Wheel and Axle
Wheel and axle mechanism in mechanical systems
Libraries:
Simscape /
Foundation Library /
Mechanical /
Mechanisms
Description
The Wheel and Axle block represents a wheel and axle mechanism shown in the following schematic.
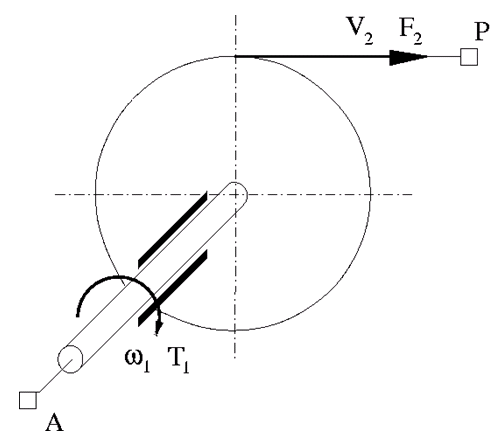
The wheel and the axle have the same axis, and the axis is assumed to be rigidly connected to the frame, thus making this mechanism an ideal converter of mechanical rotational into mechanical translational motion. The mechanism has two connections: a mechanical rotational port A, which corresponds to the axle, and a mechanical translational port P, which corresponds to the wheel periphery. The mechanism is described with the following equations:
where
T is torque on the axle.
F is force on the wheel periphery.
ω is angular velocity.
v is linear velocity on the wheel periphery.
r is wheel radius.
or is mechanism orientation indicator. The value is +1 if axle rotation in the globally assigned positive direction is converted into translational motion in positive direction. The value is –1 if positive rotation results in translational motion in negative direction.
Use the block in simulation of rack-pinions, steering wheels, hoisting devices, windlasses, and so on.
The block positive directions are from A to the reference point and from the reference point to P.
Variables
To set the priority and initial target values for the block variables prior to simulation, use the Initial Targets section in the block dialog box or Property Inspector. For more information, see Set Priority and Initial Target for Block Variables.
Nominal values provide a way to specify the expected magnitude of a variable in a model. Using system scaling based on nominal values increases the simulation robustness. Nominal values can come from different sources, one of which is the Nominal Values section in the block dialog box or Property Inspector. For more information, see Modify Nominal Values for a Block Variable.
Examples
Ports
Conserving
Parameters
Extended Capabilities
Version History
Introduced in R2007a

