Design Position and Attitude Controllers for ArduCopter
This example shows how to use the UAV Toolbox Support Package for ArduPilot® Autopilots to design position and attitude controllers for ArduCopter in Simulink®. This example is designed to run with the ArduPilot Host Target, allowing you to perform Software-in-the-Loop (SITL) simulation.
Prerequisites
If you are new to Simulink, watch the Simulink Quick Start video.
If you have not performed the hardware setup, complete it before proceeding. For more information, see Launch and Complete Hardware Setup and Hardware Setup Steps. Also, Select
ArduCopteras the Vehicle type during hardware setup.
Model
Open the PositionAltitudeAttitudeController model by entering the
following command in the MATLAB Command Window:
PositionAttitudeControllerCopter
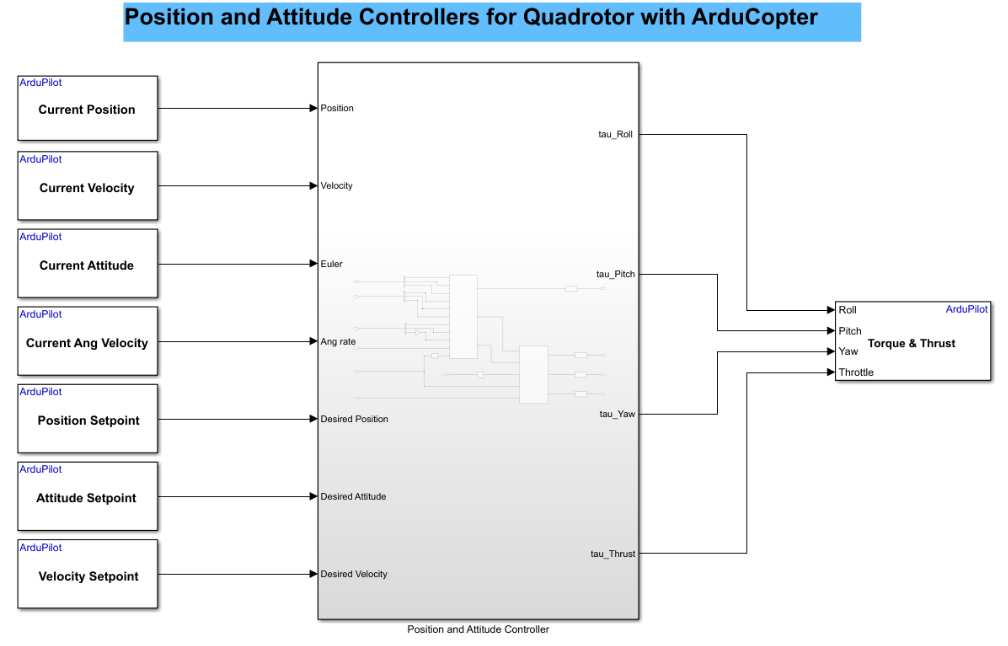
This model consists of two subsystems:
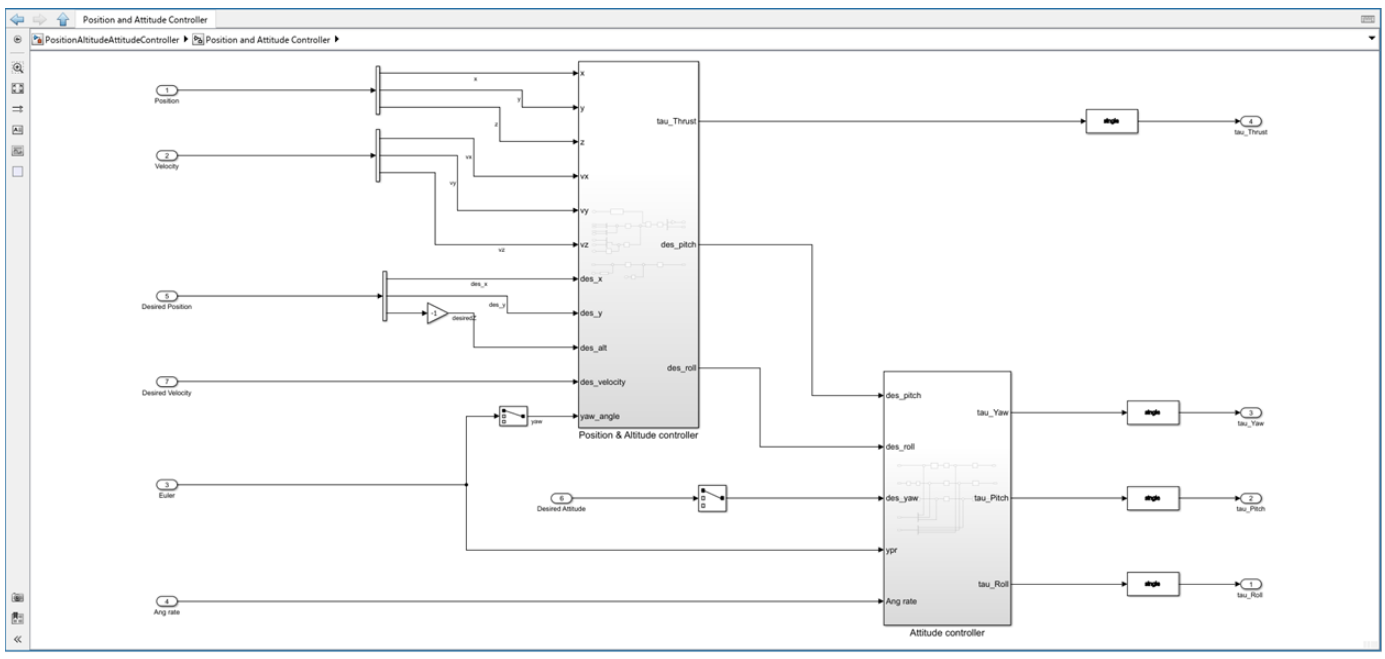
Position & Altitude Controller
Attitude Controller
Position & Attitude Controller
This controller is responsible for managing the overall position (X,Y) and altitude (Z) of the ArduCopter.
It takes in the current state (position and velocity) and the desired state (desired position and velocity), and computes:
The required thrust to maintain or change altitude.
