponRate = [RepoCouponRate;BondCouponRate];
Instruments = [Settle Maturity CleanPrice CouponRate];
InstrumentPeriod = [repmat(0,6,1);repmat(2,31,1)];
CurveSettle = datenum('30-Apr-2008');Choose parameters for Lambdafun.
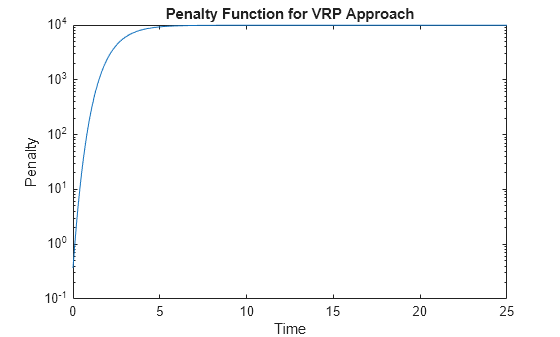
L = 9.2; S = -1; mu = 1;
Define the Lambdafun penalty function.
lambdafun = @(t) exp(L - (L-S)*exp(-t/mu)); t = 0:.1:25; y = lambdafun(t); figure semilogy(t,y); title('Penalty Function for VRP Approach') ylabel('Penalty') xlabel('Time')
Use the fitSmoothingSpline function to fit the interest-rate curve and model the Lambdafun penalty function.
VRPModel = IRFunctionCurve.fitSmoothingSpline('Forward',CurveSettle, ... Instruments,lambdafun,'Compounding',-1, 'InstrumentPeriod',InstrumentPeriod);
Plot the smoothing spline interest-rate curve for forward rates.
PlottingDates = CurveSettle+20:30:CurveSettle+365*25;
TimeToMaturity = yearfrac(CurveSettle,PlottingDates);
VRPForwardRates = getForwardRates(VRPModel, PlottingDates);
plot(TimeToMaturity,VRPForwardRates)
title('Smoothing Spline Model of UK Instantaneous Nominal Forward Curve')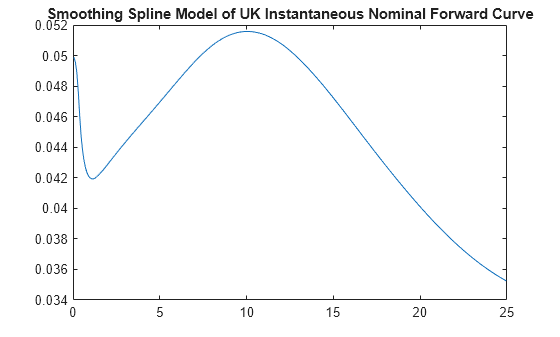
Using fitFunction to Create Custom Fitting Function
When using an IRFunctionCurve object, you can
create a custom fitting function with the fitFunction function. To use
fitFunction, you must define a
FunctionHandle. In addition, you must also use IRFitOptions to define an
IRFitOptions object to support an
InitialGuess for the parameters of the curve function.
Create Custom Fitting Function
This example shows how to use fitFunction with a FunctionHandle and an IRFitOptions object.
Define the data.
Settle = repmat(datenum('30-Apr-2008'),[6 1]); Maturity = [datenum('07-Mar-2009');datenum('07-Mar-2011'); ... datenum('07-Mar-2013');datenum('07-Sep-2016'); ... datenum('07-Mar-2025');datenum('07-Mar-2036')]; CleanPrice = [100.1;100.1;100.8;96.6;103.3;96.3]; CouponRate = [0.0400;0.0425;0.0450;0.0400;0.0500;0.0425]; Instruments = [Settle Maturity CleanPrice CouponRate]; CurveSettle = datenum('30-Apr-2008');
Define the FunctionHandle.
functionHandle = @(t,theta) polyval(theta,t);
Define the OptOptions for IRFitOptions.
OptOptions = optimoptions('lsqnonlin','display','iter');
Define fitFunction.
