Design a Wideband Antenna for Applications in 8-12 GHz Band
This example shows how to design and analyze a compact microstrip patch antenna suitable for a variety of applications in the 8-12 GHz frequency band. The design incorporates ground plane modifications and feedline adjustments to achieve desired performance characteristics across the specified frequency range. This example is particularly useful for engineers and researchers working on communication systems, radar, and RF sensing applications.
Design Antenna Dimensions
Define dimensions of the ground plane and main patch. The ground plane acts as a reflector for the patch antenna.
gp_L = 19e-3; gp_W = 9.75e-3; patch_L = 13e-3; patch_W = 14e-3;
Create Patch And Feed Design
This section covers the design of the feed mechanism and the main radiating patch, crucial for efficient antenna performance. Use the antenna.Rectangle and antenna.Polygon objects to create radiating patch and feedline structure. The design of these structurs is crucial for efficient antenna performance.
p = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[0 0],Length=patch_L,Width=patch_W);
feed = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[0 -11.75e-3],Length=2.6e-3,Width=9.5e-3);
a = antenna.Polygon(Vertices=[-6.5e-3 7e-3 0; -1.8e-3 7e-3 0; -6.5e-3 2.6e-3 0]);
b = antenna.Polygon(Vertices=[-1.3e-3 -7e-3 0; -6.5e-3 -7e-3 0; -6.5e-3 -2.6e-3 0]);
c = antenna.Polygon(Vertices=[6.5e-3 7e-3 0; 1.8e-3 7e-3 0; 6.5e-3 2.6e-3 0]);
d = antenna.Polygon(Vertices=[6.5e-3 -2.6e-3 0; 6.5e-3 -7e-3 0; 1.3e-3 -7e-3 0]);
t = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[0 1.75e-3],Length=4e-3,Width=12e-3);
x = p + feed - a - b - c - d - t;
figure(1);
show(x)
title('Patch Structure');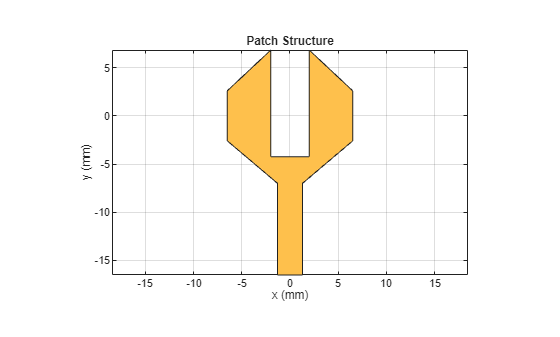
Defected Ground Structure
Modify the ground plane to create a defected ground structure (DGS), which helps in improving the bandwidth and impedance matching.
g1 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[0 -11.625e-3],Length=gp_L,Width=gp_W); g2 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[-7.6e-3 -11.625e-3 ],Length=3.8e-3,Width=9.75e-3); g3 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[-4.875e-3 -16.125e-3],Length=6e-3,Width=0.75e-3); g4 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[7.5e-3 -16.125e-3],Length=12e-3,Width=0.75e-3); g5 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[0 -10.35e-3],Length=2.6e-3,Width=7.2e-3); g6 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[0 -2.55e-3],Length=9.5e-3,Width=6e-3); gd = g1 - g2 - g3 - g4 - g5 + g6; figure(2) show(gd)
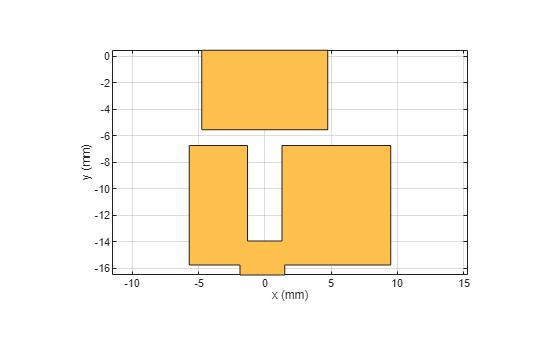
Trace and Stub Configuration
Create traces and stubs that form the radiating element and matching network of the antenna, respectively.