The desired attitude (pitch and roll commands) to move toward the target position.
Attitude Controller
This controller takes the desired attitude (from the Position & Attitude Controller) and the current attitude (from estimators).
It computes the required torques around each axis to achieve the desired orientation.
Configure and Run the Model
The example model is already configured for the ArduPilot Host target, which enables Software-In-the-Loop (SITL) simulation for ArduPilot. You can now run the model directly in Monitor and Tune mode to test and tune your algorithms in real time.
Run Monitor and Tune simulation for the model.
On the Hardware tab, in the Mode section, click Run on board and then select Run on board (External mode). If you see Connected IO selected instead of Run on board, click on it and choose Run on board (External mode).
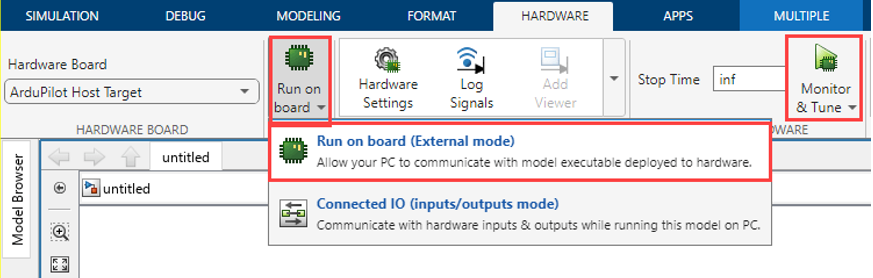
Click Monitor & Tune to configure the model for simulation.
Wait until Simulink finishes generating the code and the ArduPilot build process is complete.
Once the build is finished, the ArduPilot SITL (Software-In-The-Loop) window will automatically open along with MAVProxy terminals. Simulink will then establish a connection with SITL, and you will see the simulation progress bar advancing in Simulink.