CustomModel = IRFunctionCurve.fitFunction('Zero', CurveSettle, ... functionHandle,Instruments, IRFitOptions([.05 .05 .05],'FitType','price', ... 'OptOptions',OptOptions));
Norm of First-order
Iteration Func-count Resnorm step optimality
0 4 38036.7 4.92e+04
1 8 38036.7 10 4.92e+04
2 12 38036.7 2.5 4.92e+04
3 16 38036.7 0.625 4.92e+04
4 20 38036.7 0.15625 4.92e+04
5 24 30741.5 0.0390625 1.72e+05
6 28 30741.5 0.078125 1.72e+05
7 32 30741.5 0.0195312 1.72e+05
8 36 28713.6 0.00488281 2.33e+05
9 40 20323.3 0.00976562 9.47e+05
10 44 20323.3 0.0195312 9.47e+05
11 48 20323.3 0.00488281 9.47e+05
12 52 20323.3 0.0012207 9.47e+05
13 56 19698.8 0.000305176 1.08e+06
14 60 17493 0.000610352 7e+06
15 64 17493 0.0012207 7e+06
16 68 17493 0.000305176 7e+06
17 72 15455.1 7.62939e-05 2.25e+07
18 76 15455.1 0.000177499 2.25e+07
19 80 13317.1 3.8147e-05 3.18e+07
20 84 12865.3 7.62939e-05 7.83e+07
21 88 11779.8 7.62939e-05 7.58e+06
22 92 11747.6 0.000152588 1.45e+05
23 96 11720.9 0.000305176 2.33e+05
24 100 11667.2 0.000610352 1.48e+05
25 104 11558.6 0.0012207 3.55e+05
26 108 11335.5 0.00244141 1.57e+05
27 112 10863.8 0.00488281 6.36e+05
28 116 9797.14 0.00976562 2.53e+05
29 120 6882.83 0.0195312 9.18e+05
30 124 6882.83 0.0373993 9.18e+05
31 128 3218.45 0.00934981 1.96e+06
32 132 612.703 0.0186996 3.01e+06
33 136 13.0998 0.0253882 3.05e+06
34 140 0.0762922 0.00154002 5.05e+04
35 144 0.0731652 3.61103e-06 29.9
36 148 0.0731652 6.32308e-08 0.063
Local minimum possible.
lsqnonlin stopped because the final change in the sum of squares relative to
its initial value is less than the value of the function tolerance.
<stopping criteria details>
Plot the custom function that is defined using fitFunction.
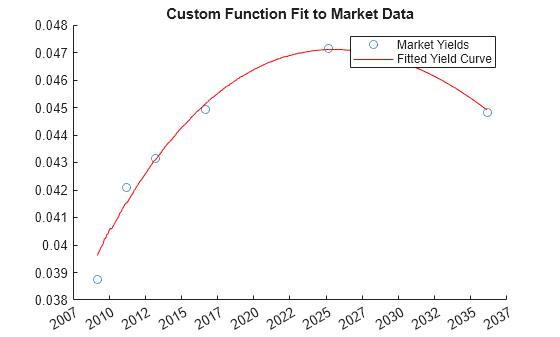
Yields = bndyield(CleanPrice,CouponRate,Settle(1),Maturity); scatter(Maturity,Yields); PlottingPoints = min(Maturity):30:max(Maturity); hold on; plot(PlottingPoints, getParYields(CustomModel, PlottingPoints),'r'); datetick legend('Market Yields','Fitted Yield Curve') title('Custom Function Fit to Market Data')
See Also
IRBootstrapOptions | IRDataCurve | IRFunctionCurve | IRFitOptions
Topics
- Creating Interest-Rate Curve Objects
- Bootstrapping a Swap Curve
- Dual Curve Bootstrapping
- Creating an IRDataCurve Object
- Converting an IRDataCurve or IRFunctionCurve Object
- Analyze Inflation-Indexed Instruments
- Fitting Interest-Rate Curve Functions
- Interest-Rate Curve Objects and Workflow
- Mapping Financial Instruments Toolbox Curve Functions to Object-Based Framework