%E-shaped Stub s1 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[1.4e-3 2.025e-3],Length=0.4e-3,Width=12.55e-3); s2 =antenna.Rectangle(Center=[5.1e-3 8.1e-3],Length=7.8e-3,Width=0.4e-3); s3 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[8.8e-3 -3.95e-3],Length=0.4e-3,Width=24.5e-3); s4 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[5.55e-3 -16.0e-3],Length=6.9e-3,Width=0.4e-3); s5 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[2.3e-3 -15.35e-3],Length=0.4e-3,Width=1.7e-3); s6 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[5.25e-3 -14.7e-3],Length=5.51e-3,Width=0.4e-3); s7 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[7.8e-3 -14.05e-3],Length=0.4e-3,Width=1.7e-3); s8 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[4.85e-3 -13.4e-3],Length=5.5e-3,Width=0.4e-3); s9 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[2.3e-3 -12.675e-3],Length=0.4e-3,Width=1.85e-3); s10 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[4.9e-3 -11.95e-3],Length=4.9e-3,Width=0.4e-3); s11 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[7.15e-3 -10.975e-3],Length=0.4e-3,Width=2.35e-3); s12 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[4.55e-3 -10e-3],Length=4.9e-3,Width=0.4e-3); s13 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[2.3e-3 -9.15e-3],Length=0.4e-3,Width=2.1e-3); s14 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[4.8e-3 -8.3e-3],Length=5.4e-3,Width=0.4e-3); s15 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[7.3e-3 -0.55e-3],Length=0.4e-3,Width=15.2e-3); x1 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[8.4e-3,-1e-3],Length=0.4e-3,Width=4e-3); x2 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[8.4e-3,-10.25e-3],Length=0.4e-3,Width=3e-3); %G-shaped Stub l1 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[1.4e-3 -3.275e-3],Length=0.4e-3,Width=1.95e-3); l2 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[0.225e-3 -2.5e-3],Length=2.75e-3,Width=0.4e-3); l3 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[-1.35e-3 2.6e-3],Length=0.4e-3,Width=10.6e-3); l4 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[-5.175e-3 8.1e-3],Length=8.05e-3,Width=0.4e-3); l5 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[-9e-3 -3.9e-3],Length=0.4e-3,Width=24.4e-3); l6 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[-7.85e-3 -5.5e-3],Length=1.9e-3,Width=0.4e-3); l7 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[-5.85e-3 -16e-3],Length=6.7e-3,Width=0.4e-3); l8 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[-2.7e-3 -12.95e-3],Length=0.4e-3,Width=6.5e-3); l9 = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[-4.65e-3 -9.5e-3],Length=4.3e-3,Width=0.4e-3); %Radiating Patch with Stubs o = x + l1 + l2 + l3 + l4 + l5 + l6 + l7 + l8 + l9 + x1 + x2 + s1 + s2 + s3 +s4 + s5 + s6 + s7 + s8 + s9 + s10 + s11 + s12 + s13 + s14 + s15; figure(3) show(o)
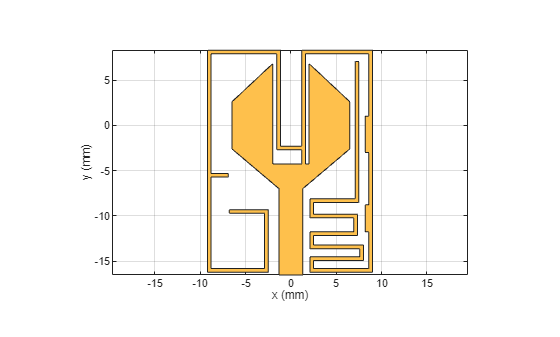
Place four ports of the MIMO orthogonal to each other in the top layer.
k = translate(o,[-18.6e-3,-11.5e-3,0]);
f1 = x + s1 + s2 + s3 + s4 + s5 + s6 + s7 + s8 + s9 + s10 + s11 + s12 + s13 + s14 + s15 + l1 + l2+ l3 +l4 + l5 + l6 + l7 + l8 + l9 + x1 + x2;
A1 = rotateZ(f1,90);
A = translate(A1,[11.5e-3,-18.6e-3,0]);
f2 = x + s1 + s2 + s3 + s4 + s5 + s6 + s7 + s8 + s9 + s10 + s11 + s12 + s13 + s14 + s15 + l1 + l2 + l3 + l4 + l5 + l6 + l7 + l8 + l9 + x1 + x2;
m1 = mirrorX(f2);
B = translate(m1,[18.6e-3,11.5e-3,0]);
f3 = x + s1 + s2 + s3 + s4 + s5 + s6 + s7 + s8 + s9 + s10 + s11 + s12 + s13 + s14 + s15 + l1 + l2 + l3 + l4 + l5 + l6 + l7 + l8+ l9 + x1 + x2;
m2 = mirrorX(f3);
C1 = rotateZ(m2,90);
C = translate(C1,[-11.5e-3,18.6e-3,0]);
patch = k+A+B+C;
figure(4);
show(patch)
title('Total Patch Structure');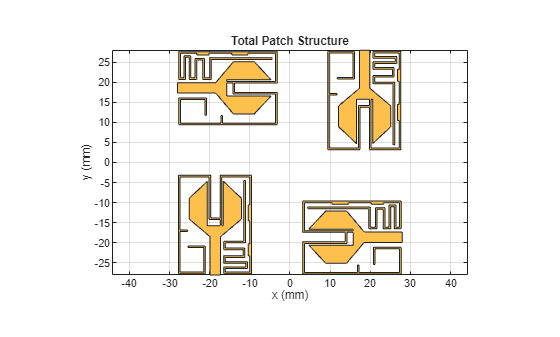
Place the individual ground planes of the MIMO orthogonal to each other.