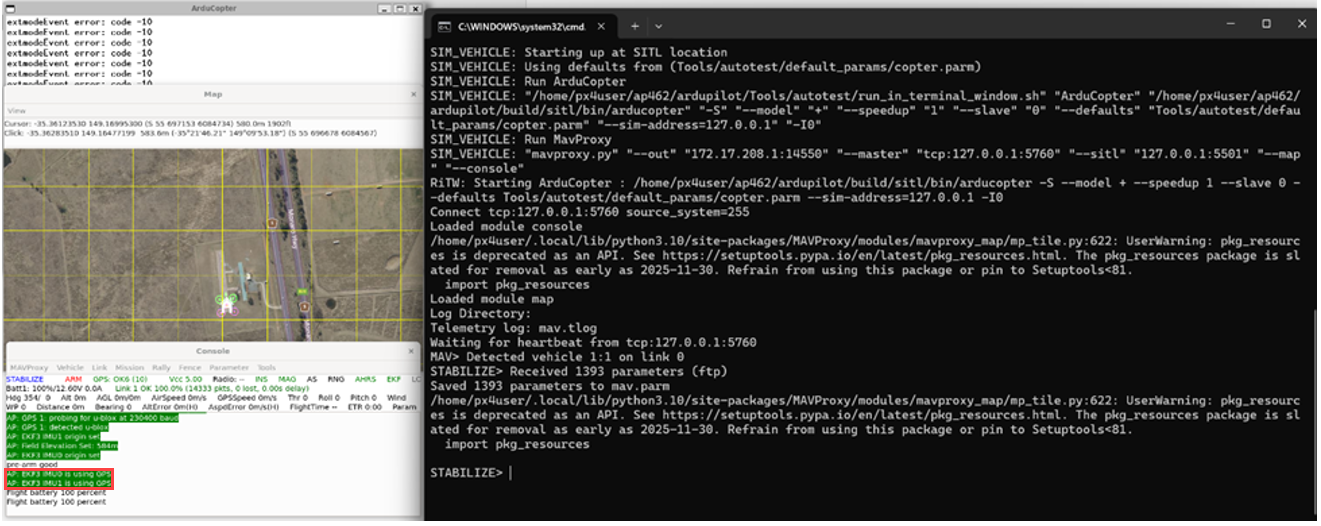

Fly the Vehicle Using MAVProxy
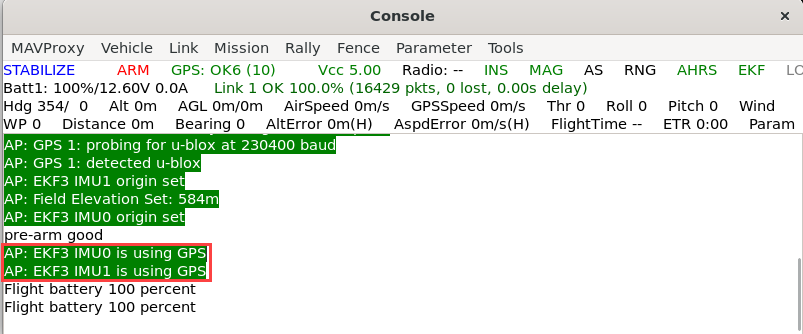
Wait for GPS Estimator Initialization.
Wait until the estimator has access to GPS data. This ensures stable position hold and accurate navigation.
Set Flight Mode to GUIDED
In the MAVProxy window, change the flight mode to GUIDED.
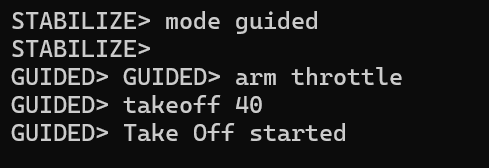
After setting the mode, arm the vehicle.
Once armed, you are ready to take off.
Take Off and Navigate.
Use the takeoff command to ascend the drone to your desired altitude (for example, 40 meters as shown in previous commands).
After reaching the target altitude, you can control the drone's position:
Right-click anywhere on the map in MAVProxy and select the option to fly the drone to that location.
The drone will autonomously navigate to the selected point.
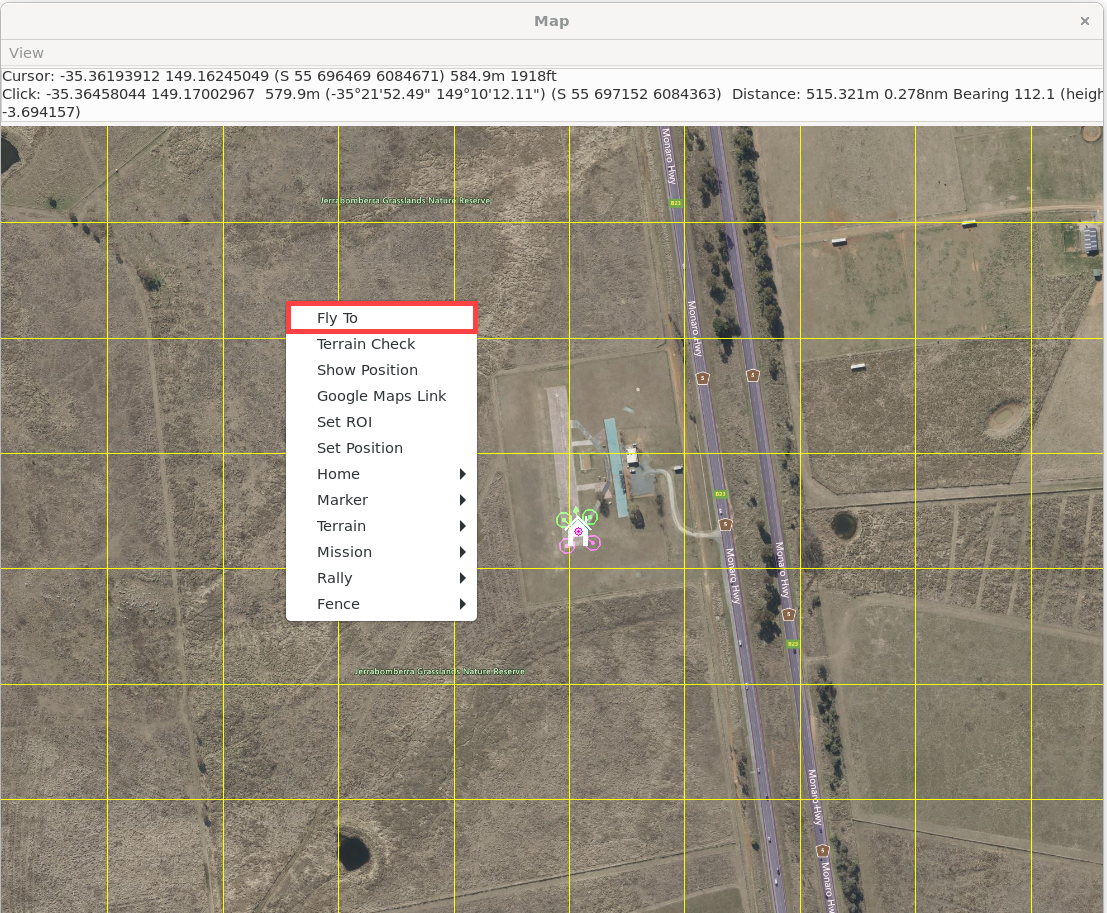
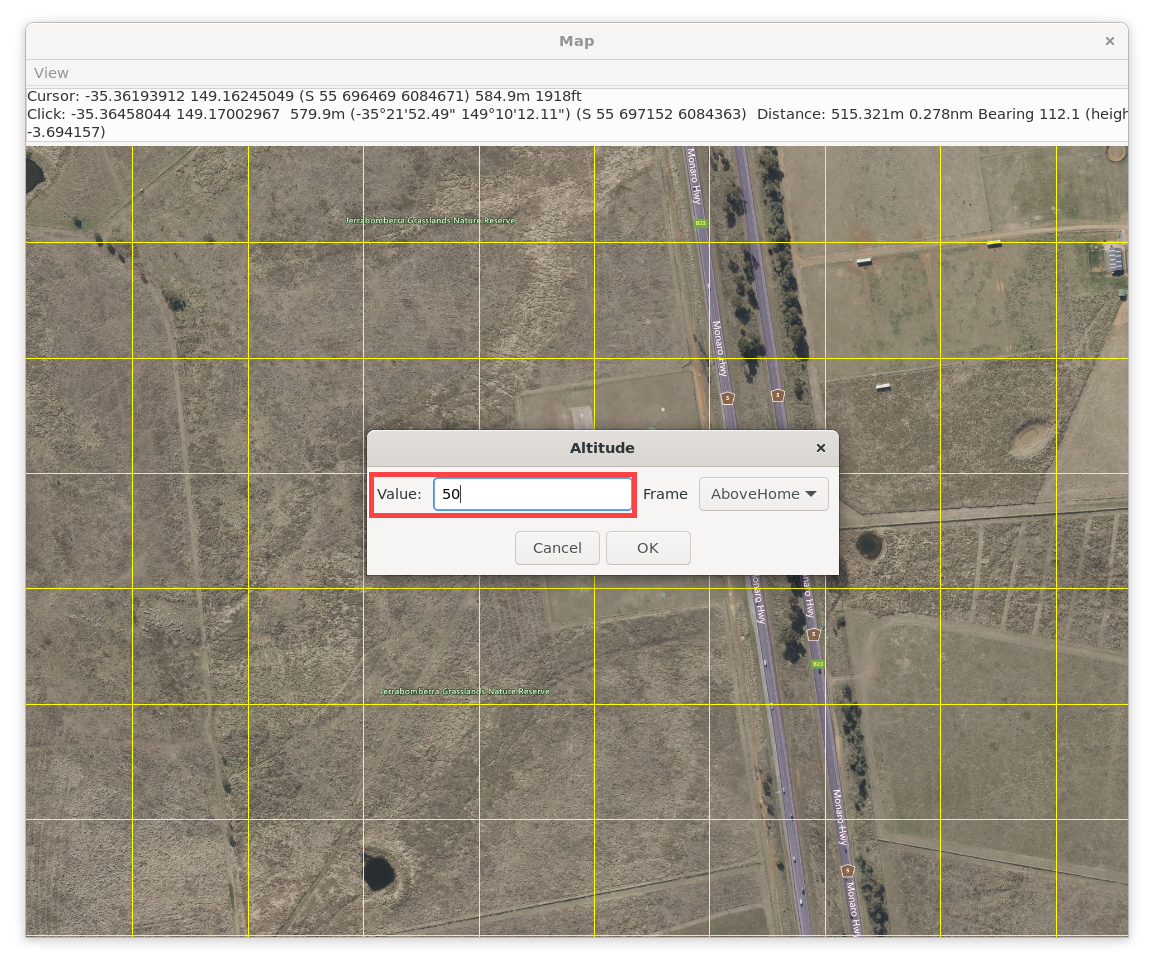
You should observe the vehicle