r1 = mirrorY(gd);
r2 = translate(r1,[-18.5e-3,-11.5e-3,0]);
gd1 = g1 - g2 - g3 - g4 - g5 + g6;
r3 = mirrorY(gd1);
r4 = rotateZ(r3,90);
r5 = translate(r3,[11.5e-3,-18.5e-3,0]);
gd2 = g1 - g2 - g3 - g4 - g5 + g6;
r6 = rotateZ(gd2,180);
r7 = translate(r6,[18.5e-3,11.5e-3,0]);
gd3 = g1 - g2 - g3 - g4 -g5 + g6;
r8 = rotateZ(gd3,270);
r9 = translate(r8,[-11.5e-3,18.5e-3,0]);
ground = r2 + r5 + r7 + r9;
figure(5);
show(ground);
title('Antenna Ground Layer');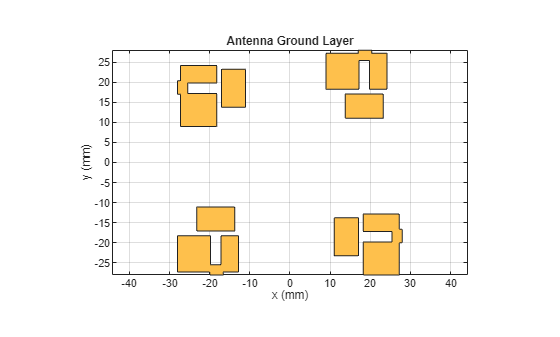
Create PCB Antenna
Use pcbStack object to create PCB antenna from the top and ground layers created in previous steps
h = 1.6e-3; d1 = dielectric(Name="FR4",EpsilonR=4.4,LossTangent=0.0260,Thickness=h); ps = pcbStack; ps.BoardThickness = h; r1bottom = antenna.Rectangle(Center=[0 0],Length=56e-3,Width=56e-3); ps.BoardShape = r1bottom; ps.Layers = {patch,d1,ground}; fx1 = -18.5e-3; fy1 = -28e-3; fx2 = 28e-3; fy2 = -18.75e-3; fx3 = 18.75e-3; fy3 = 28e-3; fx4 = -28e-3; fy4 = 18.75e-3; ps.FeedLocations = [fx1 fy1 1 3;fx2 fy2 1 3;fx3 fy3 1 3;fx4 fy4 1 3]; ps.FeedDiameter =(2.6e-3)/4; ps.FeedVoltage = [1 1 1 1]; ps.FeedPhase = [0 0 0 0]; figure(6) show(ps); title('MIMO Wideband PCB Antenna');
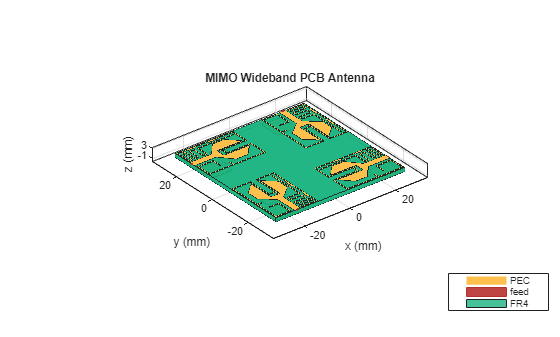
lambda = 3e8/(12e9*sqrt(4.4));
Analyze PCB antenna
Load mat-file containing S-parameters over the 8 - 12 GHz frequency band.
load('dspar_MIMO.mat'); rfplot(spar,1,1); hold on; rfplot(spar,2,2); hold on; rfplot(spar,3,3); hold on rfplot(spar,4,4);
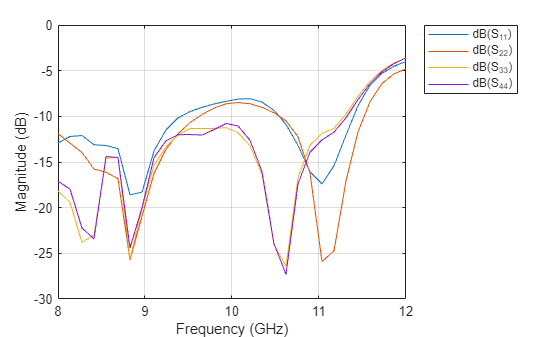
Conclusion
This designed antenna operates over the 8 to 12 GHz bandwidth with omni directinal charateristics. Stubs are integrated into the UWB monopole antenna element to achieve wideband. The proposed MIMO antenna could be helpful for GPS, RFID/Bluetooth/Wi-Fi, and V2V communications.