navigating towards the designated waypoint.
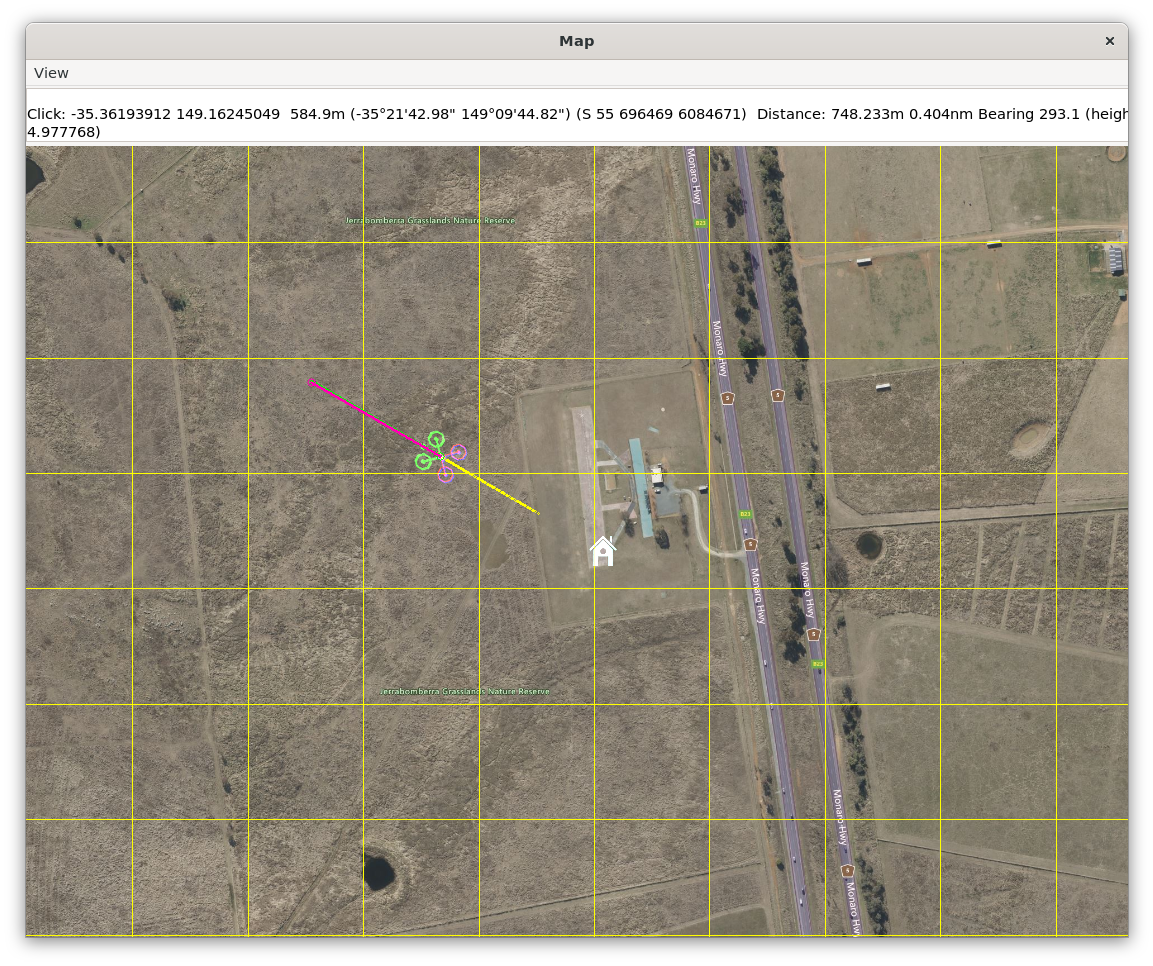
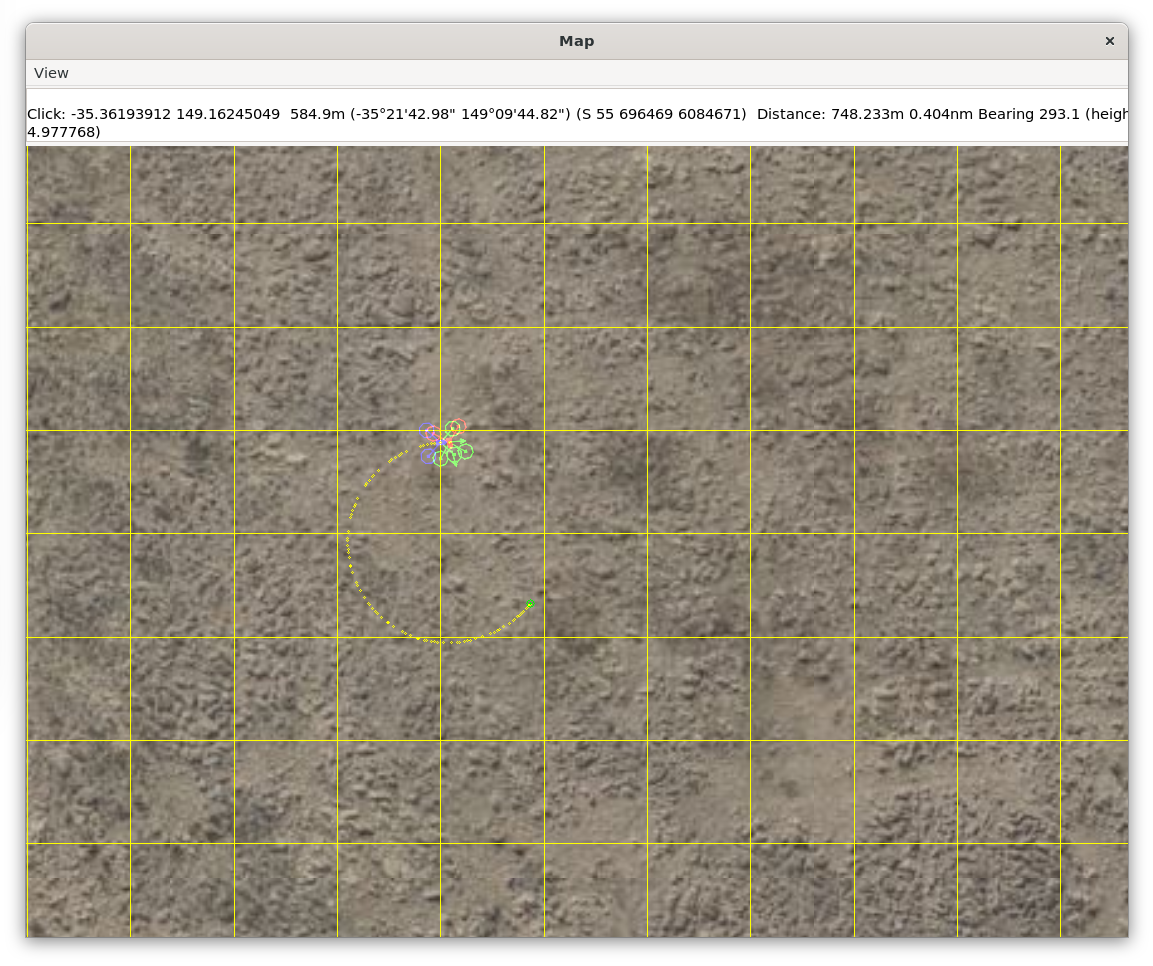
You can now activate the circle flight mode, and the vehicle will follow a circular flight path automatically.
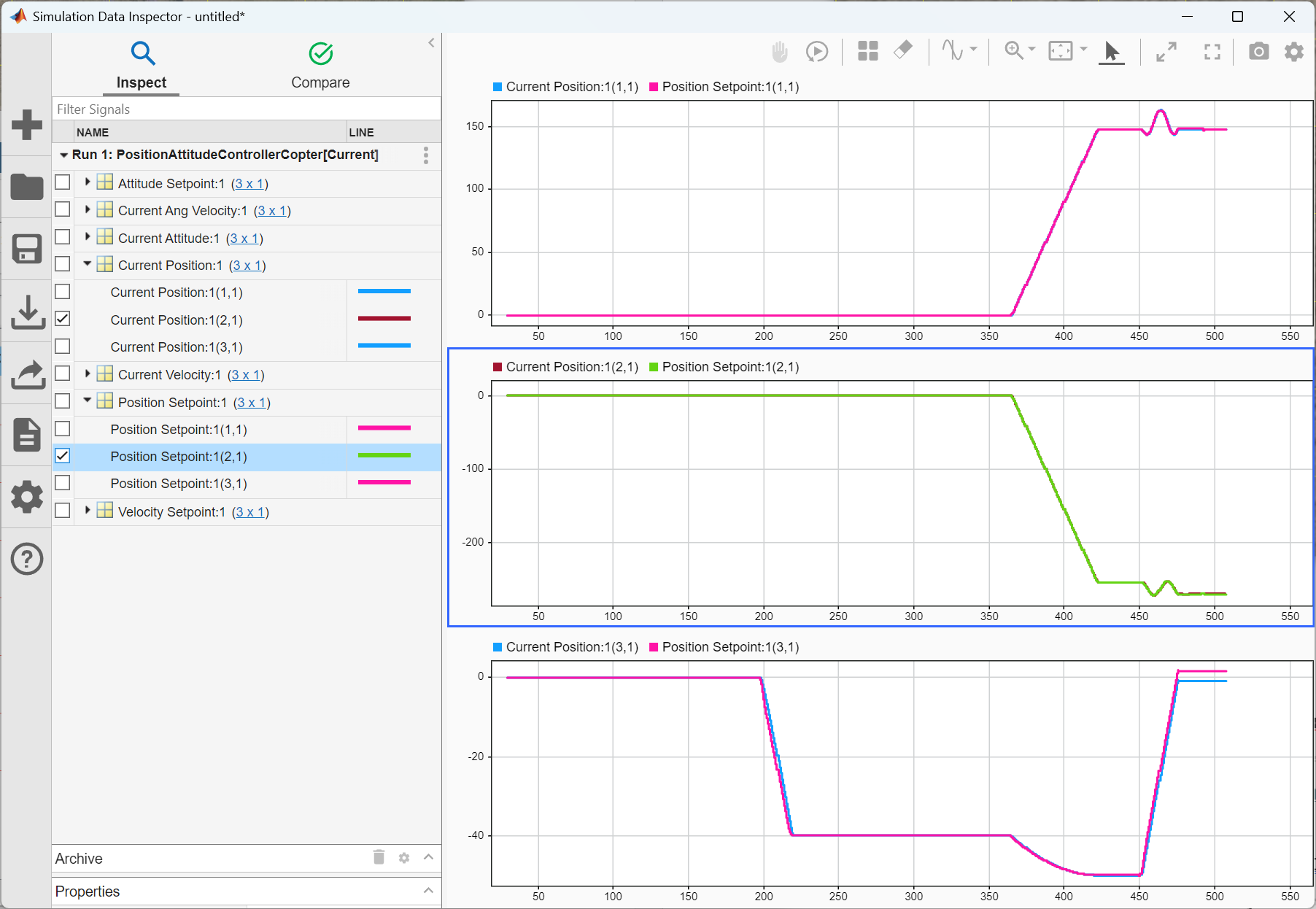
Analyzing Logged Signals Using Simulink Data Inspector
The Simulink Data Inspector provides a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing logged signals within your model. In this case, all block inputs in the model are configured for logging.
Using the Data Inspector, you can easily plot and compare signals. For example, the plot below illustrates both the position setpoint and the current position. As shown, the current position closely tracks the position setpoint, indicating that the control system is functioning as intended.
Other Things to Try
Create a New Mission Using MAVProxy
You can create a new mission and command the vehicle to follow it using MAVProxy. For more information, see Copter SITL/MAVProxy Tutorial — Dev Documentation.
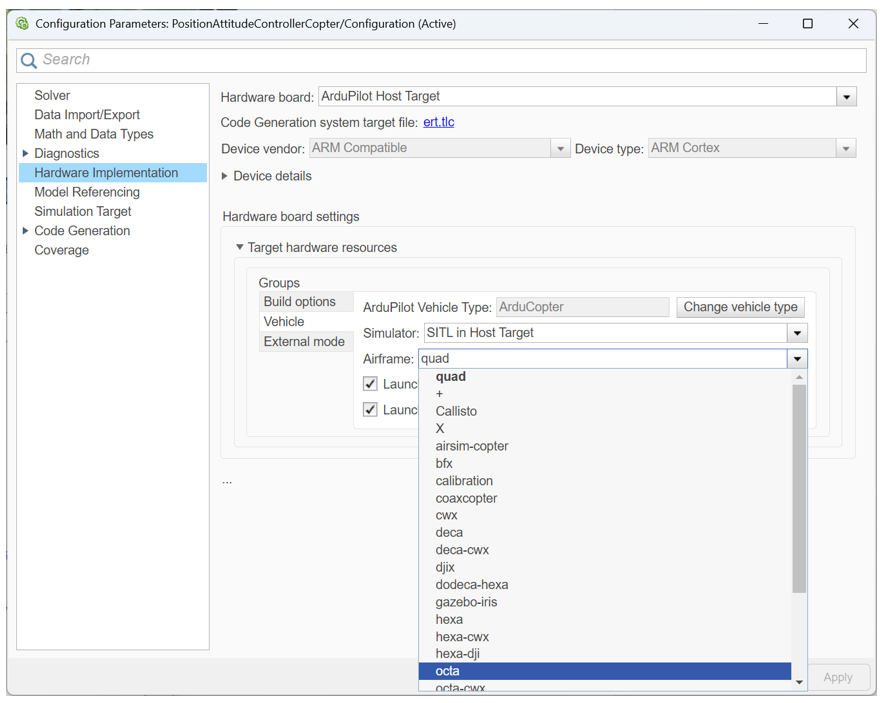
Change the Airframe
The pre-configured example model uses a quadrotor airframe. To experiment further, you can change the airframe type (for example, to a hexacopter or plane) and run the controller model again to observe different behaviors.
Connect to Mission Planner
You can also connect Mission Planner to the SITL instance and create or manage missions directly from the Mission Planner interface..
Open Mission Planner.
It should automatically connect via UDP port 14550 once MAVProxy starts.
If it does not connect automatically, manually connect using port 14550.
In Mission Planner, you can now control the drone. Create a mission and start it to initiate the flight.
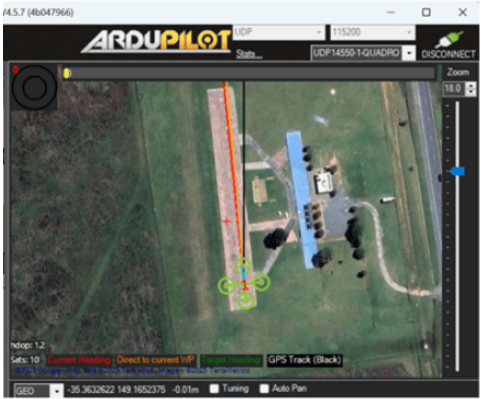
Fly the copter. For more information, see Mission Planner Flight PLAN
Once the mission starts, observe the vehicle as it follows the planned mission.
After the mission is complete, disarm the drone to ensure it is safely powered down.
See Also
Create Your First Model with Software-In-The-Loop Simulation